一、线程常见构造方法
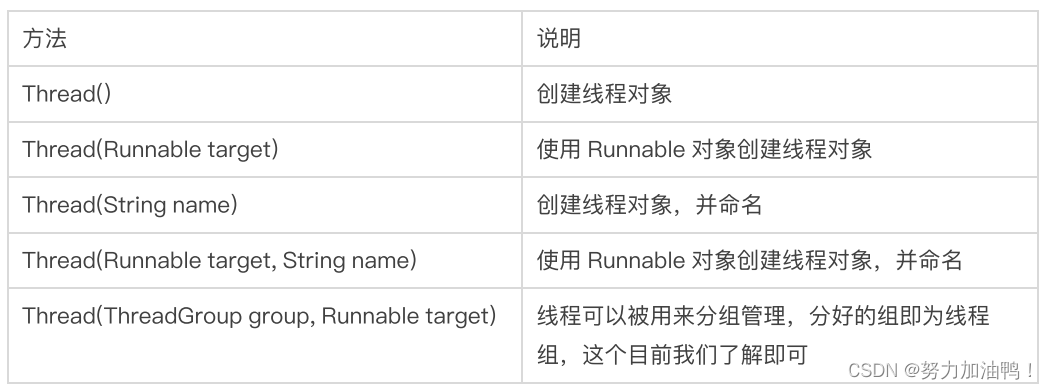
1.Thread()
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程并初始化
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程名称:" + t.getName());
}
};
thread.start();
}
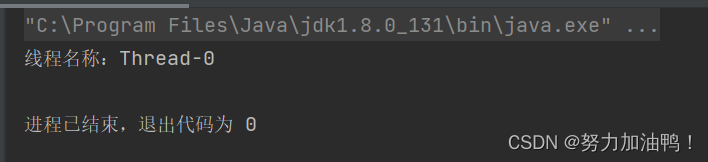
没有参数,直接创建线程对象,线程名称会以"Thread-"作为前缀加一个数字出现
2.Thread(Runnable target)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//业务代码
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程名称:" + thread.getName());
}
});
//启动线程
thread.start();
}
3.Thread(String name)
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程并初始化
Thread thread = new Thread("线程1"){
@Override
public void run() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程名称:" + t.getName());
}
};
thread.start();
}
4.Thread(Runnable target, String name)
public class ThreadDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Runnable
MyThread2 myThread2 =new MyThread2();
//创建一个线程
Thread thread = new Thread(myThread2,"线程1");
thread.start();
}
}
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//具体业务代码
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();//得到当前线程
System.out.println("线程名称:" + thread.getName());
}
}
5.Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target)
线程分组,传入参数线程分组和Runnable对象
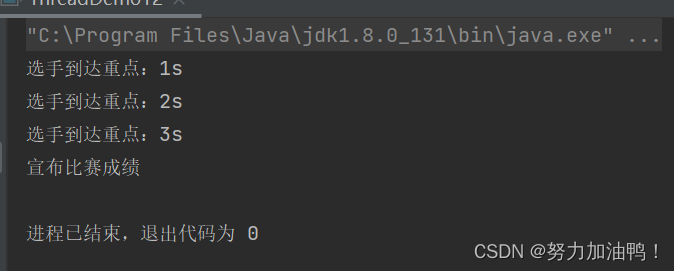
代码实现背景:模拟女子100米比赛,将三个运动员分为一组,即一个项目为一组,三个人都是从起点跑到终点,创建线程,传入分组情况及任务;启动线程即三个人开始起跑,等待三个人到达重点再宣布成绩。
import java.util.Random;
public class ThreadDemo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个分组(女子100米比赛)
ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("thread-group");
//2.定义一个公共的任务(线程的任务)
Runnable runTask = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {//任务
//生成一个1-3秒的随机数
int num = (1 + new Random().nextInt(3));
try {
//跑了n秒之后达到了终点
Thread.sleep(num*1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("选手到达重点:" + num + "s");
}
};
//3.线程(运动员)
Thread t1 = new Thread(group,runTask);//选手1
Thread t2 = new Thread(group,runTask);//选手2
Thread t3 = new Thread(group,runTask);//选手3
//运动员1开跑
t1.start();
//运动员2开跑
t2.start();
//运动员3开跑
t3.start();
//所有选手全部到达终点之后宣布成绩
while (group.activeCount() > 0){
}
System.out.println("宣布比赛成绩");
}
}
二、线程常用属性
1.ID( getId() )
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//得到(执行当前任务的)当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//打印线程id
