A.Triangles
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/A
首先判断这个三角形是否存在,当有向量n1=(x1,y1),与向量n2=(x2,y2)共线时三角形不存在,即x1.y2-x2.y1=0。
之后运用高中向量知识:
当向量n1=(x1,y1),与向量n2=(x2,y2)的角为直角时,n1.n2=0,即x1.x2+y1.y2=0;
三角形为直角三角形。
当有钝角时,n1.n2<0,三角形为钝角三角形。
没有钝角时,没有直角时,即三个角的每个角的两个边向量的数量积都大于0时,三角形为锐角三角形。
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
#define pb push_back
const int N = 1e4+5;
int n;
double x1;
double Y1;
double x2,x3,y2,y3;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio;
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
cin>>x1>>Y1>>x2>>y2>>x3>>y3;
double nx12=x2-x1;
double ny12=y2-Y1;
double nx13=x3-x1;
double ny13=y3-Y1;
double nx21=x1-x2;
double ny21=Y1-y2;
double ny23=y3-y2;
double nx23=x3-x2;
double nx31=x1-x3;
double ny31=Y1-y3;
double nx32=x2-x3;
double ny32=y2-y3;
double a=nx12*ny13-nx13*ny12;
double b=nx21*ny23-nx23*ny21;
double c=nx31*ny32-nx32*ny31;
double a1=nx12*nx13+ny12*ny13;
double b1=(nx21*nx23+ny21*ny23);
double c1=(nx31*nx32+ny31*ny32);
if(a==0||b==0||c==0)
{
cout<<"invalid\n";
continue;
}
double ans=min(a1,b1);
ans=min(ans,c1);
if(a1==0||c1==0||b1==0||ans==0)
{
cout<<"right\n";
}else if(ans<0)
{
cout<<"obtuse\n";
}else if(ans>0)
cout<<"acute\n";
}
return 0;
}
当时写的非常朴实无华。
B.Yuki with emofunc and playf
原题网址:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/B
解题思路
k是n的倍数,满足k%n==0。 以上两种类型的操作可以转换为:
1.k=(k*10)%n
2.k=(k+x-1)%n
这样就把k(实际上是k%n)能到达的范围缩小到(0,n)了。起点从1开始,终点为0。
BFS:从队头取数,判断是否能整除N,整除则得到结果,否则将K进行两种不同的操作,即不同操作后的K%n可能与队列元素相同,记录第一次出现后如果后面重复出现可直接跳过,因为第一次出现使用的操作次数最少,当无解时,输出-1。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
# define rep(i,be,en) for(int i=be;i<=en;i++)
# define pre(i,be,en) for(int i=be;i>=en;i--)
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
#define pb push_back
const int N = 1e6+1,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,x;
bool st[N];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio;
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>x;
queue<PII>qe;
qe.push({1%n,0});
st[1%n]=1;
while(qe.size())
{
auto t=qe.front();
qe.pop();
if(t.x%n==0)
{
cout<<t.y<<endl;
return 0;
}
if(!st[(t.x*10)%n]) {
qe.push({t.x*10%n,t.y+1});
st[(t.x*10)%n]=1;
}
if(!st[(x-1+t.x)%n])
{
qe.push({(t.x+x-1)%n,t.y+1});
st[(t.x+x-1)%n]=1;
}
}
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
