
代码:
public class foodTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、构建一个数组
food[] arr = new food[3];
//2、创建三个商品对象
food f1 = new food("apple","123",3.2,500);
food f2 = new food("pear","456",4.0,300);
food f3 = new food("paper","567",1.5,504);
//3、把商品添加到数组中
arr[0]=f1;
arr[1]=f2;
arr[2]=f3;
//4、验证数组
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
food food =arr[i];
System.out.println(food.getName()+","+food.getId()+","+food.getPrice()+","+food.getRemain());
}
}
}public class food {
private String name;
private String id;
private double price;
private int remain;
public food() {
}
public food(String name, String id, double price, int remain) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.price = price;
this.remain = remain;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public int getRemain() {
return remain;
}
public void setRemain(int remain) {
this.remain = remain;
}
}
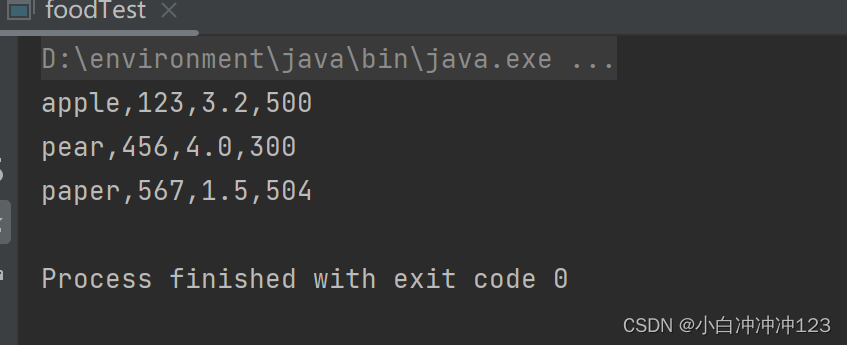
