Eonathan Eostar decided to learn the magic of multiprocessor systems. He has a full binary tree of tasks with height hh. In the beginning, there is only one ready task in the tree — the task in the root. At each moment of time, pp processes choose at most pp ready tasks and perform them. After that, tasks whose parents were performed become ready for the next moment of time. Once the task becomes ready, it stays ready until it is performed.
You shall calculate the smallest number of time moments the system needs to perform all the tasks.
Input
The first line of the input contains the number of tests tt (1≤t≤5⋅1051≤t≤5⋅105). Each of the next tt lines contains the description of a test. A test is described by two integers hh (1≤h≤501≤h≤50) and pp (1≤p≤1041≤p≤104) — the height of the full binary tree and the number of processes. It is guaranteed that all the tests are different.
Output
For each test output one integer on a separate line — the smallest number of time moments the system needs to perform all the tasks.
Example
Input
3 3 1 3 2 10 6
Output
7 4 173
Note
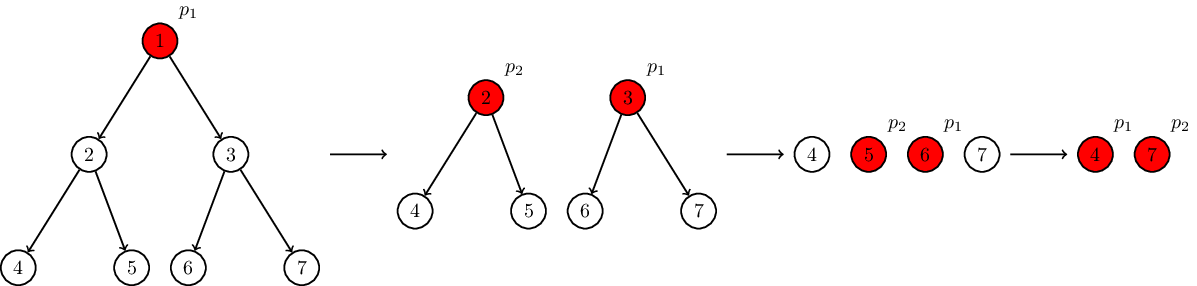
Let us consider the second test from the sample input. There is a full binary tree of height 33 and there are two processes. At the first moment of time, there is only one ready task, 11, and p1p1 performs it. At the second moment of time, there are two ready tasks, 22 and 33, and the processes perform them. At the third moment of time, there are four ready tasks, 44, 55, 66, and 77, and p1p1 performs 66 and p2p2 performs 55. At the fourth moment of time, there are two ready tasks, 44 and 77, and the processes perform them. Thus, the system spends 44 moments of time to perform all the tasks.
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll n,m,mx;
void dfs(ll num,ll t,ll res)
{
if(num==n)
{
if(res>0)t++;
mx=t;
return;
}
//ll s=1<<num,error ,<<运算,只能到30位(也就是说num最大只能为30)
ll s=pow(2,num);
s+=res;
if(s<=m) dfs(num+1,t+1,0);
else
{
ll x=s/m;
dfs(num+1,t+x,s%m);
}
return;
}
int main()
{
ll i,j,k;
ll x,t;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
dfs(0,0,0);
printf("%lld\n",mx);
}
return 0;
}



















 543
543











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








