单链表的概念
1)单链表是线性表的另一种表现方式:链式存储
2)特点:逻辑相邻,但是物理上不一定相邻,因为数据元素在物理上并不要求连续,则失去了顺序表可以直接随机访问的优势
3)单链表的定义:用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(这组数据可以连续,也可以不连续),所以为了表示每个节点An和其后继节点An+1之间的逻辑关系,每一个节点不仅仅需要保存自己的有效值(数据域),还需要保存下一个节点的地址(指针域)。
单链表一般分为两种方式:带头结点和不带头结点的:
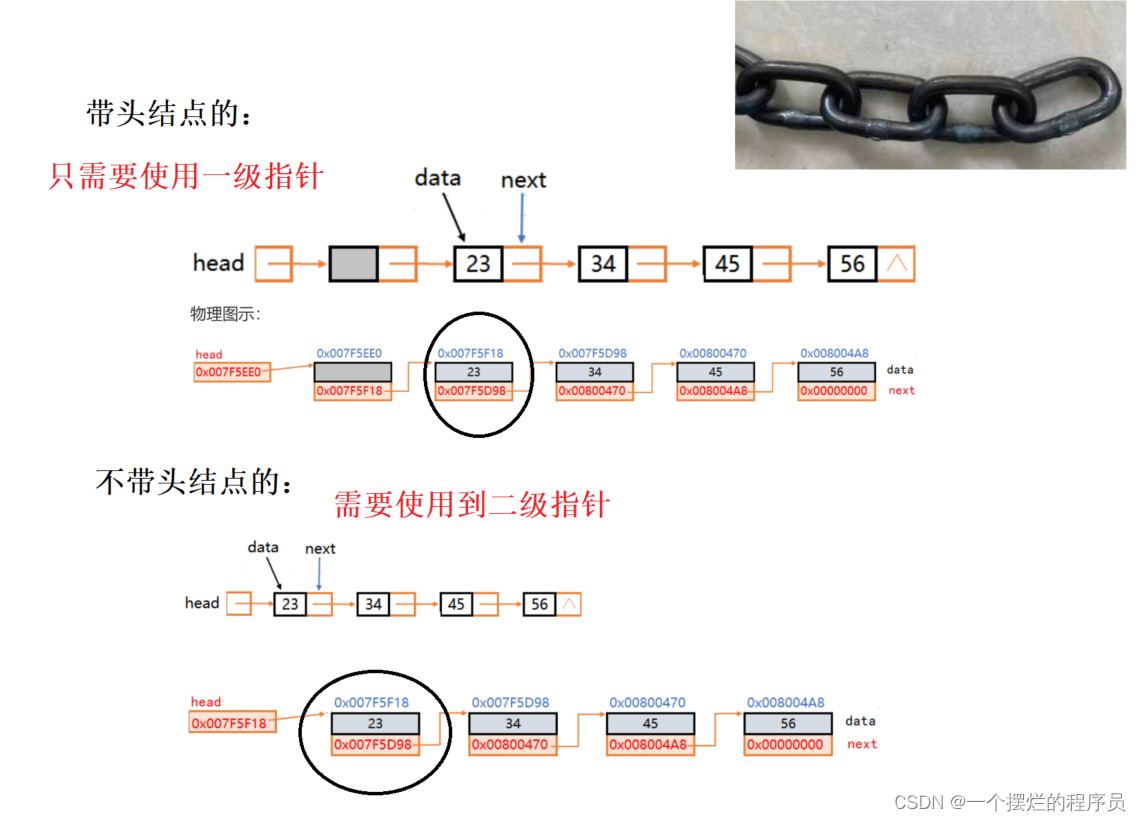
所以当我们遇到练习题目时候:如果带有头结点、刚好
如果不带头结点:额外申请一个辅助头结点,这时就变成了带有头结点的,按照我们学的方式,处理掉这个题目,最后这个辅助头结点,释放掉即可
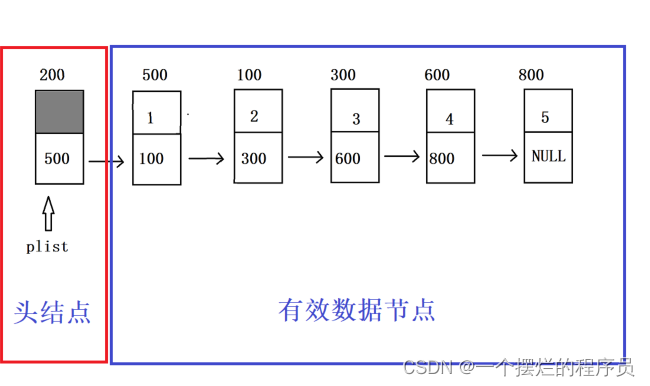
用代码实现单链表
设置.h头文件
#pragma once
//带头结点的单链表的结构体设计
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
typedef struct Node {
ELEM_TYPE data;//数据域(保存数据的有效值)
struct Node* next;//指针域(保存下一个有效结点的地址)
}Node,*PNode;
//初始化
void Init_list(struct Node* plist);
//头插
bool Insert_head(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//尾插
bool Insert_pos(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PNode plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val);
//头删
bool Del_head(PNode plist);
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PNode plist);
//按位置删
bool Del_pos(PNode plist, int pos);
//按值删
