本文讲解非系统表的创建逻辑([<fontcolor=0000dd>普通表和索引表]),其入口函数为heap_create,内部公共接口函数为RelationBuildLocalRelation和RelationCreateStorage相关知识回顾见:
postgres源码解析38 表创建执行全流程梳理–1
postgres源码解析38 表创建执行全流程梳理–2
postgres源码解析38 表创建执行全流程梳理–3
heap_create 执行逻辑
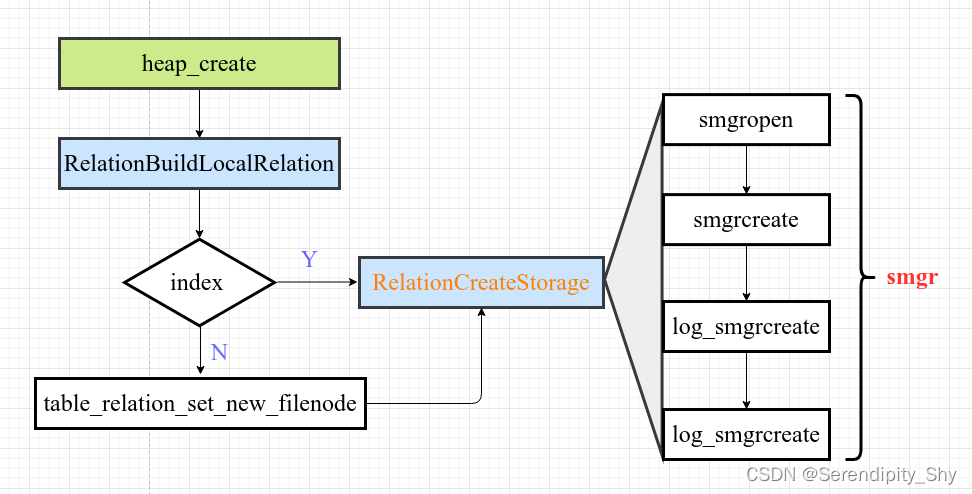
1)首先进行安全性检查,不允许在系统表中创建relations,判断是否需要创建持久化文件等;
2)根据表名、表空间、表对象标识符和文件节点relfilenode等信息调用 RelationBuildLocalRelation在内存中构建Relation,并插入全局relcache 哈希表中;
3)结合relation类型调用相应的接口函数进行relation的创建,[普通表/TOAST/物化视图: table_relation_set_new_filenode,索引/序列:RelationCreateStorage];
4) 对于无需创建持久化的relation且用户指定表空间,则需要在 pg_tablespace 中注册对应的信息。
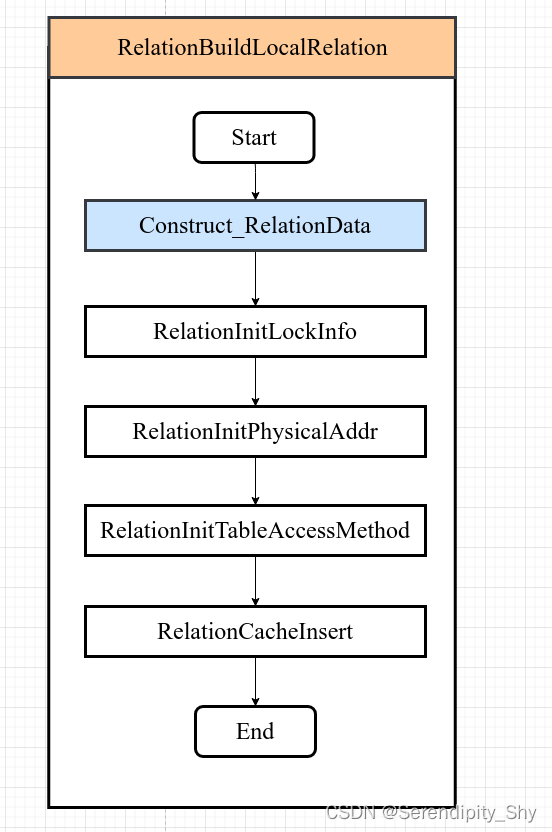
RelationBuildLocalRelation
该函数目的是在内存中构建创建表的relcache Entry,并插入全局Relcache 哈希表中,用于加速后续对此表的访问。
1)如果不存在CacheMemoryContext,则创建此上下文,后续操作均在此上下文进行;
2)分配并初始化Relation结构体,结合入参的TueDesc填充Relation结构体中rd_att字段:字段属性的详细信息;
3)分配并根据入参填充Relation结构体中rd_att字段的Form_pg_class字段:表名、命名空间、字段属性/数目等;
4)调用 RelationInitLockInfo初始化relation描述符锁信息;
5)调用 RelationInitPhysicalAddr 初始化relation描述符对应的物理地址:spcNode/dbNode//RelNode [表空间/数据库/表]
6)将上述构建好的RelCache Entry插入全局ralcache 哈希表中,并增加该条目的引用计数
*
* RelationBuildLocalRelation
* Build a relcache entry for an about-to-be-created relation,
* and enter it into the relcache.
