处理并发问题,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象,这时候我们就需要线程同步。 相乘同步就是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入对象的等待池 形成队列,等待前面线程使用完毕,下一个线程在使用 package com. syn ;
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "苦逼的我" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "牛逼的你们" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "可恶的黄牛党" ) . start ( ) ;
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10 ;
boolean flag = true ;
@Override
public void run ( ) {
while ( flag) {
try {
buy ( ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
}
}
private void buy ( ) throws InterruptedException {
if ( ticketNums<= 0 ) {
flag = false ;
return ;
}
Thread . sleep ( 100 ) ;
System . out. println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + "拿到了第 " + ticketNums-- + " 张票" ) ;
}
}
package com. syn ;
import com. oop. demo05. A ;
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Account account = new Account ( 100 , "结婚基金" ) ;
Drawing husband = new Drawing ( account, 50 , "husband" ) ;
Drawing wife = new Drawing ( account, 100 , "wife" ) ;
husband. start ( ) ;
wife. start ( ) ;
}
}
class Account {
int money;
String name;
public Account ( int money, String name) {
this . money = money;
this . name = name;
}
}
class Drawing extends Thread {
Account account;
int drawingMoney;
int nowMoney;
public Drawing ( Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super ( name) ;
this . account = account;
this . drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
@Override
public void run ( ) {
if ( account. money- drawingMoney< 0 ) {
System . out. println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + "钱不够,取不了" ) ;
return ;
}
try {
Thread . sleep ( 1000 ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
account. money = account. money - drawingMoney;
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
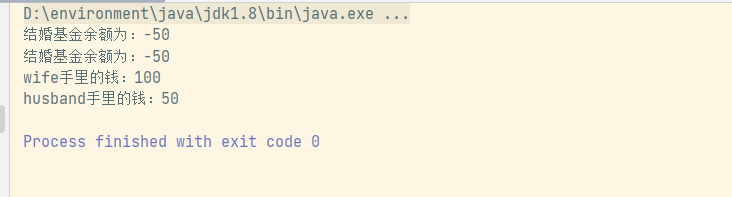
System . out. println ( account. name+ "余额为:" + account. money) ;
System . out. println ( this . getName ( ) + "手里的钱:" + nowMoney) ;
}
}
package com. syn ;
import java. util. ArrayList ;
import java. util. List ;
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) throws InterruptedException {
List < String > = new ArrayList < String > ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++ ) {
new Thread ( ( ) -> {
list. add ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) ) ;
} ) . start ( ) ;
}
Thread . sleep ( 10 ) ;
System . out. println ( list. size ( ) ) ;
}
}
由于同一进程的多个线程共享同一块存储空间,在带来方便的同时,也带来了访问冲突问题﹐为了保证数据在方法中被访问时的正确性﹐在访问时加入锁机制 synchronized ,当一个线程获得对象的排它锁,独占资源,其他线程必须等待,使用后释放锁即可﹒存在以下问题:
一个线程持有锁会导致其他所有需要此锁的线程挂起; 在多线程竞争下,加锁﹐释放锁会导致比较多的上下文切换和调度延时,引起性能问题; 如果一个优先级高的线程等待一个优先级低的线程释放锁会导致优先级倒置,引起性能问题. 由于我们可以通过private关键字来保证数据对象只能被方法访问﹐所以我们只需要针对方法提出一套机制,这套机制就是synchronized关键字, 它包括两种用法∶synchronized方法 和synchronized块 .同步方法:public synchronized void method(int args) synchronized方法控制对“对象”的访问﹐每个对象对应一把锁﹐每个synchronized方法都必须获得调用该方法的对象的锁才能执行,否则线程会阻塞,方法一旦执行,就独占该锁,直到该方法返回才释放锁,后面被阻塞的线程才能获得这个锁,继续执行缺陷:若将一个大的方法申明为 synchronized 将会影响效率 synchronized 同步方法,默认锁的是this package com. syn ;
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "苦逼的我" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "牛逼的你们" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( station, "可恶的黄牛党" ) . start ( ) ;
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10 ;
boolean flag = true ;
@Override
public void run ( ) {
while ( flag) {
try {
buy ( ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
}
}
private synchronized void buy ( ) throws InterruptedException {
if ( ticketNums<= 0 ) {
flag = false ;
return ;
}
Thread . sleep ( 100 ) ;
System . out. println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + "拿到了第 " + ticketNums-- + " 张票" ) ;