bool Del_val(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//查找 找到,返回的是查找到的这个节点的地址
struct Node* Search(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PNode plist);
//清空
void Clear(PNode plist);
//销毁1
void Destory1(PNode plist);
//销毁2
void Destory2(PNode plist);
//打印
void Show(PNode plist);
//获取有效值个数
int Getlength(PNode plist);
在.cpp文件实现
//带头结点的单链表
//初始化
void Init_list(struct Node* plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
plist->next = NULL;
}
//头插
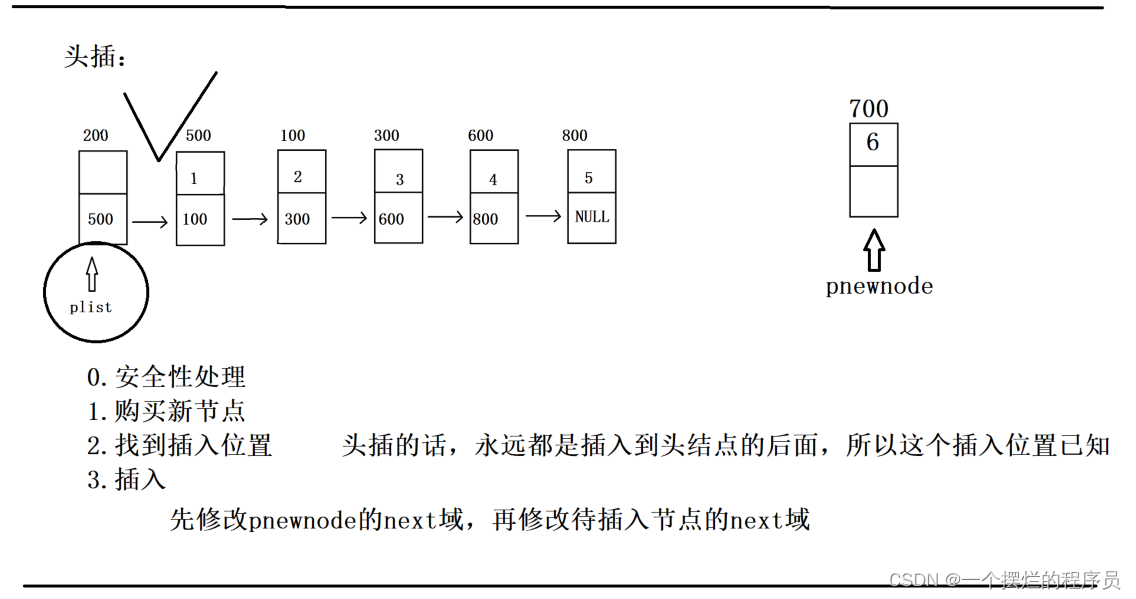
bool Insert_head(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
//0.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);
//1.购买新节点
struct Node* pnewnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
//2.找到合适位置插入
//3.插入
pnewnode->next = plist->next;
plist->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//尾插
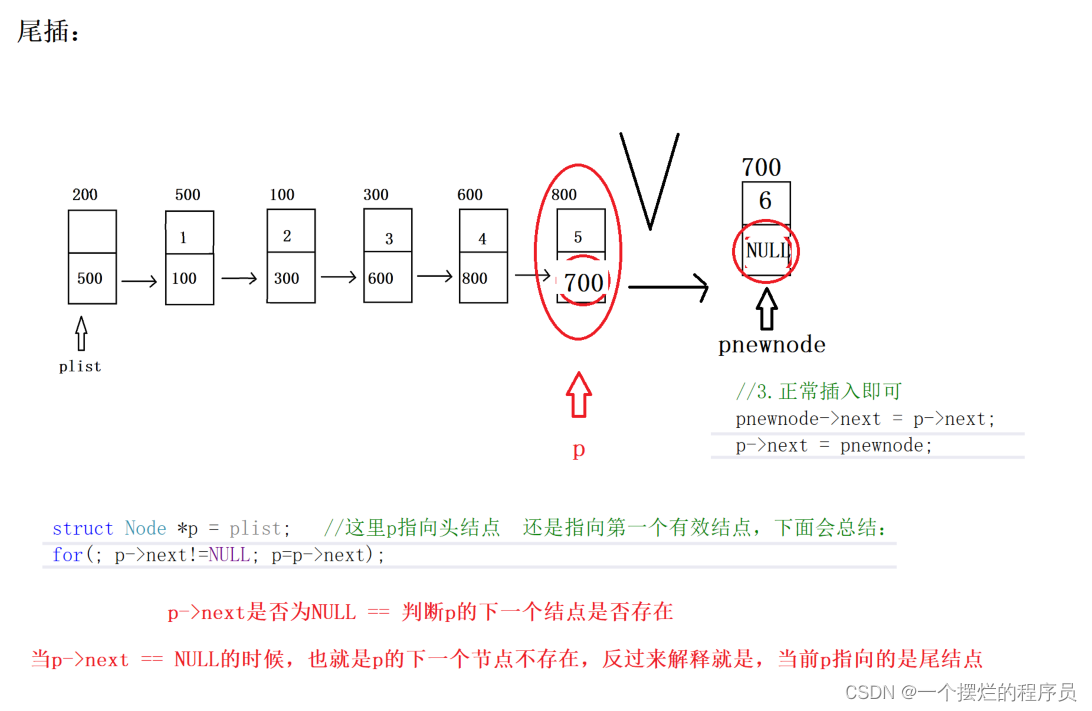
bool Insert_pos(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
//1.安全新处理
assert(plist != NULL);
//2.购买新节点
struct Node* pnewnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
//3.找到合适位置插入
struct Node* p = plist;
for (; p->next != NULL; p++);
