目录
认识BOM
BOM定义
BOM: browser object model (浏览器规则)
Bom 就是浏览器的对象 【模型】,我们如何操控这个对象模型?
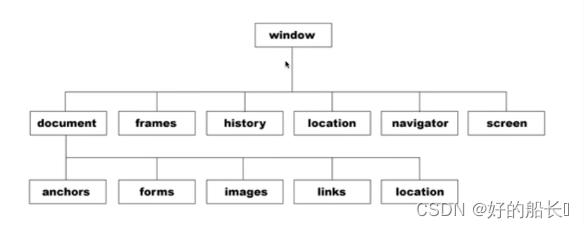
系统对话框涉及到的方法
window 方法 (一般情况下window可以省略)
alert(); 弹出警告框
所有的属性和方法和变量前面都可以跟一个window
<script>
alert("hello");
window.alert("world");
function show(){
alert("hello world");
}
window.show();//hello world
show(); //hello world
</script>confirm( ) 弹出一个待确定和取消的提示框
返回值:如果点击确定,返回true
如果点击取消,返回false
var res = confirm("你确定要离开么?");
alert(res);prompt( ) 弹出一个带输入框的提示框
参数:
第一个参数:面板上显示的内容
第二个参数:输入框里面的默认(可以不传入)
返回值:点击确定,返回输入框的内容
点击取消,返回null
var res = prompt("请输入内容",100);
alert(res);open方法
- 第一个参数:跳转的url( ) (可以打开多个相同的窗口)
- 第二个参数:字符串,给打开的窗口起个名字 (再次打开窗口仍然为第一次打开的窗口)
- 第三个参数:一串特殊含义的字符串,可以控制打开窗口的属性
<script>
function btnClick(){
//window.open();
open("https://baidu.com","xxx",'width=400,height=400,top=200,left=200');
}
</script>
<body>
<button onclick = "btnClick()">打开窗口</button>
</body>窗口特征(有些属性在浏览器中可能不兼容,火狐包容度最高)
| channelmode = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否使用剧院模式显示窗口,默认为no |
| directories = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否添加目录按钮。默认为yes |
| fullscreen = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否使用全屏模式显示浏览器。默认是no。处于全屏模式的窗口必须同时处于剧院模式 |
| height = pixels | 窗口文档显示区域的高度,以像素计 |
| left = pixels | 窗口的x坐标。以像素计 |
| location = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否显示地址字段。默认是yes |
| menubar = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否显示菜单栏。默认是yes |
| resizable = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 窗口是否可调节尺寸。默认是yes |
| scrollbars = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否显示滚动条,默认是yes |
| status = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否添加状态栏,默认是yes |
| titlebar = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否显示标题栏。默认是yes |
| toolbar = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 是否显示浏览器的工具栏。默认是yes |
| top = yes | no | 1 | 0 | 窗口的y坐标 |
| width = pixels | 窗口的文档显示区的宽度。以像素计。 |
history对象
window.history 掌管的是当前窗口(注意不是浏览器)历史记录(只要加载url不一样就会产生历史记录)
属性:history.length 输出当前窗口历史记录的条数
方法:
history.back( ) 返回上一条历史记录
history.forward( ) 前进到下一条历史记录
history.go( )
参数: 0 刷新当前页面
正整数 前进n条记录
负整数 后退n条记录
<body>
<button onclick="alert(history.length)">获取历史记录的条数</button>
<button onclick="history.back()">back</button>
<button onclick="history.forward()">forward</button>
<button onclick="history.go(2)">go</button> <!-- 正数:往前跳n个页面;负数:往后跳n个页面;前提:页面存在 -->
</body>location对象
url:统一资源定位符 协议:// IP(域名) / :端口号 / 路径 /?查询字符串 #锚点
<script>
/* url:统一资源定位符
协议:// IP(域名) / :端口号 / 路径 /?查询字符串 #锚点
*/
/* 需要安装服务器才能显示
location.protocol file:本地磁盘文件访问
http:
https:(证书认证协议)
*/
alert(location.protocol);
/* location.hostname 主机名 IP(在全球范围内找到你当前网络的地址)
域名 IP的别称
*/
alert(location.hostname);
/* location.port 端口号(默认隐藏的)
【注】是当前电脑中使用网络的软件,随机给他分配一个编号 0 ~ 65535