运行结果:


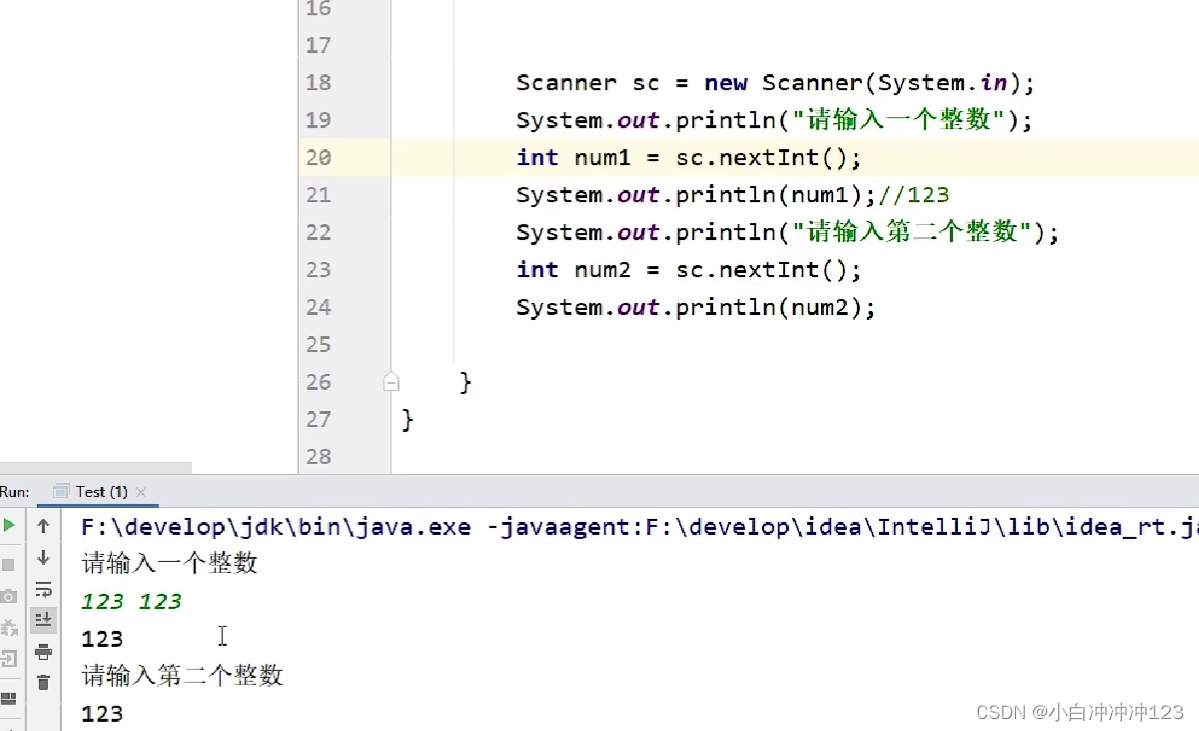
由于在键盘录入中123与123之间有空格,则第一个只会输出一个123,并不会出现第二次键盘录入,会直接将第二个的123赋值给num2;

键盘录入的两套体系是不能混用的:
代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class scanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner (System.in);
System.out.println("输入一个整数:");
int b1 = input.nextInt();
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String b111 = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(b111);
}
}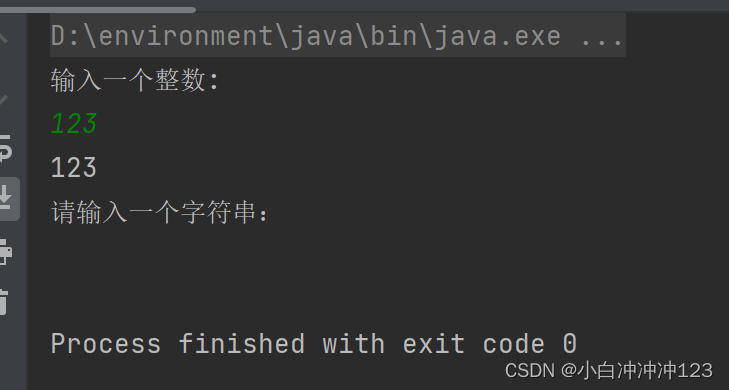
输入一个123+回车,字符串输入没有让输入,而是接受了回车,接收不到数据;
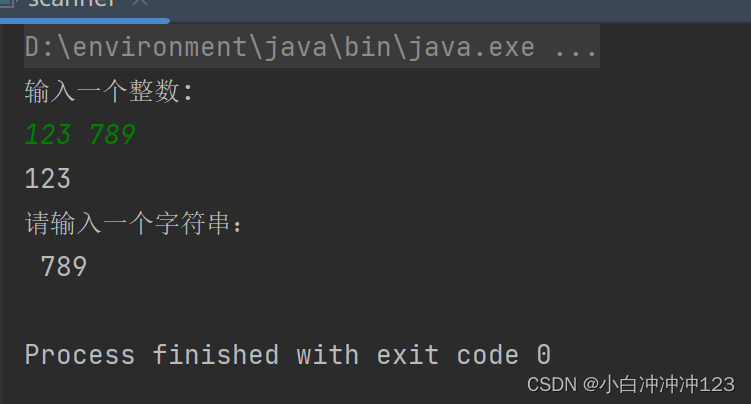
输入123 789,由于第一套体系遇到空格会停止接受,所以自动将 789赋值给b111;
弊端:先用nextInt(),再用nextLine()会使next Line()接受不到数据;
代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class carsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
cars [] arr = new cars [3];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
cars c1 = new cars();
System.out.println("输入一个汽车品牌:");
