一、补充上节课的知识点
单链表和顺序表的区别
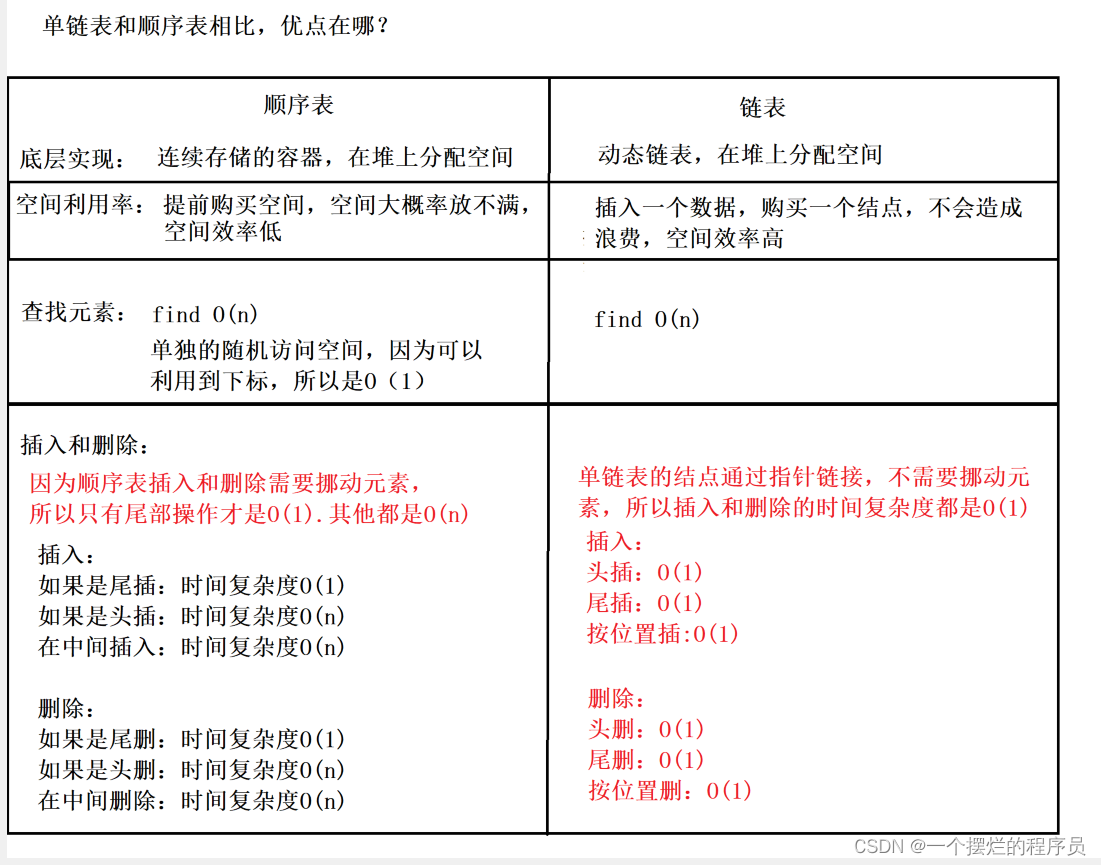
顺序表和单链表的使用场景分析
1)结点个数大概能预估出来就使用顺序表,预估不出来就使用单链表
2)如果经常使用插入删除操作,就使用单链表,因为不需要挪动元素
3)如果只考虑尾插和尾删,也可以考虑顺序表
4)如果经常访问元素,则考虑顺序表,因为顺序表可以通过下标随机访问
二、认识单循环链表
单循环链表就一点和单链表不同,就是单循环链表的next域不再指向NULL,而是保存头结点的地址
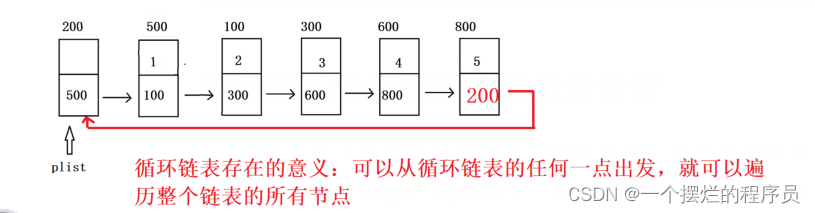
1)将单循环链表的增删改查用画图方式展现出来

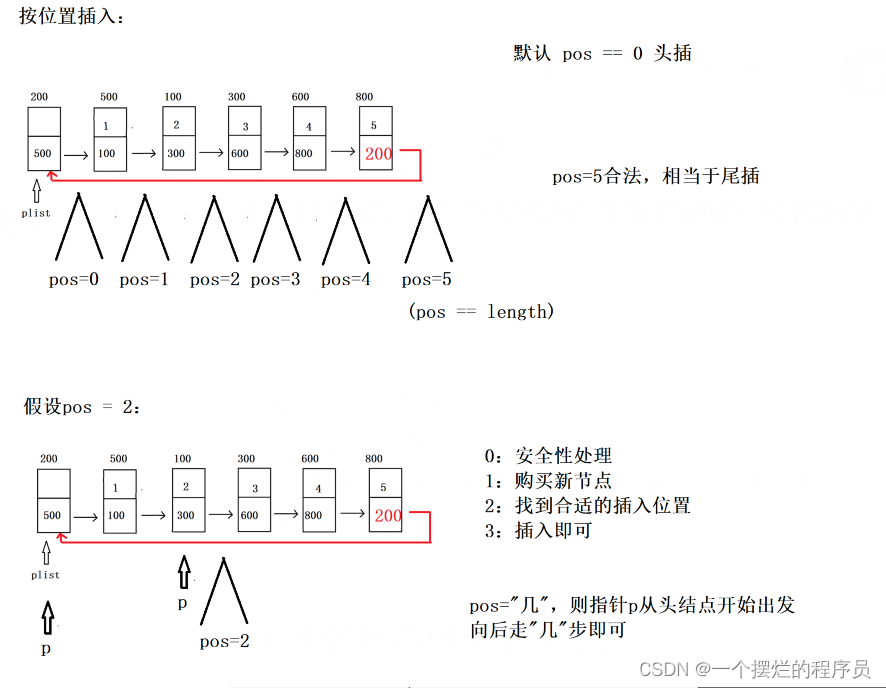

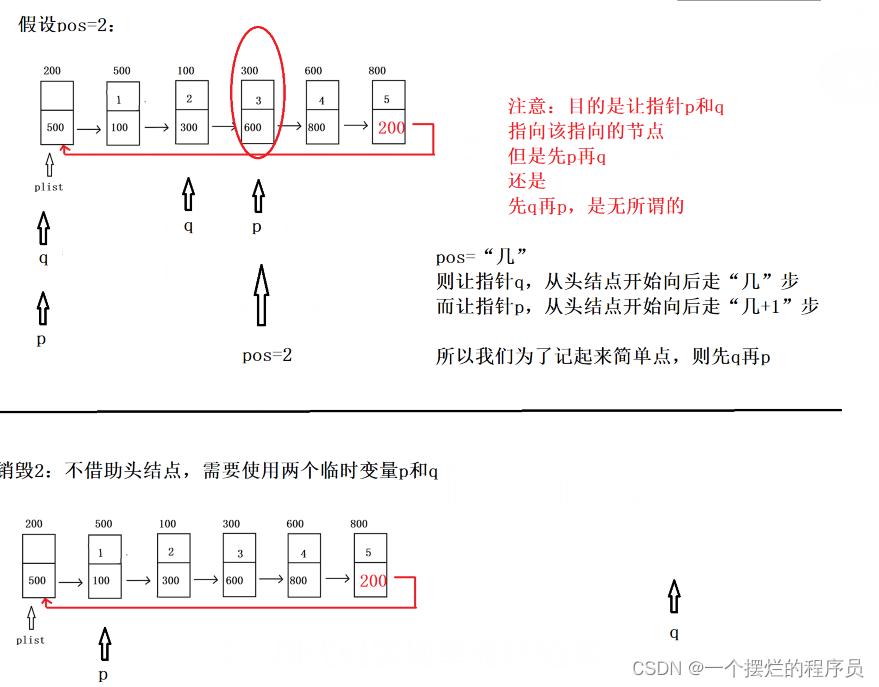
2)用代码实现单循环链表
头文件.h 进行函数的声明
typedef int ELEM_TYPE;
typedef struct CNode {
ELEM_TYPE data;
struct CNode* next;
}CNode,*PCNode;
//初始化
void Init_list(struct CNode* plist);
//头插
bool Insert_head(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//尾插
bool Insert_tail(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PCNode plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val);
//头删
bool Del_head(PCNode plist);
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PCNode plist);
//按位置删
bool Del_pos(PCNode plist, int pos);
//按值删
bool Del_val(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//查找 找到,返回的是查找到的这个节点的地址
struct CNode* Search(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val);
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PCNode plist);
//清空
void Clear(PCNode plist);
//销毁1
void Destory1(PCNode plist);
//销毁2
void Destory2(PCNode plist);
//打印
void Show(PCNode plist);
//获取有效值个数
int Getlength(PCNode plist);
.cpp 进行函数的实现
//初始化
void Init_list(struct CNode* plist) {
//1.判断plist是否为空地址
assert(plist != NULL);
//2.对plist指向的头节点里面的每一个成员进行赋值
//3.因为头节点直接借用的是有效节点的结构体设计,省事,但是多了一个数据域用不到
// 既然数据域用不到,那就浪费掉,只用指针域就可
//plist->data; //头结点的数据域不使用
plist->next = plist;
}
//头插
bool Insert_head(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
//0.安全性处理
assert(plist != NULL);//保证pclist这个指针 指向的单循环链表的头结点 确确实实存在
//1.购买新结点
struct CNode* pnewnode = (struct CNode*)malloc(1 * sizeof(CNode));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