*/
Relation
RelationBuildLocalRelation(const char *relname,
Oid relnamespace,
TupleDesc tupDesc,
Oid relid,
Oid accessmtd,
Oid relfilenode,
Oid reltablespace,
bool shared_relation,
bool mapped_relation,
char relpersistence,
char relkind)
{
Relation rel;
MemoryContext oldcxt;
int natts = tupDesc->natts;
int i;
bool has_not_null;
bool nailit;
AssertArg(natts >= 0);
/*
* check for creation of a rel that must be nailed in cache.
*
* XXX this list had better match the relations specially handled in
* RelationCacheInitializePhase2/3.
*/
switch (relid)
{
case DatabaseRelationId:
case AuthIdRelationId:
case AuthMemRelationId:
case RelationRelationId:
case AttributeRelationId:
case ProcedureRelationId:
case TypeRelationId:
nailit = true;
break;
default:
nailit = false;
break;
}
/*
* check that hardwired list of shared rels matches what's in the
* bootstrap .bki file. If you get a failure here during initdb, you
* probably need to fix IsSharedRelation() to match whatever you've done
* to the set of shared relations.
*/
if (shared_relation != IsSharedRelation(relid))
elog(ERROR, "shared_relation flag for \"%s\" does not match IsSharedRelation(%u)",
relname, relid);
/* Shared relations had better be mapped, too */
Assert(mapped_relation || !shared_relation);
/*
* switch to the cache context to create the relcache entry.
*/
if (!CacheMemoryContext)
CreateCacheMemoryContext();
oldcxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(CacheMemoryContext);
/*
* allocate a new relation descriptor and fill in basic state fields.
*/
rel = (Relation) palloc0(sizeof(RelationData));
/* make sure relation is marked as having no open file yet */
rel->rd_smgr = NULL;
/* mark it nailed if appropriate */
rel->rd_isnailed = nailit;
rel->rd_refcnt = nailit ? 1 : 0;
/* it's being created in this transaction */
rel->rd_createSubid = GetCurrentSubTransactionId();
rel->rd_newRelfilenodeSubid = InvalidSubTransactionId;
rel->rd_firstRelfilenodeSubid = InvalidSubTransactionId;
rel->rd_droppedSubid = InvalidSubTransactionId;
/*
* create a new tuple descriptor from the one passed in. We do this
* partly to copy it into the cache context, and partly because the new
* relation can't have any defaults or constraints yet; they have to be
* added in later steps, because they require additions to multiple system
* catalogs. We can copy attnotnull constraints here, however.