——————————————————————————————
D.Queuing
原题网址:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/D
我们假设有 m个窗口, n个人。我们先直接给出答案公式:
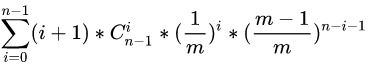
它的含义就是枚举第 号人前有多少个人,然后用权值去乘以这个权值出现的概率。其实去枚举权值是一样的,就是把上面的 做了一个整体替换,但是感觉这么写更好算。可以对比两种枚举方式发现枚举前面有多少人计算起来更加简单。
我们接下来就对式子进行展开:
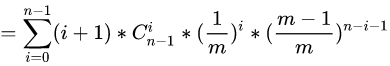
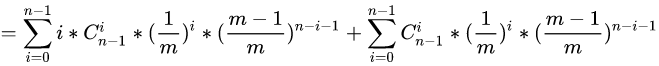
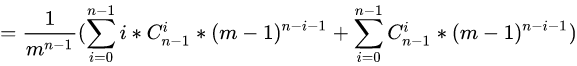
括号里右边依据二项式定理有:
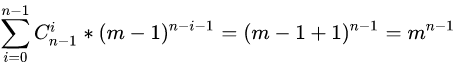
那么我们现在考虑化简括号里面的左边:
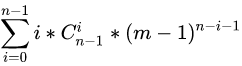
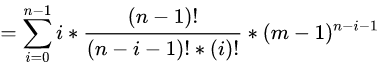
这里我们发现 i=0 的时候对答案没有贡献,可以从 i=1 开始(这样做后面化简更简单,大家可以不这么做往下走试试,最后发现还是要舍去 的情况),那么这里我们注意到此时有限制条件了 :
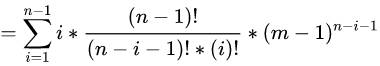
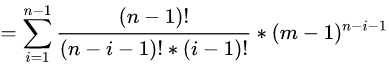
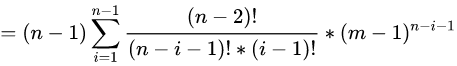
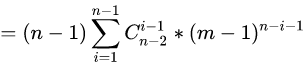
我们用 t+1=i 进行整体替换:
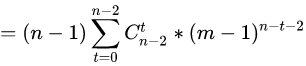
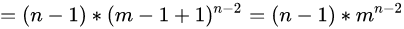
我们最终将化简后的括号里面的左右部分代入:
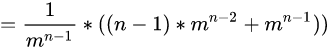
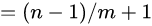
代码简洁:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double n,m;
int main()
{
while(cin>>n>>m){
printf("%.8f\n",(m-1)*1.0/n+1);
}
return 0;
}
F.Team
原题链接如下:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/F
这个签到题用unsigned long long 或者int 128,或者高精度加法就行了!
或者直接用python,毕竟python自带大数和高精度!
(python yyds! )
a=int(input())
b=int(input())
c=int(input())
print(a+b+c)
或者:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void scan(__int128_t &x)//输入
{
x = 0;
int f = 1;
char ch;
if((ch = getchar()) == '-') f = -f;
else x = x*10 + ch-'0';
while((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9')
x = x*10 + ch-'0';
x *= f;
}
void _print(__int128_t x)
{
if(x > 9) _print(x/10);
putchar(x%10 + '0');
}
void print(__int128_t x)//输出
{
if(x < 0)
{
x = -x;
putchar('-');
}
_print(x);
}
int main()
{
__int128_t a, b,c;
scan(a); scan(b); scan(c);
print(a + b+c);
return 0;
}
G.Binbin’s string
原题链接如下:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/G
此题首先明白最多三种情况: 0,1,2
我在其中分了三个情况:
1.原串和目标串长度相等
此时如果原串与目标串一模一样,即ans=0;
此时如果原串和目标串不一样,那么必须两次操作,ans=2;
2.原串长度大于目标串
此时如果目标串是原串的字串,ans=1;
此时如果目标串不是原串的字串但是原串可通过删除一部分连续的字串得到目标串,那么ans=1;
上面两个条件都不满足,ans=2;
原串长度小于目标串
此时如果原串是目标串的字串,或者如果原串不是目标串的字串但是目标串可通过删除一部分连续的字串得到原串。那么ans=1;
不满足条件,ans=1;
此题分析完毕!!!