hostname:port 可以直接定位到当前使用网络的程序
小细节:浏览器 8080
http 80
https 443
location.pathname 路径
location.search 查询字符串(前后端交互)
location.hash 锚点
*/
alert(location.search);
alert(location.hash);
</script>location对象方法
window.location === window.document.location;
location 地址栏(输入url的地方)
属性:
方法:
location.assign(url) 【注】在当前窗口跳转带这个url
location.replace(url) 【注】在当前窗口替换成新的url
location.reload() 【注】刷新窗前窗口
location.reload(true) 不经过浏览器缓存强制从服务器重载
<body>
<button onclick="location.assign('https://www.baidu.com')">assign</button> <!-- 单双引号交替使用;会有历史记录,可以前进和后退 -->
<button onclick="location.replace('https://www.baidu.com')">replace</button><!-- 不产生历史记录,不可以后退 -->
<button onclick="location.reload()">reload</button><!-- -->
</body>认识DOM
DOM
document object model(文档对象模型) 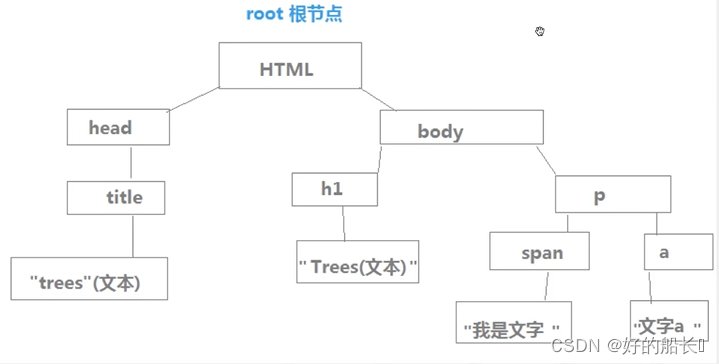
- 节点类型:
- 元素节点 <div></div>
- 属性节点 id = " div1 "
- 文本节点 div文本
- 元素节点的获取
- document.getElementById(id)
- 功能:通过id获取符合元件的元素. (id必须是唯一的)
- 返回值:就是符合条件的一个节点
- document.getElementById(id)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- <script>
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv); //null;原因:代码是按顺序执行
</script> -->
<!-- <script>
//解决方案二
window.onload = function(){
//写在这里的代码,是整个页面加载完成以后执行
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv); //[object HTMLDivElement]
}
</script> -->
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
/* 获取行间属性的值 */
alert(oDiv.id); //div1
alert(oDiv.title); //hello
/* 不能直接.class;原因是其为一个关键字
访问行间class 通过className访问
*/
alert(oDiv.className); //box
/* 设置行间属性的值,在网页内检查代码框可以看见被修改 */
oDiv.id = "div2";
oDiv.title = "world";
oDiv.className = "box4";
/* 想要获取行间属性的样式 */
alert(oDiv.style); //[object CSSStyleDeclaration]
alert(oDiv.style.width); //300px
alert(oDiv.style.height); //300px
/* 如果css样式带‘-’,将‘-’去掉,从第二个单词开始首字母大写 */
alert(oDiv.style.backgroundColor); //red
/* 修改宽高和背景颜色 */
oDiv.style.backgroundColor = "blue";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 行间样式写在标签内的通过Js中的获取行间样式属性方法可以访问到,但如果将样式写在css中,用该方法不能获取属性值 -->
<div id="div1" title="hello" class="box" style="width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: red;">div文本</div>
</body>
<!-- 解决方案一:放在boay下面
<script>
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv); //[object HTMLDivElement]
</script> -->
</html>获取元素节点
- node.getElementsByTagName(标签名);
- 功能:从node节点开始,通过标签名获取符合条件的元素节点
- node.getElementsByClassName(class名字) IE8以下不兼容
- 功能:通过class名字获取符合条件的元素节点
- document.getElemrntsByName(name属性的值,只能在全局查找)
- 功能:通过name属性的值获取符合条件的元素节点
- 【注】一般使用在表单元素里
- 【注】node可以是任意节点,想要获取全局,使用document,document代表整个页面所有标签,但返回的都是伪数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var aLis1 = document.getElementsByTagName("li");
// alert(aLis1); //[object HTMLCollection],返回的是个对象,使用起来和数组类似,一般情况,把这种叫做伪数组/类数组(人为命名,官方没有这种概念).