*/
rel->rd_att = CreateTupleDescCopy(tupDesc);
rel->rd_att->tdrefcount = 1; /* mark as refcounted */
has_not_null = false;
for (i = 0; i < natts; i++)
{
Form_pg_attribute satt = TupleDescAttr(tupDesc, i);
Form_pg_attribute datt = TupleDescAttr(rel->rd_att, i);
datt->attidentity = satt->attidentity;
datt->attgenerated = satt->attgenerated;
datt->attnotnull = satt->attnotnull;
has_not_null |= satt->attnotnull;
}
if (has_not_null)
{
TupleConstr *constr = (TupleConstr *) palloc0(sizeof(TupleConstr));
constr->has_not_null = true;
rel->rd_att->constr = constr;
}
/*
* initialize relation tuple form (caller may add/override data later)
*/
rel->rd_rel = (Form_pg_class) palloc0(CLASS_TUPLE_SIZE);
namestrcpy(&rel->rd_rel->relname, relname);
rel->rd_rel->relnamespace = relnamespace;
rel->rd_rel->relkind = relkind;
rel->rd_rel->relnatts = natts;
rel->rd_rel->reltype = InvalidOid;
/* needed when bootstrapping: */
rel->rd_rel->relowner = BOOTSTRAP_SUPERUSERID;
/* set up persistence and relcache fields dependent on it */
rel->rd_rel->relpersistence = relpersistence;
switch (relpersistence)
{
case RELPERSISTENCE_UNLOGGED:
case RELPERSISTENCE_PERMANENT:
rel->rd_backend = InvalidBackendId;
rel->rd_islocaltemp = false;
break;
case RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP:
Assert(isTempOrTempToastNamespace(relnamespace));
rel->rd_backend = BackendIdForTempRelations();
rel->rd_islocaltemp = true;
break;
default:
elog(ERROR, "invalid relpersistence: %c", relpersistence);
break;
}
/* if it's a materialized view, it's not populated initially */
if (relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW)
rel->rd_rel->relispopulated = false;
else
rel->rd_rel->relispopulated = true;
/* set replica identity -- system catalogs and non-tables don't have one */
if (!IsCatalogNamespace(relnamespace) &&
(relkind == RELKIND_RELATION ||
relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW ||
relkind == RELKIND_PARTITIONED_TABLE))
rel->rd_rel->relreplident = REPLICA_IDENTITY_DEFAULT;
else
rel->rd_rel->relreplident = REPLICA_IDENTITY_NOTHING;
/*
* Insert relation physical and logical identifiers (OIDs) into the right
* places. For a mapped relation, we set relfilenode to zero and rely on
* RelationInitPhysicalAddr to consult the map.
*/
rel->rd_rel->relisshared = shared_relation;
RelationGetRelid(rel) = relid;
for (i = 0; i < natts; i++)
TupleDescAttr(rel->rd_att, i)->attrelid = relid;
rel->rd_rel->reltablespace = reltablespace;
if (mapped_relation)
{
rel->rd_rel->relfilenode = InvalidOid;
/* Add it to the active mapping information */
RelationMapUpdateMap(relid, relfilenode, shared_relation, true);
}
else
rel->rd_rel->relfilenode = relfilenode;
RelationInitLockInfo(rel); /* see lmgr.c */
RelationInitPhysicalAddr(rel);
rel->rd_rel->relam = accessmtd;
/*
* RelationInitTableAccessMethod will do syscache lookups, so we mustn't
* run it in CacheMemoryContext. Fortunately, the remaining steps don't
* require a long-lived current context.
*/
MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldcxt);
if (relkind == RELKIND_RELATION ||
relkind == RELKIND_SEQUENCE ||
relkind == RELKIND_TOASTVALUE ||
relkind == RELKIND_MATVIEW)
RelationInitTableAccessMethod(rel);
/*
* Okay to insert into the relcache hash table.
*
* Ordinarily, there should certainly not be an existing hash entry for
* the same OID; but during bootstrap, when we create a "real" relcache
* entry for one of the bootstrap relations, we'll be overwriting the
* phony one created with formrdesc. So allow that to happen for nailed
* rels.
*/
RelationCacheInsert(rel, nailit);
/*
* Flag relation as needing eoxact cleanup (to clear rd_createSubid). We
* can't do this before storing relid in it.
*/
EOXactListAdd(rel);
/* It's fully valid */
rel->rd_isvalid = true;
/*
* Caller expects us to pin the returned entry.