String brand = input.next();
c1.setBrand(brand);
System.out.println("请输入它的价钱:");
double price = input.nextDouble();
c1.setPrice(price);
System.out.println("请输入该汽车的颜色:");
String color = input.next();
c1.setColor(color);
arr[i]=c1;
}
for(int i=0;i< arr.length;i++){
cars car = arr[i];
System.out.println(car.getBrand()+","+car.getPrice()+","+car.getColor());
}
}
}
public class cars {
private String brand;
private double price;
private String color;
public cars() {
}
public cars(String brand, double price, String color) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
this.color = color;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
}
代码结果:
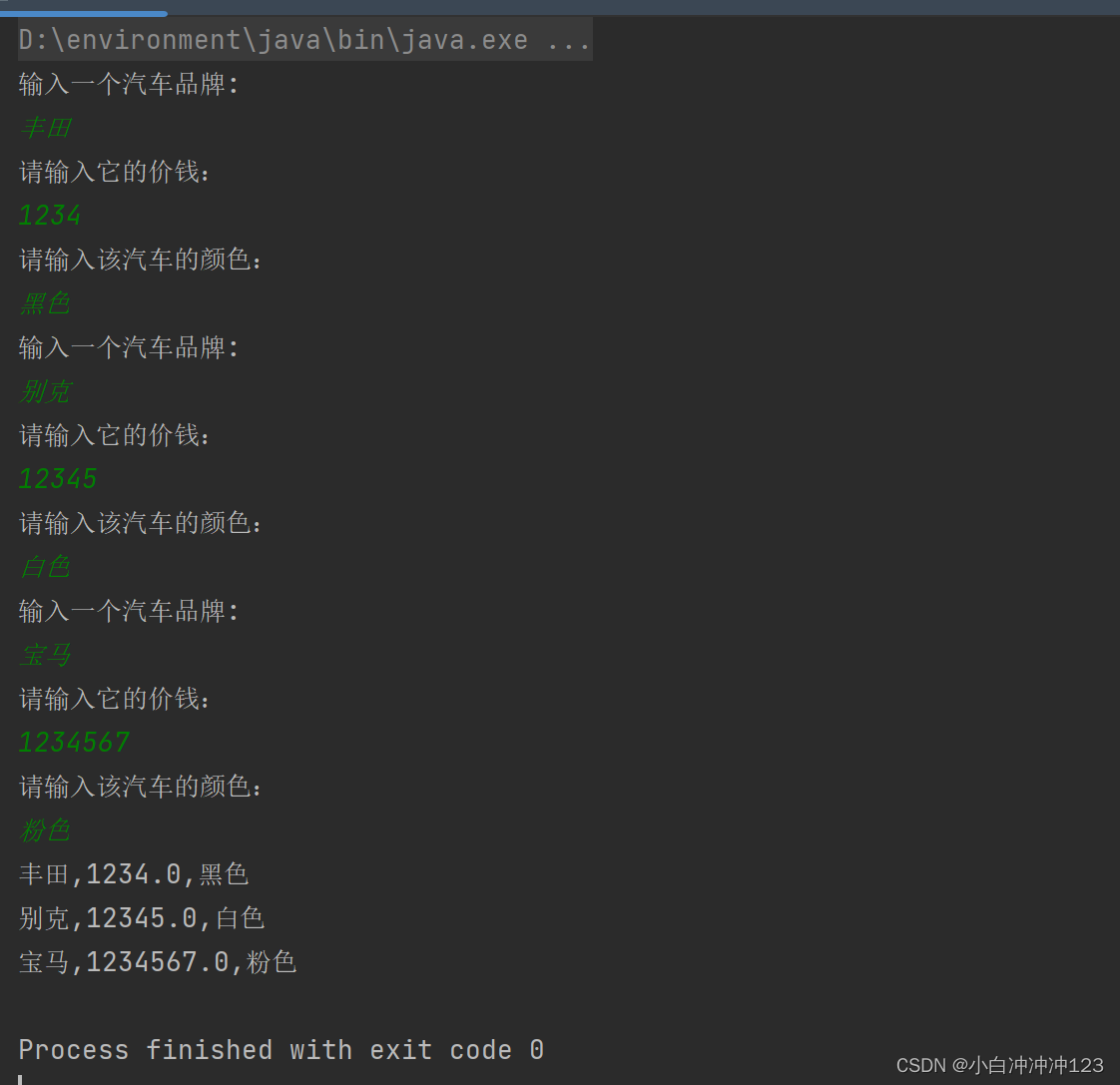
代码细节:如果将创建对象写在了for循环的外面,那么输出的结果将如下图所示:
(打印出来的都是第三个的信息)


创建在外面,则只是创建了一个对象,循环第二次的时候只是修改了第一个的信息,循环第三次的时候只是修改了第二个的信息,从头到尾,只有那一个对象。






















 829
829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








