JavaSE——java8新特性
1、Lambda表达式
lambda的本质:作为接口的实例,只有函数式接口(接口中只声明了一个函数)能用。
- 无参、无返回值
public static void main(String[] args) {
//正常写法
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("dcd");
}
};
runnable.run();
//lambda表达式写法
Runnable runnable1 = ()->System.out.println("np");
runnable1.run();
}
- 有参数,没有返回值
public static void main(String[] args) {
//正常写法
Consumer<String> consumer = new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
};
consumer.accept("dcd");
//lambda表达式
Consumer<String> consumer1=(s)->{System.out.println(s);};//(){}括号可以省
consumer1.accept("np");
}
- 多参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparator<Integer> comparator = (o1,o2)->{
System.out.println("这是一个多少参数");
return Integer.compare(o1,o2);
}
System.out.println(comparator.compare(12,15));
}
2、函数式(Functional)接口
只有一个抽象方法,可以通过lambda表达式来创建该接口对象
@FunctionalInterface
public interface MyInterface {
void fun();
}

@Test
public void fun(){
fun(200, (m)->System.out.println("花了"+m));
}
public void fun(int m, Consumer<Integer> c){
c.accept(m);
}
3、方法引用和构造器引用
当要传递给lambda体的在操作已经有实现的方法了,就可以使用方法引用,因此方法引用也是函数式接口的实例
对象::非静态方法
类::静态方法
类::非静态方法
使用要求:接口中的抽象方法的形参列表和返回值类型与方法引用的形参列表返回值类型相同
- 情况一:对象 :: 实例方法
Consumer中的void accept(T t)和PrintStream中的void println(T t)相似,可以替换
Supplier中的T get()和String getName()
public static void main(String[] args) {
Consumer<String> a=str->System.out.println(str);
a.accept("dcdnp");
//引用写法
PrintStream out = System.out;
Consumer<String> b= out::println;
b.accept("np");
}
-
类::静态方法


-
类::非静态方法



- 构造器引用




4、强大的Sream API




-
创建流
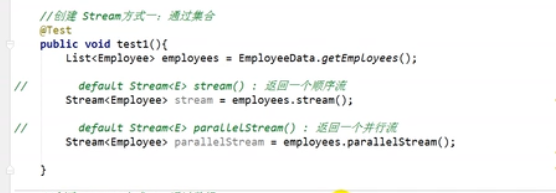
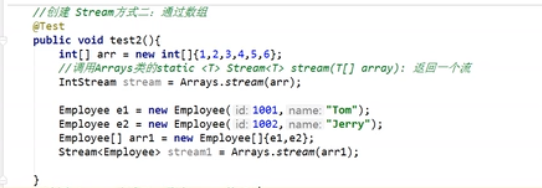
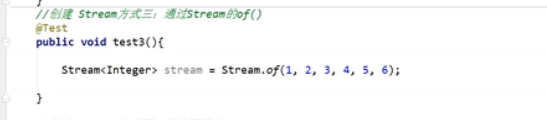
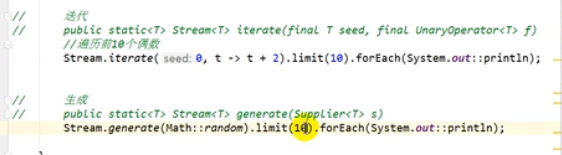
-
中间操作


public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//筛选和切片
//筛选流
ArrayList<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("lx",20));
people.add(new Person("lxj",19));
Stream<Person> stream = people.stream();
stream.filter(a->a.getAge()<20).forEach(System.out::println);
//limit截断流
people.stream().limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
//skip跳过元素
people.stream().skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
//distinct筛选,通过流生成的hashCode()和equals()去除重复元素
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
System.out.println(people);
people.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
//映射map,flatMap
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","bb","cc");
list.stream().map(str->str+"hhh").forEach(System.out::println);
//排序
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(13,22,12);
list.stream().soted().forEach(System.out::println);
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(12,22,33);
list.stream().sorted((e1,e2)->-Integer.compare(e1,e2)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
- 终止操作

public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("lx",20));
people.add(new Person("lxj",19));
//检查是否匹配所有元素
boolean b = people.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() < 20);
System.out.println(b);
//匹配任意一个就可以
boolean b1 = people.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge() < 20);
System.out.println(b1);
//检查是否没有匹配的元素
boolean z = people.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getName().startsWith("z"));
System.out.println(z);
//查找第一个元素
Optional<Person> first = people.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println(first);
//查找任意一个元素
Optional<Person> any = people.parallelStream().findAny();
System.out.println(any);
//求个数
long count = people.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() < 20).count();
System.out.println(count);
//求最大
Stream<Integer> integerStream = people.stream().map(e -> e.getAge());
Optional<Integer> max = integerStream.max(Integer::compare);
System.out.println(max);
//求最小
Optional<Person> min = people.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge()));
System.out.println(min);
//foreach
people.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
//reduce可以将流中的元素反复结合起来,得到一个值返回T
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6);
Integer reduce = list.stream().reduce(10, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(reduce);
//
ArrayList<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("lx",20));
people.add(new Person("lxj",19));
Stream<Integer> integerStream = people.stream().map(e -> e.getAge());
Optional<Integer> reduce1 = integerStream.reduce((a1,a2)->a1+a2);
System.out.println(reduce1);
}


public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Person> people = new ArrayList<>();
people.add(new Person("dcd",18));
people.add(new Person("lx",20));
people.add(new Person("lxj",19));
List<Person> collect = people.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge() < 20).collect(Collectors.toList());
for(Person i :collect){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
5、Optional类


public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person();
p=null;//变成空指针
Optional<Person> p1 = Optional.ofNullable(p);
System.out.println(p1);
Person dcd = p1.orElse(new Person("dcd", 18));
System.out.println(dcd);
}
/*
Optional.empty
Person{name='dcd', age=18}
*/






















 564
564











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