//2.找到合适的插入位置
//因为是头插,永远都是插入在头节点后面,所以不用找,直接用plist即可
//3.插入
pnewnode->next = plist->next;
plist->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//尾插
bool Insert_tail(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plist != NULL);
struct CNode* pnewnode = (struct CNode*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct CNode));
assert(pnewnode != NULL);
pnewnode->data = val;
//pnewnode->next = NULL;//这行代码可以省略,也可以留下
struct CNode* p = plist;//这里p指向头节点,还是指向第一个有效节点,下面会总结
for (; p->next != plist; p = p->next);
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//按位置插
bool Insert_pos(PCNode plist, int pos, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plist != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0);
struct CNode* pnewnode = (struct CNode*)malloc(1 * sizeof(struct CNode));
pnewnode->data = val;
struct CNode* p = plist;//判断这个是插入函数,需要使用带前驱的头结点
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
p = p->next;
}
pnewnode->next = p->next;
p->next = pnewnode;
return true;
}
//头删
bool Del_head(PCNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(plist)) {
return false;
}
struct CNode* p = plist->next;
struct CNode* q = plist;
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//尾删
bool Del_tail(PCNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(plist)) {//保证plist指向的头结点后面 存在有效结点
return false;
}
struct CNode* p = plist;
for (; p->next != plist; p = p->next);
struct CNode* q = plist;
for (; q->next != p; q = q->next);
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//按位置删
bool Del_pos(PCNode plist, int pos) {
assert(plist != NULL);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < Getlength(plist));
struct CNode* q = plist;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
q = q->next;
}
struct CNode* p = q->next;
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//按值删