//4.插入
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
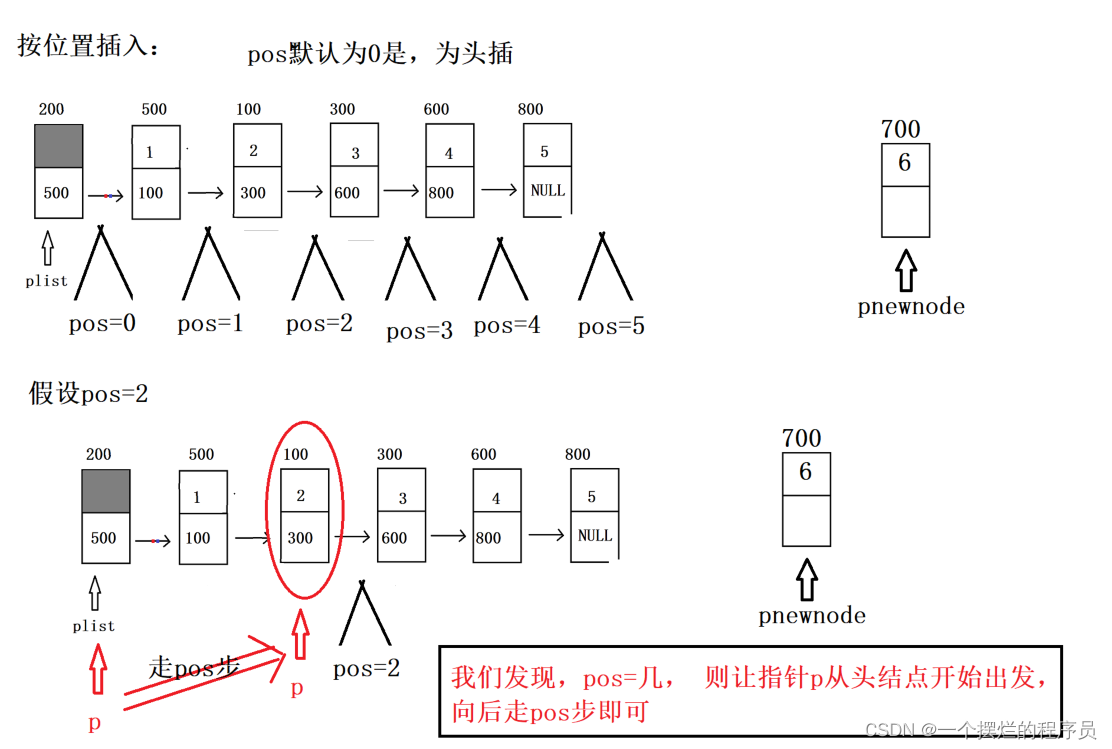
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PNode plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val) {
//1.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <=Getlength(plist));
//2.购买新节点
struct Node* pnewnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
//3.找到合适位置插入
struct Node* p = plist;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
p = p->next;
}
//4.插入
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
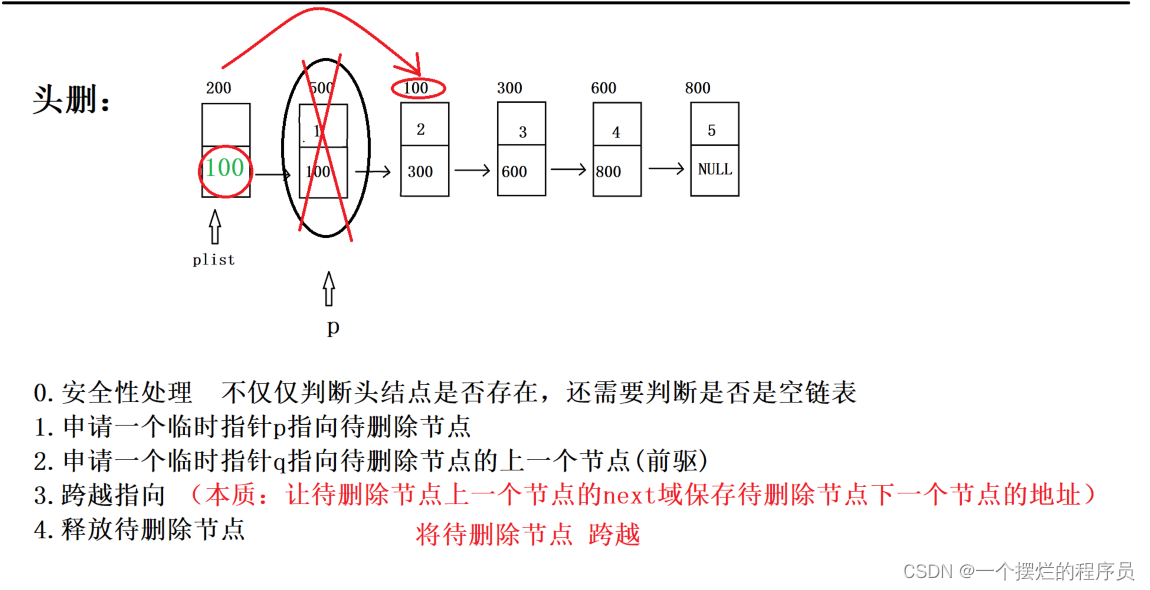
//头删
bool Del_head(PNode plist) {
//1.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);
//2.判空操作
if (IsEmpty(plist)) {
return true;
}
//3.找到合适的位置删除
struct Node* p = plist->next;
//4.删除操作
plist->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
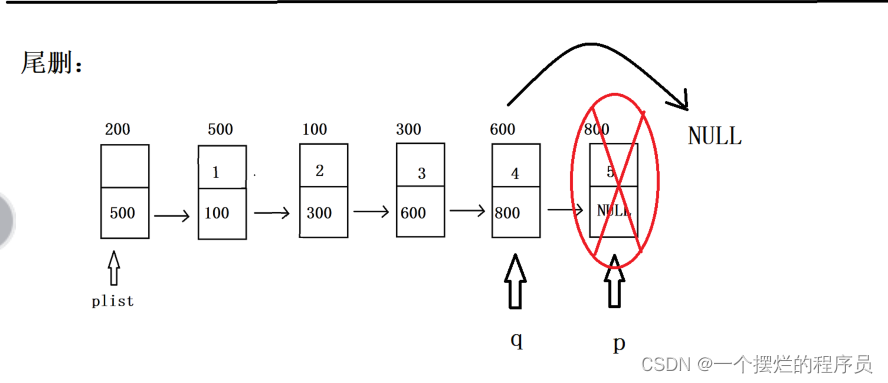
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PNode plist) {
//0.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);
//1.判空
if (IsEmpty(plist)) {
return true;
}
//2.找到合适位置删除
struct Node* p = plist->next;