alert(aLis1.length); //10
}
window.onload = function(){
var oOl = document.getElementById("ol1");
var aLis2 = oOl.getElementsByTagName("li");
//获取ol下的li节点
alert(aLis2.length); //4
for(var i = 0; i < aLis2.length; i++){
aLis2[i].style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
var nodes1 = document.getElementsByClassName("box");
alert(nodes1.length); //5
for(var i = 0; i < nodes1.length; i++){
nodes1[i].style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
var oUl = document.getElementById("ul1");
var nodes2 = oUl.getElementsByClassName("box");
alert(nodes2.length); //3
for(var i = 0; i < nodes2.length; i++){
nodes2[i].style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
var nodes3 = document.getElementsByName("hello");
alert(nodes3.length); //3
for(var i = 0; i < nodes3.length; i++){
nodes3[i].style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="ul1">
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li name="hello">111</li>
<div class="box" name="hello">div</div>
</ul>
<input type="text" name="hello"/>
<span name="hello">span</span>
<ol id="ol1">
<li>222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li>222</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>- document.querySelector( )
- 返回值:一个元素节点,找到符合条件的第一个元素节点
- document.querySelectorAll( )
- 返回值:返回值是一个伪数组
- 参数:字符串 CSS选择器格式字符串
<script>
window.onload = function(){
/* document.querySelector:符合条件的第一个节点 */
//id = ol1
var node = document.querySelector("#ol1"); //调用格式使用css格式
node.style.backgroundColor = "red";
//tagName = "li"
var node1 = document.querySelector("li"); //第一个元素节点
node1.style.backgroundColor = "yellow";
//class = box
var node2 = document.querySelector(".box"); //调用格式使用css格式
node2.style.backgroundColor = "purple";
//获取ol下第一个 class = box
var node3 = document.querySelector("ol .box"); //调用格式使用css格式,注意空格
node3.style.backgroundColor = "black";
//name = hello
var node4 = document.querySelector("[name = hello]"); //调用格式使用css格式
node4.style.backgroundColor = "pink";
/* document.querySelectorAll:符合条件的所有节点 */
// var nodes = document.querySelectorAll("ol .box"); //返回的是伪数组
// alert(nodes.length);
// for(var i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++){
// nodes[i].style.backgroundColor = "blue";
// }
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="ul1">
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li name="hello">111</li>
<div class="box" name="hello">div</div>
</ul>
<input type="text" name="hello"/>
<span name="hello">span</span>
<ol id="ol1">
<li>222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li>222</li>
</ol>
</body>自定义byClassName方法
<script>
/*
node.getElementsByClassName();
*/
function elementsByClassName(node,classStr){
//1、获取node这个节点下所有的子节点
var nodes = node.getElementsByTagName("*");
var arr = []; //存放符合条件的节点
for(var i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++){
if(nodes[i].className === classStr){
arr.push(nodes[i]);
}
return arr;
}
window.onload = function(){
var oL = document.getElementById("ol1");
var nodes = elementsByClassName(oL,"box");
alert(nodes.length);
for(var i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++){
nodes[i].style.backgroundColor = "red";
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<ul id="ul1">