*/
RelationIncrementReferenceCount(rel);
return rel;
}
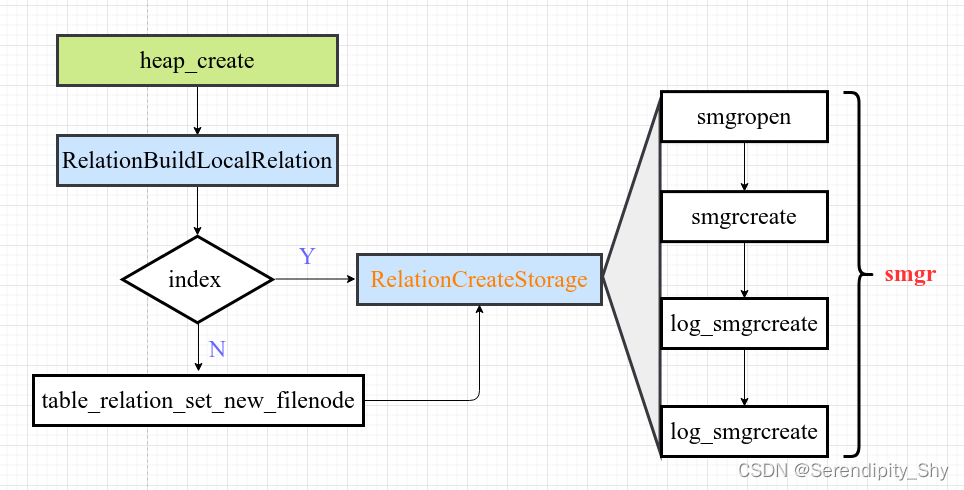
RelationCreateStorage
物理文件的创建由磁盘管理器负责,pg中所有文件系统均调用这统一接口,而RelationCreateStorage 函数的实现就是通过调用这些函数进一步封装而成,期执行流程如下:
1)对于持久化的relation,设置字段表示need_wal,表明需要写WAL日志,对于临时relation或者unlogged relation无需此操作;
2)根据输入的RelFileNode调用 smgropen返回 SMgrRelation对象,不存在会创建一个;
3)结合上述返回的 SMgrRelation和ForkNumber号调用 smgrcreate创建relation的物理文件;
4)如需写WAL日志,调用 log_smgrcreate函数记录下此relation的实际物理信息;
5)最后将其添加至PendingRelDelete链表尾,在事务真正提交的时候如需回滚则可通过此信息将创建的文件删除,并返回 SMgrRelation对象。
/*
* RelationCreateStorage
* Create physical storage for a relation.
*
* Create the underlying disk file storage for the relation. This only
* creates the main fork; additional forks are created lazily by the
* modules that need them.
*
* This function is transactional. The creation is WAL-logged, and if the
* transaction aborts later on, the storage will be destroyed.
*/
SMgrRelation
RelationCreateStorage(RelFileNode rnode, char relpersistence)
{
PendingRelDelete *pending;
SMgrRelation srel;
BackendId backend;
bool needs_wal;
Assert(!IsInParallelMode()); /* couldn't update pendingSyncHash */
switch (relpersistence)
{
case RELPERSISTENCE_TEMP:
backend = BackendIdForTempRelations();
needs_wal = false;
break;
case RELPERSISTENCE_UNLOGGED:
backend = InvalidBackendId;
needs_wal = false;
break;
case RELPERSISTENCE_PERMANENT:
backend = InvalidBackendId;
needs_wal = true;
break;
default:
elog(ERROR, "invalid relpersistence: %c", relpersistence);
return NULL; /* placate compiler */
}
srel = smgropen(rnode, backend);
smgrcreate(srel, MAIN_FORKNUM, false);
if (needs_wal)
log_smgrcreate(&srel->smgr_rnode.node, MAIN_FORKNUM);
/* Add the relation to the list of stuff to delete at abort */
pending = (PendingRelDelete *)
MemoryContextAlloc(TopMemoryContext, sizeof(PendingRelDelete));
pending->relnode = rnode;
pending->backend = backend;
pending->atCommit = false; /* delete if abort */
pending->nestLevel = GetCurrentTransactionNestLevel();
pending->next = pendingDeletes;
pendingDeletes = pending;
if (relpersistence == RELPERSISTENCE_PERMANENT && !XLogIsNeeded())
{
Assert(backend == InvalidBackendId);
AddPendingSync(&rnode);
}
return srel;
}






















 539
539











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