struct Node* q = plist;
for (; p->next != NULL; p++);
for (; q->next != p; q++);
//3.插入
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
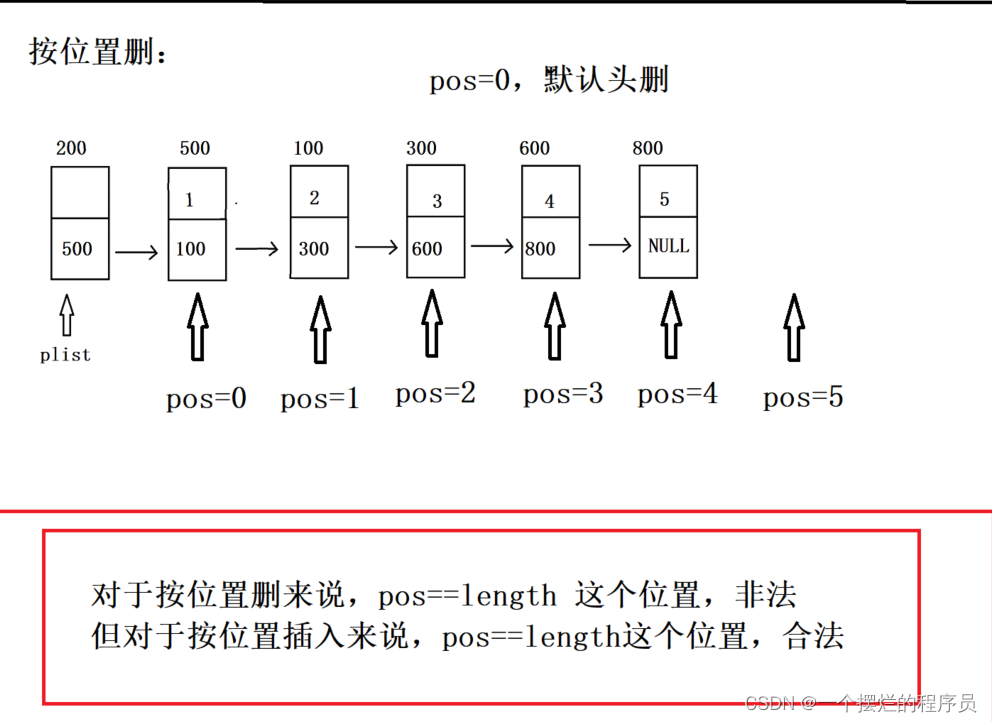
//按位置删
bool Del_pos(PNode plist, int pos) {
//1.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < Getlength(plist));
//2.判空
if (IsEmpty(plist)) {
return false;
}
//3.找到合适位置
struct Node* q = plist;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
q = q->next;
}
struct Node* p = q->next;
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return ture;
}
//按值删
bool Del_val(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plist != NULL);
struct Node* p = Search(plist, val);
if (p == NULL) {
return false;
}
struct Node* q = plist;
for (; q->next != p; q++) {
q = q->next;
}
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//查找 找到,返回的是查找到的这个节点的地址
struct Node* Search(PNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plist != NULL);
struct Node* p = plist->next;
for (; p != NULL; p++) {
if (p->data == val) {
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PNode plist) {
if (plist->next == NULL) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//清空
void Clear(PNode plist) {
Destory1(plist);
}
//销毁 方法一,无限头删
void Destory1(PNode plist) {
while (plist->next != NULL) {
Del_head(plist);
}
}
//销毁2
void Destory2(PNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
//1.定义两个指针p和q,p指向第一个有效节点,q先不赋值
struct Node* p = plist->next;
struct Node* q;
//2.断开头结点,因为不借助头节点,所以一开始就将投头结点变为最终销毁的样子
plist->next = NULL;
//3.两个指针合作,循环释放后续节点
while (p != NULL) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
//打印
void Show(PNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
struct Node* p = plist->next;
for (; p!= NULL; p=p->next) {
printf("%d\n", p->data);
}
}
//获取有效值个数
int Getlength(PNode plist) {
int count = 0;
if (plist->next != NULL) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
测试代码
int main() {
struct Node list;
Init_list(&list);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Insert_head(&list, i);
}
Show(&list);
}
重点内容
1)关于两种for循环的实现

2)图示法表示






















 5151
5151











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