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li>111</li>
<li class="box">111</li>
<li name="hello">111</li>
<div class="box" name="hello">div</div>
</ul>
<input type="text" name="hello"/>
<span name="hello">span</span>
<ol id="ol1">
<li>222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li class="box">222</li>
<li>222</li>
</ol>
</body>获取当前有效样式
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
/*
通过 .style.xxx的方式只能访问内联的css样式。
权重最高的css样式才能生效
*/
// alert(oDiv.style.width); //200px
// alert(oDiv.style.backgroundColor); //red
// alert(oDiv.style.height); //无输出
/*
获取当前的有效样式:
系统提供了两个方法(不同浏览器):
*/
// alert(oDiv.currentStyle['height']); //IE兼容
// alert(getComputedStyle(oDiv)["height"]); //300px,火狐、谷歌兼容
// alert(getStyle(oDiv,"height")); //300px
/*
设置样式
.style.xxx方式设置css样式
*/
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
oDiv.style.backgroundColor = "orange";
oDiv.style.height = "500px";
}
}
//跨浏览器的兼容
function getStyle(node,cssStyle){
return node.currentStyle ? node.currentStyle[cssStyle] : getComputedStyle(node)[cssStyle];
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1" style="width: 200px; background-color: red;" class="box"></div>
<button id="btn1">修改样式</button>
</body>改变字体颜色和大小案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#div1{width: 400px; height: 200px; background-color: white; border: 1px solid black; margin: 100px auto; text-align: center; line-height: 200px; font-size: 18px;}
</style>
<script>
//跨浏览器的兼容
function getStyle(node,cssStyle){
return node.currentStyle ? node.currentStyle[cssStyle] : getComputedStyle(node)[cssStyle];
}
/*
写一个定时器,每一秒修改一次div文本颜色和文字大小,
最开始这个文字是默认大小,大小开始增大,当增大了6次以后,
文字大小开始缩小,缩小6次,文字再开始增大。
*/
/*
颜色随机:
rgba(255,255,255,0);
parseInt(Math.random() * 256)
*/
function randomColor(){
var str = "rgba(" + parseInt(Math.random() * 256) + "," + parseInt(Math.random() * 256) + "," + parseInt(Math.random() * 256) + "," + parseInt(Math.random() * 256) + ")";
return str;
}
// alert(randomColor());
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
var speed = 5; //每一次变化的大小
var count = 0; //计数
setInterval(function(){
oDiv.style.color = randomColor();
//1、将字体上一次的字体大小取出
var iCur = parseInt(getStyle(oDiv,'fontSize'));
// alert(iCur);
//2、变化字体大小,重新赋值回去
oDiv.style.fontSize = (iCur + speed) + "px";
count++;
if(count % 6 == 0){
speed *= -1;
}
}, 1000);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
div文本
</div>
</body>
</html>attribute和元素节点属性
setAttribute
getAttribute
removeAttribute
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv.id); //div1
alert(oDiv.title); //hello
alert(oDiv.name); //undefined
/*
区别:
1、class的访问
2、支持自定义属性
3、
*/
alert(oDiv.getAttribute("id")); //div1
alert(oDiv.getAttribute("title")); //hello
alert(oDiv.className); //box
alert(oDiv.getAttribute("class")); //box
alert(oDiv.xxx); //undefined
alert(oDiv.getAttribute("xxx")); //yyy
oDiv.className = 'box4';
oDiv.zzz = 'ooo'; //添加成功,但行间显示不了
alert(oDiv.zzz); //000
oDiv.setAttribute("class",'box5');
oDiv.setAttribute("zzz",'ooo');
oDiv.className = ''; //只是用空字符串替换了
oDiv.removeAttribute("title"); //真正的删除
}![]()
![]()
![]()
innerHTML 获取标签间内容 会解析标签
innerText 获取标签间纯文本 不会解析标签,设置纯文本
outerHTML 从外标签开始到外标签结束 会解析标签
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv.innerHTML);