System.out.println("线程ID:" + t.getId());
//打印线程名称
System.out.println("线程名称:" + t.getName());
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable,"线程1");
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable,"线程2");
thread2.start();
}
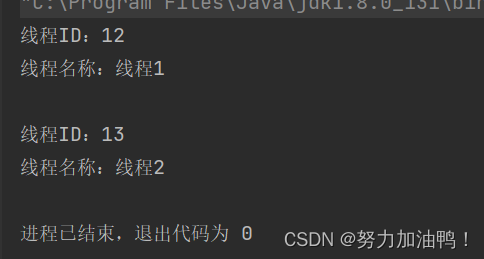
可以看到每个线程ID是不同,动态分配的
2.名称( getName() )
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//得到(执行当前任务的)当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//打印线程id
System.out.println("线程ID:" + t.getId());
//打印线程名称
System.out.println("线程名称:" + t.getName());
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable,"线程1");
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println();
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable,"线程1");
thread2.start();
}
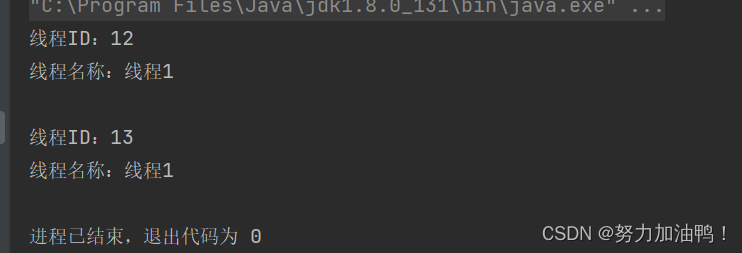
将两个线程的名称都改为线程1,可以发现是能正常输出的;
说明线程名称是可以重复的,而线程ID是不可以重复的
3.线程状态( getState() )
线程在没有启动前是新建状态NEW,在启动之后是就绪态RUNNABLE,线程任务执行完之后是终止状态TERMINATED。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//拿到当前线程
Thread thread=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程状态2:"+thread.getState());
}
});
System.out.println("线程状态1:"+t.getState());
t.start();
//再次打印线程状态
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("线程状态3:"+t.getState());
}
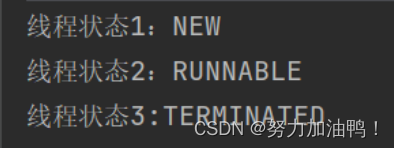
4.优先级( getPriority() )
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//得到当前线程,并打印优先级
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println("线程优先级:" + t.getPriority());
}
});
System.out.println("线程优先级2:" + thread.getPriority());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("线程优先级3:" + thread.getPriority());
}
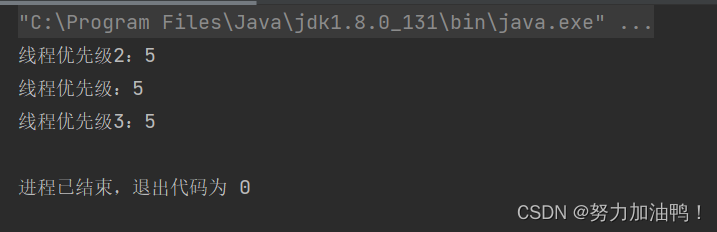
可以看到线程的优先级从创建开始就存在且默认值为5,优先级最低为1,最大为10

优先级高的线程理论上说更容易被调度到。但是同时开启多个线程,多个线程设置了不同的优先级,并不是等优先级高的全部执行完再执行优先级低的,而是优先级高的线程获取到cpu的时间片概率更大,也就是更容易被调度到。
5.是否守护线程( isDaemon() )
5.1线程分类
用户线程
守护线程(后台线程)
5.2守护线程作用
守护线程是为⽤户线程服务的,⽤户线程全部结束之后,守护线程会跟随结束。
5.3守护线程的使用
5.3.1 thread.isDaemon()——获取当前线程是否为守护线程:
true=守护线程
false=用户线程
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//得到当前线程
Thread thread=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+"是否是守护线程"+thread.isDaemon());
Thread thread1=new Thread(()->{
//得到当前线程
