目录
什么是栈
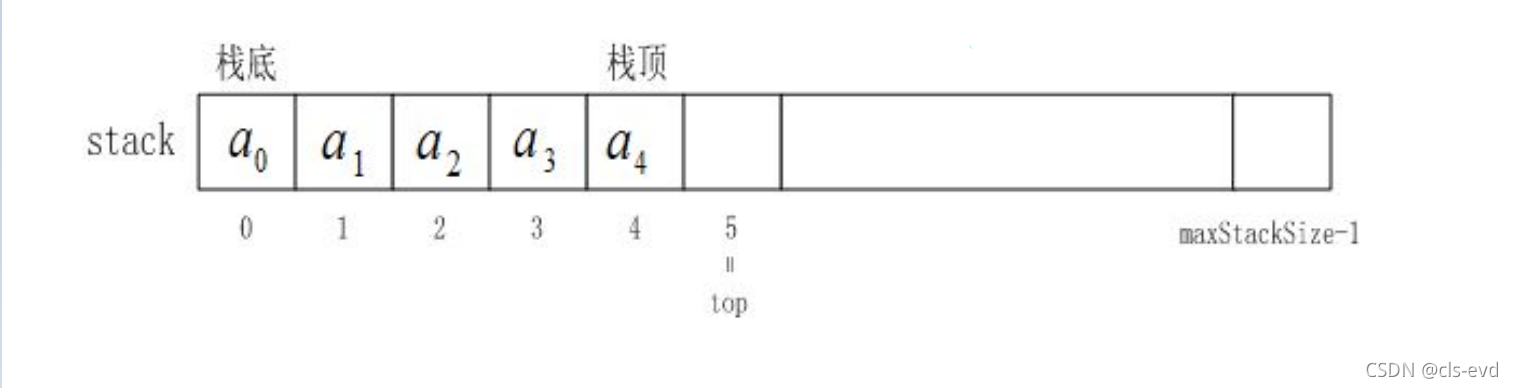
栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。
进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。 栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出 LIFO ( Last In First Out )的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈 / 压栈 / 入栈, 入数据在栈顶 。出栈:栈的操作叫做出栈。 出数据也在栈顶 。
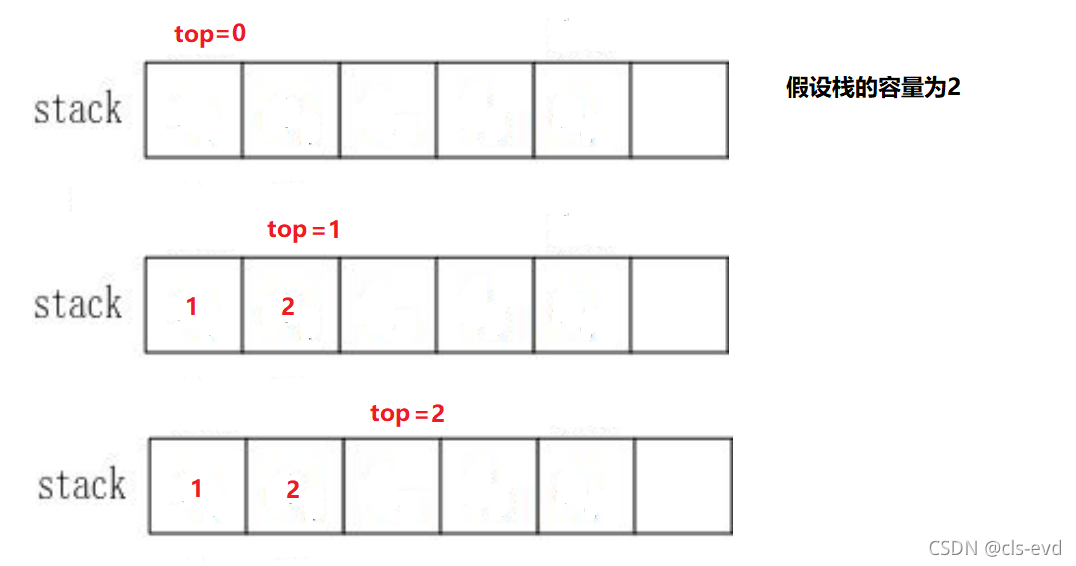
入栈及出栈示意图:

了解完入栈出栈原理后,先来两道题练练手

3题很简单,根据先入后出规则,答案是B
4题有一些难度,因为进栈过程中可以出栈
A. 1进栈,1出栈,2进栈,3进栈,4进栈,4出栈,3出栈,2出栈
所以出栈顺序就是1 4 3 2
B C D同理,希望读者可自行推导,最终答案为C
栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用
数组或者链表实现
,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。
到这我们会发现栈的实现和我们当初实现的顺序表相似的很,传送门:数据结构之【顺序表的实现(详解)】_cls的博客-CSDN博客
栈可以分为静态的栈与动态的栈
静态的栈:
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 100
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType array[N]; //静态的栈就是一个数组
int top; //栈顶
}Stack;动态的栈:
typedef int STDataType;
struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量,方便增容
};
typedef struct Stack Stack; //另外一种给结构体取名字的方法为了方便起见,我们采取动态的栈
下面我们实现这样几种接口:
void StackInit(Stack* pst); //初始化
void StackDestory(Stack* pst); //销毁
//性质决定在栈顶出入数据
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x); //入栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst); //出栈
//取栈顶的数据
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //判断栈是否为空
int StackSize(Stack* pst); //统计栈中的数据初始化的实现
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}这是一种方式,但我们为了方便起见,我们可以提前就开辟四个空间
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*4);
pst->capacity = 4;
pst->top = 0;
}销毁的实现
void StackDestory(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
入栈的实现

void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType)*(pst->capacity * 2));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc失败\n");
exit(-1); //结束程序
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity *= 2;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}出栈的实现
很简单
栈顶减减即可,注意要判断一下栈是否为空,为空就不执行
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}取栈顶数据的实现
同样需要栈不为空

STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}判断栈是否为空接口的实现
这里我们用 bool 实现,成真返回True(1),成假返回FALSE(0)
我们只要判断栈顶top 是不是为我们初始化的数据 0 即可

bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}统计栈中的数据
top的值即代表数组中共有多少个数据
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top ;
}到这栈已经完成了,是不是非常的简单!
原码及其效果演示
Stack.h 部分
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//typedef int BOOL;
//#define TURE 1;
//#define FALSE 0;
// 静态的栈
//typedef int STDataType;
//typedef struct Stack
//{
// STDataType array[1000]; //静态的栈就是一个数组
// int top; //栈顶
//
//}Stack;
// 动态的栈
typedef int STDataType;
struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量,方便增容
};
typedef struct Stack Stack;
//同样传指针,形参改变不影响实参,实参传过去是它的拷贝
void StackInit(Stack* pst); //初始化
void StackDestory(Stack* pst); //销毁
//性质决定在栈顶出入数据
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x); //入栈
void StackPop(Stack* pst); //出栈
//取栈顶的数据
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst);
// 空返回1,非空返回0
//int StackEmpty(Stack* pst);
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst); //判断栈是否为空
int StackSize(Stack* pst); //统计栈中的数据
Stack.c 部分
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
/*pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;*/
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*4);
pst->capacity = 4;
pst->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a,sizeof(STDataType)*(pst->capacity * 2));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc失败\n");
exit(-1); //结束程序
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity *= 2;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(!StackEmpty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
int StackSize(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top ;
}Test.c 部分
#include"Stack.h"
void TestStack()
{
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
StackPush(&st, 1);
StackPush(&st, 2);
StackPush(&st, 3);
StackPush(&st, 4);
printf("%d \n", StackSize(&st));
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&st));
StackPop(&st);
}
StackDestory(&st);
}
int main()
{
TestStack();
} 效果演示 





















 6737
6737











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