//赋值
oDiv.innerHTML = "<h1>hello world</h1>"; /* 解析标签间的内容 */
alert(oDiv.innerText); //div文本em文本strong文本
alert(oDiv.outerHTML); //<div id="div1">div文本<em>em文本</em><strong>strong文本</strong></div>
oDiv.outerHTML = "<h1>hello world </h1>";
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">div文本<em>em文本</em><strong>strong文本</strong></div>
</body>获取子节点
childNodes 访问当前节点下所有的子节点
firstChild 访问子节点中的首位
lastChild 访问子节点中的最后一位
nextSibling 访问当前节点兄弟节点中的下一个节点
previousSibling 访问当前节点兄弟节点中的上一个节点
【注】上述这些属性都包含文本节点
【注】上下方法功能一致,但下述方法只获取子节点中的元素节点(IE8以下不兼容)
children
firstElementChild
lastElementChild
nextElementSibling
previousElementSibling
nodeType nodeName nodeValue
元素节点 1 标签名 null
属性节点 2 属性名 属性值
文本节点 3 #text 文本内容
/*
nodeType nodeName nodeValue
元素节点 1 标签名 null
属性节点 2 属性名 属性值
文本节点 3 #text 文本内容
*/
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv.childNodes.length); //3
alert(oDiv.childNodes[0]); //[object HTMLElement]
alert(oDiv.childNodes[1]); //[object Text]; 文本节点 文本节点通过元素节点的子节点获取
alert(oDiv.childNodes[2]); //[object HTMLElement]
alert(oDiv.childNodes[0].nodeType); //1 元素节点
alert(oDiv.childNodes[1].nodeType); //3 文本节点
alert(oDiv.childNodes[2].nodeType); //1 元素节点
alert(oDiv.childNodes[0].nodeName); //EM
alert(oDiv.childNodes[1].nodeValue);//div文本
alert(oDiv.childNodes[2].nodeValue);//null
alert(oDiv.firstChild.nodeName); //EM
alert(oDiv.lastChild.nodeName); //STRONG
}空格、回车、换行 看不见,但是字符
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv.childNodes.length); //5
for(var i = 0; i < oDiv.childNodes.length; i++){
alert(oDiv.childNodes[i].nodeType);//3,1,3,1,3
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em文本</em>
div文本
<strong>strong文本</strong>
</div>
</body><script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
alert(oDiv.childNodes.length); //5
for(var i = 0; i < oDiv.childNodes.length; i++){
alert(oDiv.childNodes[i].nodeType);//3,1,3,1,3
}
alert(oDiv.children.length);//2
alert(oDiv.firstElementChild.nodeName);//EM
alert(oDiv.lastElementChild.nodeName);//STRONG
alert(oDiv.firstElementChild.nextSibling.nodeValue);//div文本
alert(oDiv.firstElementChild.nextElementSibling.nodeName);//STRONG
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em文本</em>
div文本
<strong>strong文本</strong>
</div>
</body>属性节点attributes
attributes:获取当前元素节点上的所有的属性的节点
<script>
/*
集合:
1、无序
2、不重复
*/
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
// alert(oDiv.attributes);//[object NamedNodeMap] 属性节点集合对象
//获取其中的某一个属性节点
//title = hello
alert(oDiv.attributes.getNamedItem("title")); //[object Attr]
alert(oDiv.attributes.getNamedItem("title").nodeName);//title
alert(oDiv.attributes.getNamedItem("title").nodeType);//2
alert(oDiv.attributes.getNamedItem("title").nodeValue);//hello
/* 简化版 */
alert(oDiv.attributes["title"].nodeName);
alert(oDiv.attributes["title"].nodeType);
alert(oDiv.attributes["title"].nodeValue);
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1" title="hello" class="box">div文本</div>
</body>DOM的节点操作
- document.write( ) 会覆盖页面原有内容
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
document.write("<h1>hello world</h1>");
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body>

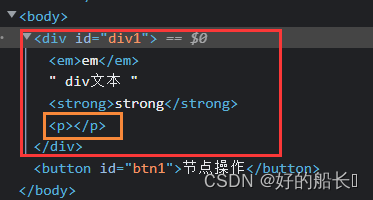
- creatElement( )
格式:document.creatElement( )