Thread thread2=Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread2.getName()+"--是否是守护线程:"+thread2.isDaemon());
},"子线程1");
thread1.start();
}
结论:
1.main线程(主线程)默认是用户线程(非守护线程)
2.在用户线程中创建的子线程也是用户线程
5.3.2 thread.setDaemon(true)——设置守护线程
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//得到当前线程(main 主线程)
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
//main线程为用户线程
System.out.println("是否为守护线程:" + thread.isDaemon());
//在main线程(用户线程)中创建的子线程也会是用户线程(默认情况下)
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
//得到当前线程t1
Thread cThread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(cThread.getName() + "--是否为守护线程:" + cThread.isDaemon());
//得到当前线程tt1
Thread tt1 = new Thread(() -> {
//得到当前线程
Thread cThread2 = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(cThread2.getName() + "--是否为守护线程" + cThread2.isDaemon());
},"子线程的子线程1");
tt1.start();
},"子线程1");
//手动指定线程为守护线程
t1.setDaemon(true);//线程类型的设置不能在start之后进行
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
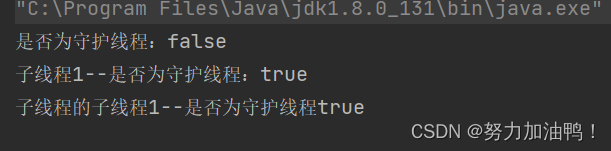
可以看到,在设置了子线程为守护线程之后,这个子线程的子线程也是守护线程。
5.3.3 守护线程 VS 用户线程
他们的区别在于:JVM会在一个进程的所有用户线程执行结束后,结束运行;但是不会等所有守护线程结束后再结束运行。
因为守护线程是为用户线程服务的,当用户线程结束后,守护线程也就没有存在的必要了,JVM中的垃圾回收器就是典型的守护线程,当用户线程执行完任务时他也会跟着结束。
6.是否存活( isAlive() )
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t=new Thread(()->{
//得到线程
Thread thread=Thread.currentThread();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("线程执行完了");
});
t.start();
while (t.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("线程确定执行完了");
}
当还有线程存活时,while循环就会一直进行,知道线程的任务执行完毕,while才会结束循环。
7. 线程终止
⽬前常⻅的有以下两种⽅式:
1.通过⾃定义标记符来进⾏中断。
2. 调⽤ interrupt() ⽅法来中断。
7.1自定义标识符
public class ThreadInterrupt {
//声明一个自定义标识符
private static volatile boolean flag = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
while (!flag){
System.out.println("正在转帐....");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("啊!差点误了大事");
});
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
//终止线程
flag = true;
System.out.println("有内鬼,终止交易");
}
}
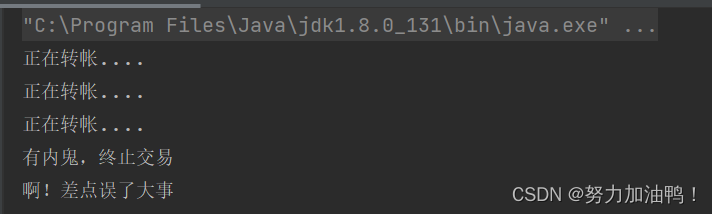
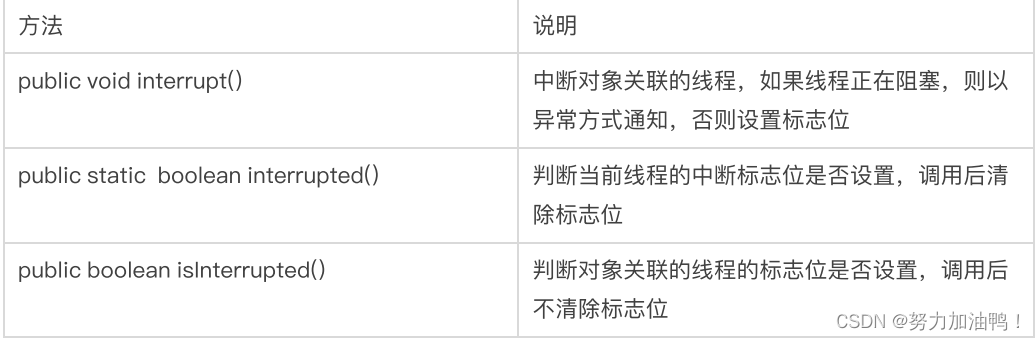
7.2使⽤Interrupt()
使⽤ Thread.interrupted() 或者 Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() 代替⾃定义标志位.
Thread 内部包含了⼀个 boolean 类型的变量作为线程是否被中断的标记.