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
#define pb push_back
const int N = 1e4;
string s,s1;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio;
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>s>>s1;
int l1=s.size();
int l2=s1.size();
if(s.size()==s1.size())//等长时 要么相等 要么两步
{
bool f=0;
for(int i=0;i<l1;i++)
{
if(s[i]!=s1[i])
{
f=1;
break;
}
}
if(f==0) cout<<0<<endl;
else cout<<2<<endl;
}else if(l1>l2) //原字符长 、、先扫一下,能不能一部到位,即s1为类字串 否则2
{
int i=0,j=0;
bool f=0;
while(j<l2)
{
if(s[i]==s1[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}else if(s[i]!=s1[j]&&f==0&&j!=l2-1)
{
i+=l1-l2;
f=1;
}else break;
}
if(j==l2) cout<<1<<endl;
else cout<<2<<endl;
} else //目标字符大于元字符 1或2 ,先扫一下,
{
int i=0,j=0;
bool f=0;
while(i<l1)
{
if(s[i]==s1[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}else if(s[i]!=s1[j]&&f==0&&i!=l1-1)
{
j+=l2-l1;
f=1;
}else break;
}
if(i==l1) cout<<1<<endl;
else cout<<2<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
I.Binbin and Balls
原题链接如下:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/I

代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long t,n;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
long long l=1,r=2e9;
while(l<r)
{
long long mid=l+r>>1;
if(mid*(mid+1)/2>=n) r=mid;
else l=mid+1;
}
cout<<l<<endl;
}
}
L.Cracked Pipes
原题链接如下:
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/18196/L
主要此题有一大坑点!!!:
二维数组会爆,之前代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
#define pb push_back
const int N = 30000;
int n,m;
static int g[N][N];
static bool st[N][N];
bool bfs()
{
queue<PII>q;
q.push({0,0});
st[0][0]=1;
while(q.size())
{
auto t=q.front();
q.pop();
int a=t.x,b=t.y;
int te=g[t.x][t.y];
if(te==1)
{
if(a-1>=0&&(g[a-1][b]==6||g[t.x-1][t.y]==3||g[a-1][b]==1)&&!st[t.x-1][t.y])
{
st[a-1][b]=1;
q.push({a-1,b});
}
if(a+1<n&&(g[t.x+1][t.y]==4||g[t.x+1][t.y]==5||g[a+1][b]==1)&&!st[a+1][b])
{
st[a+1][b]=1;
q.push({a+1,b});
}
}else if(te==2)
{
if((b-1>=0&&(g[a][b-1]==3||g[a][b-1]==5||g[a][b-1]==6||g[a][b-1]==2)&&!st[a][b-1]))
{
st[a][b-1]=1;
q.push({a,b-1});
}
if(b+1<m&&(g[a][b+1]==4||g[a][b+1]==5||g[a][b+1]==6||g[a][b+1]==2)&&!st[a][b+1])
{
st[a][b+1]=1;
q.push({a,b+1});
}
}else if(te==3)
{
if(b+1<m&&(g[a][b+1]==2||g[a][b+1]==4||g[a][b+1]==5||g[a][b+1]==6)&&!st[a][b+1])
{
st[a][b+1]=1;
q.push({a,b+1});
}
if(a+1<n&&(g[a+1][b]==1||g[a+1][b]==4||g[a+1][b]==5)&&!st[a+1][b])
{
st[a+1][b]=1;
q.push({a+1,b});
}
}else if(te==4)
{
if(b-1>=0&&(g[a][b-1]==2||g[a][b-1]==3||g[a][b-1]==5||g[a][b-1]==6)&&!st[a][b-1])
{
st[a][b-1]=1;
q.push({a,b-1});
}
if(a-1>=0&&(g[a-1][b]==1||g[a-1][b]==3||g[a-1][b]==6)&&!st[a-1][b])
{
st[a-1][b]=1;
q.push({a-1,b});
}
}else if(te==5)
{
if(b-1>=0&&(g[a][b-1]==2||g[a][b-1]==3||g[a][b-1]==6||g[a][b-1]==5)&&!st[a][b-1])
{
st[a][b-1]=1;
q.push({a,b-1});
}
if(b+1<m&&(g[a][b+1]==2||g[a][b+1]==4||g[a][b+1]==6||g[a][b+1]==5)&&!st[a][b+1])
{
st[a][b+1]=1;
q.push({a,b+1});
}
if(a-1>=0&&(g[a-1][b]==1||g[a-1][b]==3||g[a-1][b]==6)&&!st[a-1][b])
{
st[a-1][b]=1;
q.push({a-1,b});
}
}
else if(te==6)
{
if(b-1>=0&&(g[a][b-1]==2||g[a][b-1]==3||g[a][b-1]==5||g[a][b-1]==6)&&!st[a][b-1])
{
st[a][b-1]=1;
q.push({a,b-1});
}
if(a+1<n&&(g[a+1][b]==1||g[a+1][b]==4||g[a+1][b]==5)&&!st[a+1][b])
{
st[a+1][b]=1;
q.push({a+1,b});
}
if(b+1<m&&(g[a][b+1]==2||g[a][b+1]==4||g[a][b+1]==5||g[a][b+1]==6)&&!st[a][b+1])
{
st[a][b+1]=1;
q.push({a,b+1});
}
}
if(st[n-1][m-1]) return true;
}
if(st[n-1][m-1]) return true;
else return false;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio;