参数:标签名
返回值:创建好的这个节点
- appendChild( )
格式:node1.appendChild(node2);
功能:将node2节点插入到node1节点子节点的末尾
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var oP = document.createElement("p");
oDiv.appendChild(oP);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body>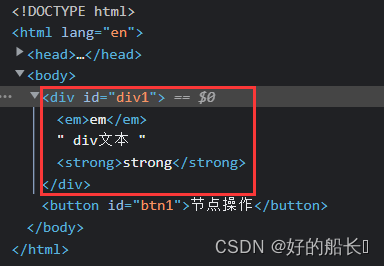
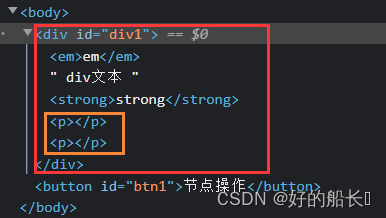
- creatTextNode( )
格式:document.creatTextNode(文本);
功能:创建文本节点(纯文本)
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var oP = document.createElement("p");
var oTxt = document.createTextNode("<h1>hello world</h1>");
oP.appendChild(oTxt);
oDiv.appendChild(oP);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body> 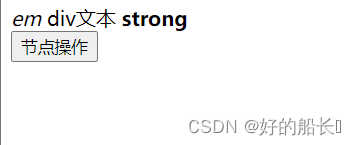



- insertBefore( )
格式:box1.parentNode.insertBefore(box2,box1);
功能:将box2添加到box1的前面
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var oP = document.createElement("p");
var oTxt = document.createTextNode("<h1>hello world</h1>");
oP.appendChild(oTxt);
//将oP节点插入到oDiv节点的前面
document.body.insertBefore(oP,oDiv);
}
}
</script>
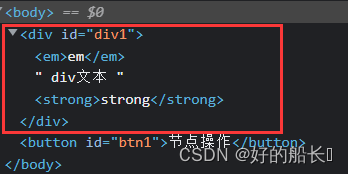
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body> 

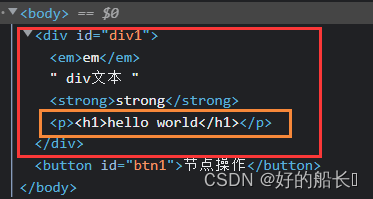
- replaceChild( )
格式:box1.parentNode.replaceChild(box2,box1);
功能:用box2节点将box1节点替换掉
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var oP = document.createElement("p");
var oTxt = document.createTextNode("<h1>hello world</h1>");
oP.appendChild(oTxt);
//用oP节点,将oDiv节点替换掉
document.body.replaceChild(oP,oDiv);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body>


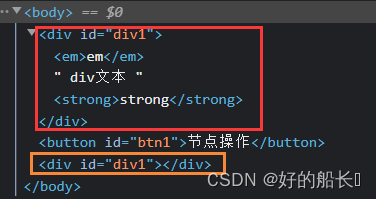
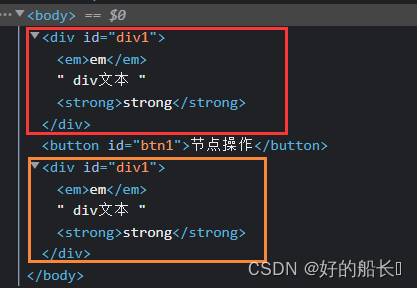
- cloneNode( )
格式1:node.cloneNode( ); 【注】标签内的嵌套标签没有被克隆
格式2:node.cloneNode(true); 克隆节点本身和子节点
返回值:克隆出来的新节点
格式1:
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var newNode = oDiv.cloneNode();
document.body.appendChild(newNode,oDiv);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body>

格式2:
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
var newNode = oDiv.cloneNode(true);
document.body.appendChild(newNode,oDiv);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body> 


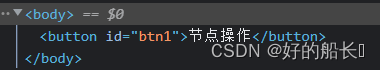
- removeChild( )
格式:box.parentNode.removeChild( box );
功能:将box节点从页面上删除
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
var oDiv = document.getElementById("div1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
//删除div节点
document.body.removeChild(oDiv);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<em>em</em>
div文本
<strong>strong</strong>
</div>
<button id="btn1">节点操作</button>
</body>


节点操作案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#div1{width: 400px; height: 100px; background-color: orange;}
#div2{width: 400px; height: 500px; background-color: peachpuff;}
#input1{width: 300px; height: 30px; font-size: 18px; margin: 5px 10px;}
#div1 button{width: 100px; height: 30px; font-size: 18px; background-color: black; color: white; margin: 15px 10px;}
#div2 div{border-bottom: 1px dashed gray; padding: 2px; position: relative;}
#div2 div button{position: absolute; right: 0px;}
</style>
<script src="tool.js"></script>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv1 = document.getElementById("div1");
var oDiv2 = document.getElementById("div2");