bool Del_val(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
assert(plist != NULL);
//先需要判断val值是否存在于单循环链表中
struct CNode* p = Search(plist, val);
//若存在,则删除,若不存在,则返回false
if (p == NULL) {
return false;
}
struct CNode* q = plist;
for (; q->next != p; q = q->next);
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return true;
}
//查找 找到,返回的是查找到的这个节点的地址
struct CNode* Search(PCNode plist, ELEM_TYPE val) {
for (struct CNode* p = plist->next; p != plist; p = p->next) {
if (p->data == val) {
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//判空
bool IsEmpty(PCNode plist) {
if (plist->next == plist) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
//清空
void Clear(PCNode plist) {
Destory1(plist);
}
//销毁1
void Destory1(PCNode plist) {
while (plist->next != plist) {
Del_head(plist);
}
}
//销毁2
void Destory2(PCNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
if (IsEmpty(plist)) { //保证至少一个有效结点
return;
}
//1.定义两个指针p和q,p指向第一个有效节点,q先不赋值
struct CNode* p = plist->next;
struct CNode* q=p->next;//如果在定义指针q直接赋值p—>next 则一定保证指针p存在
//2.断开头结点,因为不借助头节点,所以一开始就将投头结点变为最终销毁的样子
plist->next = plist;
//3.两个指针合作,循环释放后续节点
while (p != plist) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
//打印
void Show(PCNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
struct CNode* p = plist->next;
for (; p != plist; p = p->next) {
printf("%d\n", p->data);
}
}
//获取有效值个数
int Getlength(PCNode plist) {
assert(plist != NULL);
int count = 0;
struct CNode* p = plist->next;
for (; p != plist; p = p->next) {
count++;
}
return count;
}
.main 测试代码
//单循环链表测试
int main() {
struct CNode head; //单循环链表的头结点,实例化出来
Init_list(&head);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Insert_pos(&head, i, i + 1);
}
Show(&head);
Destory2(&head);
}






















 61
61











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










