目录
一、计算属性的基本使用
现在有变量姓氏和名字,要得到完整的名字
- 使用Mastache语法拼接
<h2>{{firstName+ " " + lastName}}</h2>- 使用方法methods
<h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2>- 使用计算属性computed
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>计算属性的基本使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- Mastache语法 -->
<h2>{{firstName+ " " + lastName}}</h2>
<!-- 方法 -->
<h2>{{getFullName()}}</h2>
<!-- 计算属性 -->
<h2>{{fullName}}</h2>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.10/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
firstName:"skt t1",
lastName:"faker"
},
computed: {
fullName:function(){
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName
}
},
methods: {
getFullName(){
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>例子中计算属性computed看起来和方法似乎一样,只是方法调用需要使用(),而计算属性不用,方法取名字一般是动词见名知义,而计算属性是属性是名词,但这只是基本使用。

二、计算属性的复杂使用
现在有一个数组数据books,里面包含许多book对象,数据结构如下:
books:[
{id:110,name:"JavaScript从入门到入土",price:119},
{id:111,name:"Java从入门到放弃",price:80},
{id:112,name:"编码艺术",price:99},
{id:113,name:"代码大全",price:150},
]
要求计算出所有book的总价格totalPrice。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>计算属性的复杂使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>总价格:{{totalPrice}}</h2>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.10/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
const app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
books:[
{id:110,name:"JavaScript从入门到入土",price:119},
{id:111,name:"Java从入门到放弃",price:80},
{id:112,name:"编码艺术",price:99},
{id:113,name:"代码大全",price:150},
]
},
computed: {
totalPrice(){
let total= 0;
for (let i = 0; i < this.books.length; i++) {
result += this.books[i].price;
}
return total
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>效果如下:
总价格:448
用其他方法遍历数据
1. forEach
totalPrice() {
let total = 0;
this.books.forEach(item=>{
total += item.price
})
return total
}
2. for in
totalPrice() {
let total = 0
for (let index in this.books) {
total += this.books[index].price
}
return total
}
3. for of
totalPrice() {
let total = 0;
for(let item of this.books){
total += item.price
}
return total
}
4. map
totalPrice() {
let total = 0;
this.books.map(item=>{
total += item.price
})
return total
}
5. filter
totalPrice() {
let total = 0;
this.books.filter(item=>{
total += item.price
})
return total
}
6. reduce
totalPrice() {
return this.books.reduce((total,item)=>{
return total + item.price
},0)
}
简写
totalPrice() {
return this.books.reduce((total,item)=>total + item.price,0)
}
7. some
totalPrice() {
let total = 0;
this.books.some(item=>{
total += item.price
})
return total
}
三、计算属性中的getter 和 setter
在计算属性中其实是由这样两个方法setter和getter
computed: {
fullName:{
//计算属性一般没有set方法,只读属性
set:function(newValue){
console.log("-----")
const names = newValue.split(" ")
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[1]
},
get:function(){
return this.firstName + " " + this.lastName
}
}
}
但是计算属性一般没有set方法,只读属性,只有get方法,但是上述中newValue就是新的值,也可以使用set方法设置值,但是一般不用。
computed 的 getter/setter
计算属性 一定要有一个返回值 在页面中渲染时是不需要加小括号的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Vue计算属性的getter和setter</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2.6.10/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>计算属性:computed的getter/setter</h1>
<h2>fullName</h2>
{{fullName}}
<h2>firstName</h2>
{{firstName}}
<h2>lastName</h2>
{{lastName}}
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
firstName:"zhang",
lastName:"san",
},
computed: {
fullName:{
get:function(){
return this.firstName+" "+this.lastName
},
set:function(value){
var list = value.split(' ');
this.firstName=list[0]
this.lastName=list[1]
}
}
},
});
</script>
</body>
</html>初始化
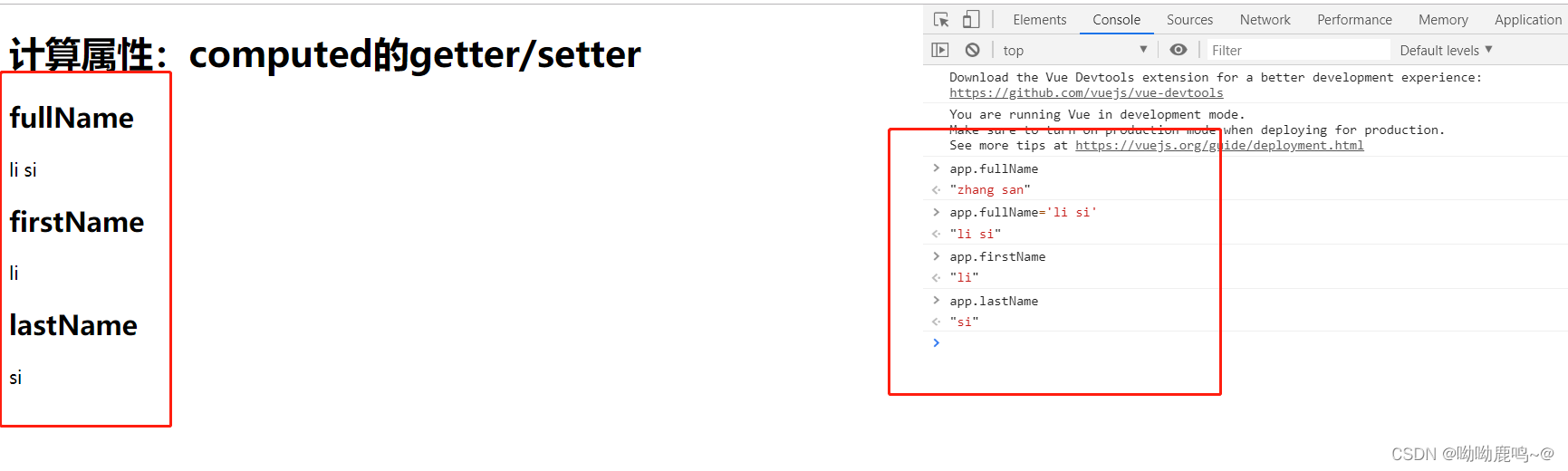
- 通过这种方式,我们可以在改变计算属性值的同时也改变和计算属性相关联的属性值。
四、计算属性和 methods 的对比
直接看代码,分别使用计算属性和方法获得fullName的值。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title></title>
<script src="js/vue.js" type="text/javascript" charset="utf-8"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h2>您的fullname是从计算属性中得到:{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从计算属性中得到:{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从计算属性中得到:{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从计算属性中得到:{{fullName}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从方法中得到:{{getFullName()}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从方法中得到:{{getFullName()}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从方法中得到:{{getFullName()}}</h2>
<h2>您的fullname是从方法中得到:{{getFullName()}}</h2>
</div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data(){
return {
firstName:'zhang',
lastName:'san'
}
},
methods:{
getFullName(){
console.log('这里调用了方法getFullName');
return this.firstName + this.lastName
}
},
computed:{//计算属性 一定要有一个返回值 在页面中渲染时是不需要加小括号的
fullName(){
console.log('这里调用了计算属性fullName');
return this.firstName + this.lastName
}
}
})
/* 总结:计算属性的性能是优于方法的 因为计算属性是具有缓存特性的 */
</script>
</body>
</html>
打印验证时更能体现两种方法的优劣处,methods调用了四次,而计算属性才调用了一次,性能上计算属性明显比methods好。而且在改动firstName的情况下,计算属性只调用一次,methods依然要调用4次。
计算属性的性能是优于方法的 因为计算属性是具有缓存特性的
























 4048
4048











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