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
cin>>g[i][j];
}
}
if(g[0][0]!=2&&g[0][0]!=5&&g[0][0]!=6)
{
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}else if(g[n-1][m-1]!=2&&g[n-1][m-1]!=5&&g[n-1][m-1]!=6)
{
cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
if(bfs())
{
cout<<"YES\n";
}else cout<<"NO\n";
return 0;
}
结果:

开到极限也过不了,所以解决方案如下:
使用map储存:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
inline int read() {
int x = 0; char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) c = getchar();
while(isdigit(c)) x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar();
return x;
}
struct node {
int x,y;
inline bool operator < (const node & a) const {return x == a.x ? y < a.y : x < a.x;}
};
struct Q {
int x,y,num;
};
int n,m;
map <node,int> vis;
vector <int> mp[maxn];
queue <Q> q;
int dir[4][2] = {1,0,0,1,-1,0,0,-1}; /// 0下 1右 2上 3左
inline bool check(int xx,int yy,int num,int i) {
if(xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m) {}
else return 0;
if(num == 1 && (i == 1 || i == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 1 && i == 0 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 3 || mp[xx][yy] == 6)) return 0;
if(num == 1 && i == 2 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 4 || mp[xx][yy] == 5)) return 0;
if(num == 2 && (i == 0 || i == 2)) return 0;
if(num == 2 && i == 1 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 2 && i == 3 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 4)) return 0;
if(num == 3 && (i == 2 || i == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 3 && i == 0 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 3 || mp[xx][yy] == 6)) return 0;
if(num == 3 && i == 1 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 4 && (i == 0 || i == 1)) return 0;
if(num == 4 && i == 2 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 4 || mp[xx][yy] == 5)) return 0;
if(num == 4 && i == 3 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 4)) return 0;
if(num == 5 && i == 0) return 0;
if(num == 5 && i == 1 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 5 && i == 2 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 4 || mp[xx][yy] == 5)) return 0;
if(num == 5 && i == 3 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 4)) return 0;
if(num == 6 && i == 2) return 0;
if(num == 6 && i == 0 && (mp[xx][yy] == 2 || mp[xx][yy] == 3 || mp[xx][yy] == 6)) return 0;
if(num == 6 && i == 1 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 3)) return 0;
if(num == 6 && i == 3 && (mp[xx][yy] == 1 || mp[xx][yy] == 4)) return 0;
return 1;
}
inline bool bfs() {
while(!q.empty()) {
Q now = q.front();
q.pop();
if(now.x == n && now.y == m) return true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = now.x + dir[i][0];
int yy = now.y + dir[i][1];
if(check(xx,yy,now.num,i) && vis.find(node{xx,yy}) == vis.end()) {
vis[node{xx,yy}] = 1;
q.push(Q{xx,yy,mp[xx][yy]});
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
n = read(), m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
mp[i].push_back(0);
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) mp[i].push_back(read());
}
if(mp[1][1] == 1 || mp[1][1] == 3 || mp[n][m] == 1 || mp[n][m] == 4) {
puts("NO");
return 0;
}
q.push(Q{1,1,mp[1][1]});
vis[node{1,1}] = 1;
if(bfs()) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}






















 927
927











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