}
}
synchronized (需要锁的对象){}
synchronized (Obj){}
Obj可以是任何对象﹐但是推荐使用共享资源作为同步监视器 同步方法中无需指定同步监视器﹐因为同步方法的同步监视器就是this ,就是这个对象本身﹐或者是class 同步监视器的执行过程
第一个线程访问,锁定同步监视器﹐执行其中代码. 第二个线程访问﹐发现同步监视器被锁定﹐无法访问. 第一个线程访问完毕,解锁同步监视器. 第二个线程访问,发现同步监视器没有锁﹐然后锁定并访问 package com. syn ;
import com. oop. demo05. A ;
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Account account = new Account ( 1000 , "结婚基金" ) ;
Drawing husband = new Drawing ( account, 50 , "husband" ) ;
Drawing wife = new Drawing ( account, 100 , "wife" ) ;
husband. start ( ) ;
wife. start ( ) ;
}
}
class Account {
int money;
String name;
public Account ( int money, String name) {
this . money = money;
this . name = name;
}
}
class Drawing extends Thread {
Account account;
int drawingMoney;
int nowMoney;
public Drawing ( Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {
super ( name) ;
this . account = account;
this . drawingMoney = drawingMoney;
}
@Override
public void run ( ) {
synchronized ( account) {
if ( account. money- drawingMoney< 0 ) {
System . out. println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + "钱不够,取不了" ) ;
return ;
}
try {
Thread . sleep ( 3000 ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
account. money = account. money - drawingMoney;
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
System . out. println ( account. name+ "余额为:" + account. money) ;
System . out. println ( this . getName ( ) + "手里的钱:" + nowMoney) ;
}
}
}
package com. syn ;
import java. util. concurrent. CopyOnWriteArrayList ;
public class TestJUC {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList < String > = new CopyOnWriteArrayList < String > ( ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++ ) {
new Thread ( ( ) -> {
list. add ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) ) ;
} ) . start ( ) ;
}
try {
Thread . sleep ( 3 * 1000 ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
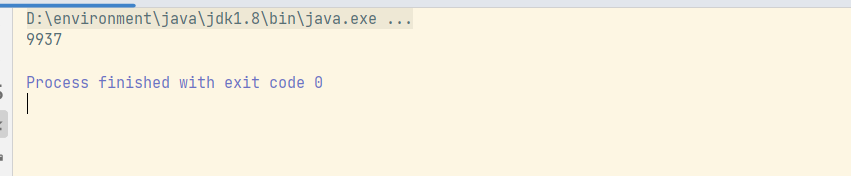
System . out. println ( list. size ( ) ) ;
}
}
从JDK5.0开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制----通过显示定义同步锁对象来实现同步。 同步锁还用Lock对象充当 java.util.concurrent.looks.Lock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具。锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象。 ReentrantLock类实现了Lock,他拥有与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可是显示加锁、释放锁 class A{
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ();
public void m(){
lock.lock ();
try {
//保证线程代码安全
}finally {
//如果同步代码有异常,要将unlock()写入finally语句块
lock.unlock ();
}
}
}
package com. senior ;
import java. util. concurrent. locks. ReentrantLock ;
public class TestLock {
public static void main ( String [ ] args) {
Lock2 lock2 = new Lock2 ( ) ;
new Thread ( lock2, "me" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( lock2, "you" ) . start ( ) ;
new Thread ( lock2, "others" ) . start ( ) ;
}
}
class Lock2 implements Runnable {
private int ticketNums = 10 ;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock ( ) ;
@Override
public void run ( ) {
while ( true ) {
try {
lock. lock ( ) ;
if ( ticketNums<= 0 ) {
break ;
} else {
System . out. println ( Thread . currentThread ( ) . getName ( ) + "获得了第 " + ticketNums-- + " 票" ) ;
}
} finally {
lock. unlock ( ) ;
try {
Thread . sleep ( 10 ) ;
} catch ( InterruptedException e) {
e. printStackTrace ( ) ;
}
}
}
}
}
lock是显示锁(手动开启和关闭锁,别忘记关闭锁)synchronized 是隐士锁,出了作用域自动释放 Lock 只有代码块锁,synchronized 有代码块锁和方法锁 使用Lock锁,JVM将花费更少的时间调度线程,性能更好。并且具有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类) 优先使用顺序:
Lock > 同步代码快(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源)> 同步方法(在方法体之外)






















 6146
6146











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