var oInput = document.getElementById("input1");
//获取div1下面所有的button
var aBtns = oDiv1.getElementsByTagName("button");
//分别给三个按钮添加不同的点击函数
aBtns[0].onclick = function(){
if(!oInput.value){
alert("输入的内容不得为空");
}else{
//获取到输入框的内容,创建节点添加到页面上
var newDiv = document.createElement("div");
var oTxt = document.createTextNode(oInput.value);
newDiv.appendChild(oTxt);
newDiv.style.backgroundColor = randomColor();
oDiv2.appendChild(newDiv);
oInput.value = '';
}
}
aBtns[1].onclick = function(){
//删除最后一个节点
oDiv2.removeChild(oDiv2.lastChild);
}
aBtns[2].onclick = function(){
//拷贝最后一个节点,再添加到页面上
var newNode = oDiv2.lastChild.cloneNode(true);
oDiv2.appendChild(newNode);
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<input type="text" id="input1" placeholder="输入内容"> <br/>
<button>增加</button>
<button>删除</button>
<button>拷贝</button>
</div>
<div id="div2">
<!-- <div>xxx <button>x</button> </div>
<div>xxx <button>x</button> </div>
<div>xxx <button>x</button> </div> -->
</div>
</body>
</html>this和快速找到当前点击按钮下标
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var aBtns = document.getElementsByTagName("button");
for(var i = 0; i < aBtns.length; i++){
aBtns[i].onclick = function(){
alert(i); //点击每一个按钮,弹出来的i的值都为3;原因:代码先执行结束,才有你的点击事件,此时i的值已经被赋为3了,所以不论点击哪一个按钮,i的值都是3
}
}
alert("循环结束,i = " + i);
}
</script>
<body>
<button>按钮1</button>
<button>按钮2</button>
<button>按钮3</button>this关键字
概念:只要封装函数,任何一个函数系统都会内置一个叫做 this的变量
this变量存储的是地址,是当前函数主任的地址。
【注】this永远指向当前函数的主人。函数的主任要通过当前上下文判断
this类似于现实生活中,用到的“我”。
<script>
var person = {
username:"钢铁侠",
sex:"男",
show: function(){
alert(person.username); //钢铁侠
alert(this.username); //钢铁侠
}
};
//给对象添加方法
person.xxx = function(){
}
// person.show();
//全局函数下,没有主人,默认为window
function show(){
alert(this);
}
// show(); //[object Window]
// window.show();//[object Window]
window.onload = function(){
var oBtn = document.getElementById("btn1");
oBtn.onclick = function(){
alert(this);
}
}
</script>
<body>
<button id="btn1">按钮</button>
</body>修改版快速找到按钮下标:
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var aBtns = document.getElementsByTagName("button");
for(var i = 0; i < aBtns.length; i++){
//给每一个按钮添加一个自定义属性
aBtns[i].index = i;
aBtns[i].onclick = function(){
alert(this.index);
}
}
alert("循环结束,i = " + i);
}
</script>
<body>
<button>按钮1</button>
<!-- index = 0 onclick = func -->
<button>按钮2</button>
<!-- index = 1 onclick = func -->
<button>按钮3</button>
<!-- index = 2 onclick = func -->
</body>选项卡
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#div1 button{width: 100px; height: 30px; background-color: gray; color: white; font-size: 18px;}
#div1 .active{background-color: orange; color: blue;}
#div1 div{width: 340px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid black; display: none;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv1 = document.getElementById("div1");
var aBtns = oDiv1.getElementsByTagName("button");
var aDivs = oDiv1.getElementsByTagName("div");
//给每一个按钮添加点击
for(var i = 0; i < aBtns.length; i++){
aBtns[i].index = i;
aBtns[i].onclick = function(){
//取消所有按钮的样式(不知道去前一个显示样式的按钮是哪一个按钮)
for(var j = 0; j < aBtns.length; j++){
aBtns[j].className = '';
aDivs[j].style.display = 'none';
}
aDivs[this.index].style.display = 'block';
