Java实现冒泡排序、选择排序、直接插入排序
一、排序的概念及稳定性
- 概念: 所谓排序,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或某些关键字的大小,递增或递减的排列起来的操作。
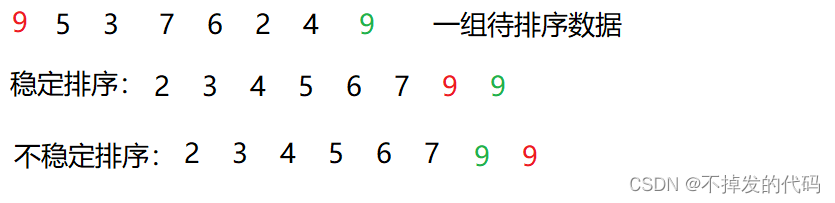
- 稳定性: 简单来说就是在一组还未排序的数据中,两个关键字具有相同属性(相当于两个数字相等,即5 = 5)再经过排序后两个关键字的顺序不变,如以下示例。
二、冒泡排序
1.基本思想
冒泡排序是一种交换排序,它的基本思想是: 两两比较相邻记录的关键字,如果反序则交换,知道没有反序的记录为止。
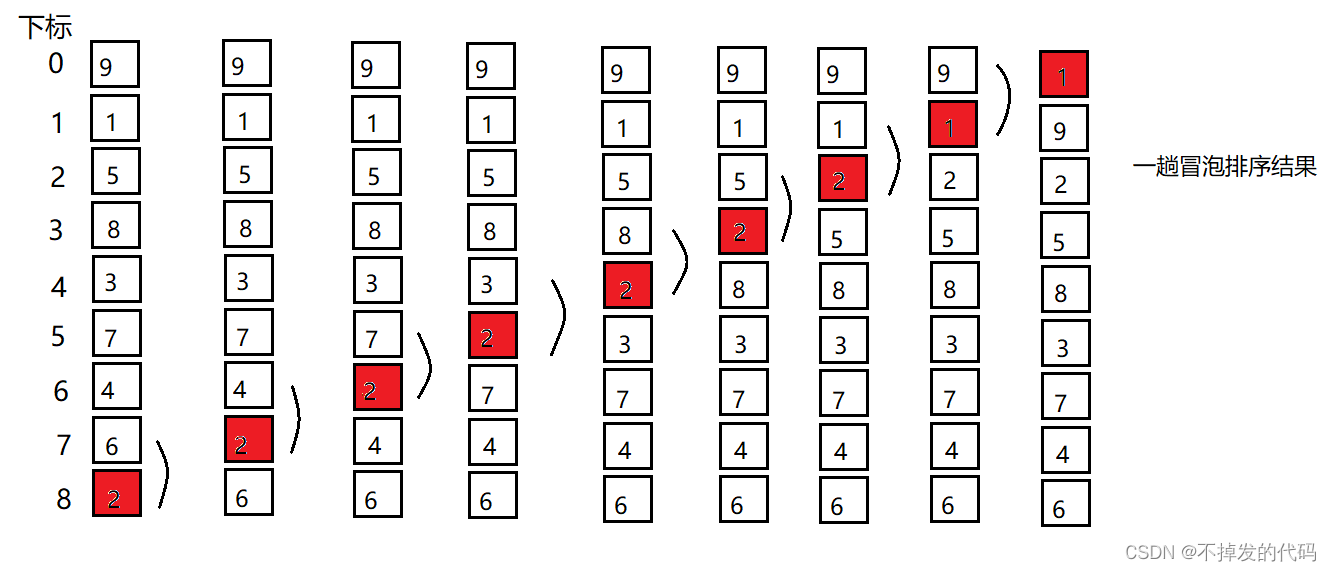
以上为一趟冒泡排序的结果,此时我们已经把一个数字放到了指定排好的位置,我们下一趟排序的时候就不对这个已排好的关键字进行操作,依次类推久能把剩下的数据排序。
2.代码实现
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Bubble {
public void sort (int[] array) {
for (int i = 0;i < array.length - 1;i++) {
for (int j = 0;j < array.length - i - 1;j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j+1]) {
swap(array,j,j+1);
}
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
public void print (int[] array) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
//测试类
public class BubbleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bubble bubble = new Bubble();
int[] array = {23, 51, 24, 82, 7, 31, 21, 36, 63};
bubble.sort(array);
bubble.print(array);
}
}
三、选择排序
1.基本思想
- 在数组中选择关键字最小(大)元素的下标
- 将找到的下标与指定位置进行交换(第一次是0下标,依次类推)
- 指定位置排序好后不在进行操作
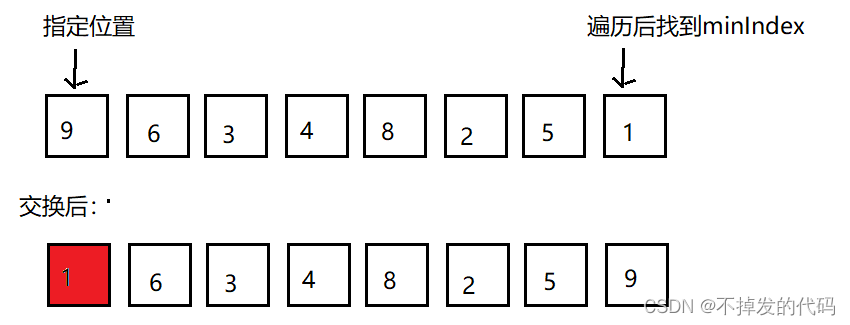
- 再进反复的操作知道数组有序
2.代码实现
public class Selection {
public void sort (int[] array) {
for (int i = 0;i < array.length;i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1;j < array.length;j++) {
if (array[minIndex] > array[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
swap(array,minIndex,i);
}
}
private void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Selection selection = new Selection();
int[] array = {23, 51, 24, 82, 7, 31, 21, 36, 63};
selection.sort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
四、直接插入排序
1.基本思想
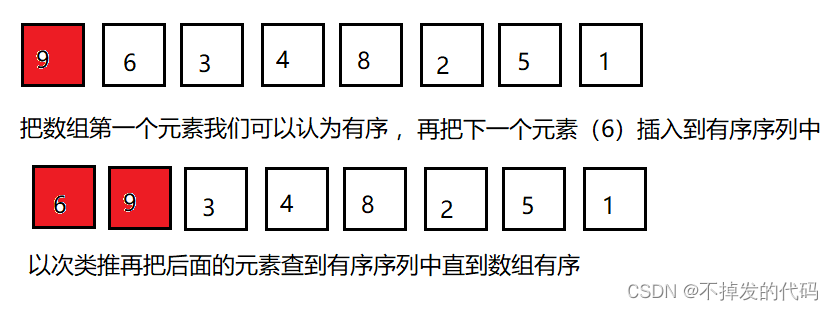
- 把待排序的记录按其关键码值的大小逐个插入到一个已经排好序的有序序列中,直到所有的记录插入完为止,得到一个新的有序序列 。实际中我们玩扑克牌时,就用了插入排序的思想。

2.代码实现
public class Insertion {
public void sort (int[] array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
for (int j = i - 1;j >= 0;j--) {
if (array[j+1] < array[j] ) {
swap(array,j+1,j);
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
public class InsertionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Insertion insertion = new Insertion();
int[] array = {23, 51, 24, 82, 7, 31, 21, 36, 63};
insertion.sort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
五、复杂度及稳定性分析
1.冒泡排序
- 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:稳定
2.选择排序
- 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:不稳定
3.直接插入排序
- 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 稳定性:稳定





















 6530
6530











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