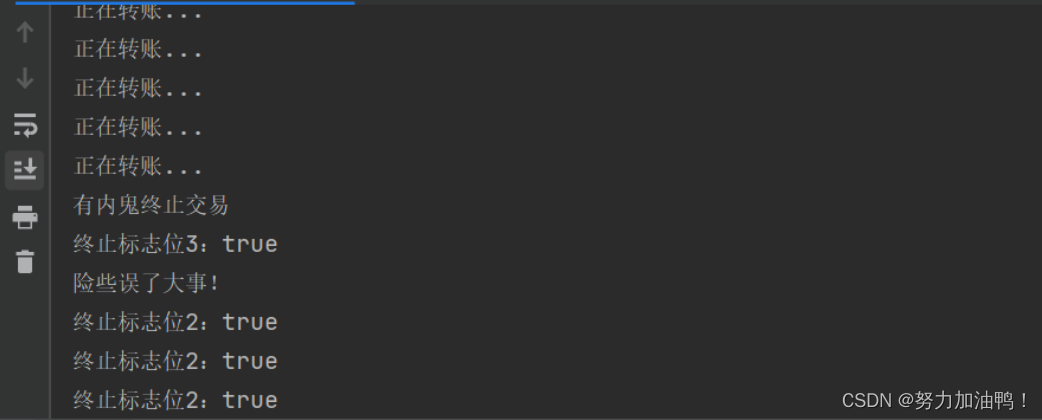
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t=new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("终止标志位:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("正在转账...");
}
System.out.println("险些误了大事!");
System.out.println("终止标志位2:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位2:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位2:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位2:"+Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("终止标志位4:"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位4:"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位4:"+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("终止标志位4:"+Thread.interrupted());
});
t.start();
Thread.sleep(100);
//终止线程
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("有内鬼终止交易");
System.out.println("终止标志位3:"+t.isInterrupted());
}
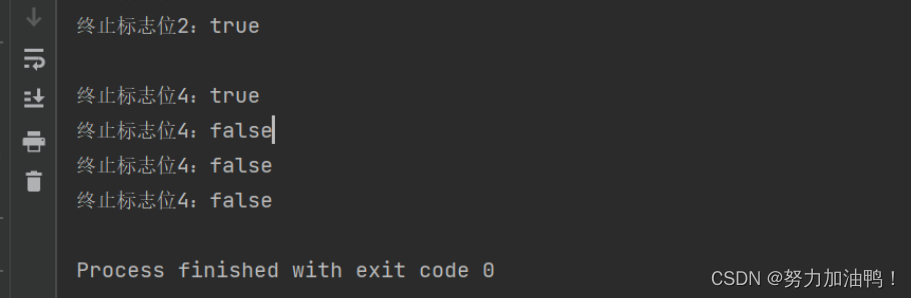
isInterrupted()和interrupted()区别:
1.interrupted()属于静态方法,所有程序都可以直接使用的全局方法;而isInterrupted()属于某个实例的方法。
2.interrupted()在使用完之后会重置中断标志符,而 isInterrupted()不会重置中断标志符。
8.线程等待 join
等待⼀个线程完成它的⼯作后,再进⾏⾃⼰的下⼀步⼯作
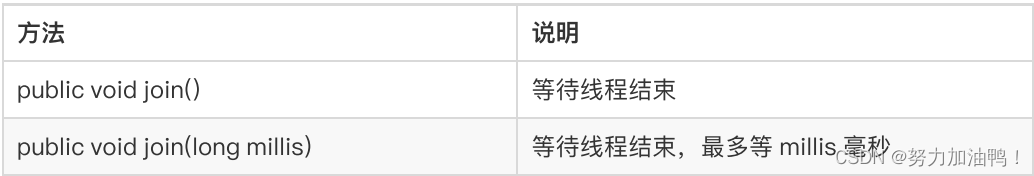
8.1 join不设置时间
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("1.张三开始上班");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.张三下班");
});
t1.start();
//等待t1执行完
t1.join();
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("1.李四开始上班");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.李四下班");
});
t2.start();
}
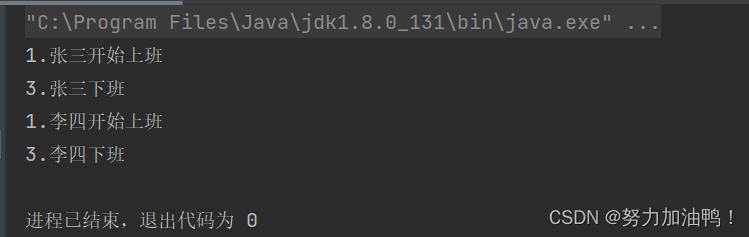
此处,李四需要等待张三上班结束,再去上班。
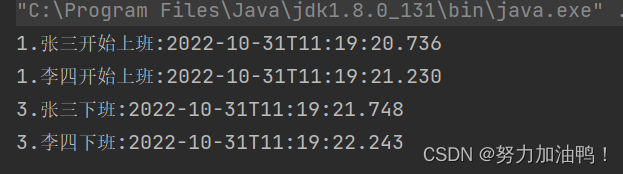
8.2 join设置时间
当join设置等待时间过短,那李四就不会等待张三上班结束再上班
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("1.张三开始上班:"+ LocalDateTime.now());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.张三下班:"+ LocalDateTime.now());
});
t1.start();
//等待t1执行完
t1.join(500);
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("1.李四开始上班:"+ LocalDateTime.now());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("3.李四下班:"+ LocalDateTime.now());
});
t2.start();
}
9.yield 让出执行权
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
Thread cThread = Thread.currentThread();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
//让出执行权
Thread.yield();
System.out.println("执行了线程:" + cThread.getName());
}
},"张三");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
Thread cThread = Thread.currentThread();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("执行线程:" + cThread.getName());
}
},"李四");
t2.start();
}
yield 不改变线程的状态, 但是会重新去排队,⽽排队之后选择谁是不确定的。





















 151
151











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