this.className = 'active';
}
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<button class="active">HTML5</button>
<button>Python</button>
<button>Java</button>
<div style="display: block;">HTML5是Web中核心语言HTML的规范,用户使用任何手段进行网页浏览时看到的内容原本都是HTML格式的。在浏览器中通过一些技术处理将其转换成了课识别的信息。HTML5在从前HTML4.01的基础上进行了一定的改进,虽然技术人员再开发过程中可能不会将这些新技术投入应用,但是对于该种技术的新特性网站开发技术人员是必须要有所了解的。</div>
<div>Python是一种计算机程序设计语言。是一种面向对象的动态类型语言,最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越来越多被用于独立的、大型项目的开发。</div>
<div>Java是一门面向对象编程语言,不仅吸收了C++语言的各种优点,还摒弃了C++里难以理解的多继承、指针等概念。因此Java语言具有功能强大和简单易用两个特征。Java语言作为静态面向对象编程语言的代表,极好的实现了面向对象理论,允许程序员以优雅的思维方式进行复杂的编程</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>offset系列方法
- offsetWidth、offsetHeight
<style>
#div1{width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: red; border: 1px solid black; padding: 8px; margin: 20px;}
</style>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv1 = document.getElementById("div1");
// alert(getStyle(oDiv1,"width")); //width这个属性的值 100px
alert(oDiv1.offsetWidth);//直接拿到的数字,没有px;会受border和padding的影响,但与margin无关
}
/* 跨浏览器兼容 */
function getStyle(node,cssStyle){
return node.currentStyle ? node.currentStyle : getComputedStyle(node)[cssStyle];
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1"></div>
</body>- offsetLeft、offsetTop:计算眼睛能看到的实际距离第一个有定位的父节点的距离
<style>
*{margin: 0px; padding: 0px;}
#div1{margin: 30px; width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: orange; position: relative;}
#div2{margin: 20px; width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: gray;}
</style>
<script>
/* 跨浏览器兼容 */
function getStyle(node,cssStyle){
return node.currentStyle ? node.currentStyle : getComputedStyle(node)[cssStyle];
}
window.onload = function(){
var oDiv2 = document.getElementById("div2");
// alert(getStyle(oDiv2,"left"));//auto
// alert(oDiv2.offsetLeft);//50,没给div1设置position时
alert(oDiv2.offsetLeft);//20
}
</script>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<div id="div2"></div>
</div>
</body>文档碎片
/* 创建10w个检点,添加到页面上 */
window.onload = function(){
console.time("test1");
//test1: 60.427978515625 ms
for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
var newDiv = document.createElement("div");
document.body.appendChild(newDiv);
}
console.timeEnd("test1");
/* 先创建好10w个节点,将10W个节点插入到一个节点上,最后将这1个节点添加到页面上 */
//test2: 53.89404296875 ms 文档碎片操作
console.time("test2");
var node = document.createElement("div");
for(var i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
var newDiv = document.createElement("div");
node.appendChild(newDiv);
}
document.body.appendChild(node);
console.timeEnd("test2");
}数组和对象的遍历方法
数组遍历:
for循环
for...in
forEach
var arr = [10, 20, 30, 40,50];
for(var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
document.write("for," + i + "," + arr[i] + "<br/>");
}
for(var i in arr){
document.write("forin," + i + "," + arr[i] + "<br/>");
}
arr.forEach(function(item, index, arr){
document.write("forEach," + index + "," + item + "<br/>");
});对象遍历
for...in
var person = {
username:"钢铁侠",
age: 18,
sex: "男"
};
for(var i in person){
//i 是当前遍历到的属性
document.write("对象遍历:" + i + "," + person[i] + "<br/>");
}




















 1518
1518











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








