C++ map容器的简单用法
1.前言
整理map的一些用法,欢迎指正~
有具体示例解释概念,欢迎品尝~
2.内容
map简介
map是STL的关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据 处理能力 【key-value 】
map内部是一颗红黑树(一 种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能
map功能
查询(log(N))、插入、删除、更改、遍历
map具体使用
1.构造
头文件: < map >
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI; //为了使用方便,可进行类型起别名
int main()
{
map<string, int> m1; //map构造函数
MSI m2;
return 0;
}
2.增加[插入]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
int main()
{
map<string, int> m1; //map构造函数
MSI m2;
//四种插入方法
//1.insert pair
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("ac", 4));
//2.insert value_type
m2.insert(map<string, int>::value_type("as", 7));
//3.数组
m2["ak"] = 11;
//4.{}
m2.insert({ "ab",1 });
//遍历 auto x=m2.begin() 也可
for (MSIIT x = m2.begin(); x != m2.end(); x++)
cout << x->first << " " << x->second << endl;
return 0;
}
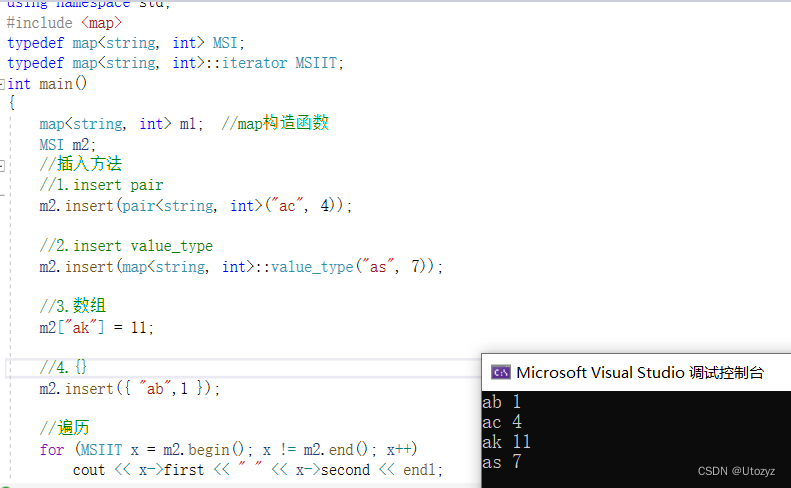
插入方法: insert方法 和 数组方法
区别:insert不可覆盖已经插入的数据,而数组方法可以
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
int main()
{
map<string, int> m1; //map构造函数
MSI m2;
//插入方法: insert方法 和 数组方法
//1.insert pair
m2.insert(pair<string, int>("ac", 4));
//2.insert value_type
m2.insert(map<string, int>::value_type("as", 7));
//3.数组
m2["ak"] = 11;
//4.{}
m2.insert({ "ab",1 });
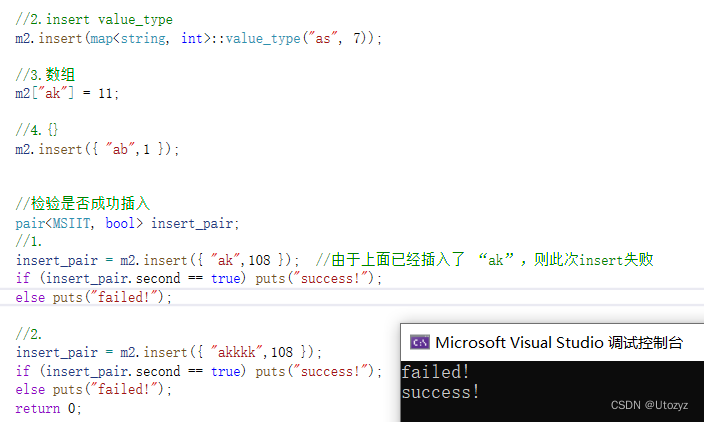
//下面一行代码检检验是否成功插入
//insert后返回iterator ,用 MSIIT接受 ,另一个bool则用来判断是否成功插入
pair<MSIIT, bool> insert_pair;
//1.
insert_pair = m2.insert({ "ak",108 }); //由于上面已经插入了 “ak”,则此次insert失败
if (insert_pair.second == true) puts("success!");
else puts("failed!");
//2.
insert_pair = m2.insert({ "akkkk",108 });
if (insert_pair.second == true) puts("success!");
else puts("failed!");
return 0;
}
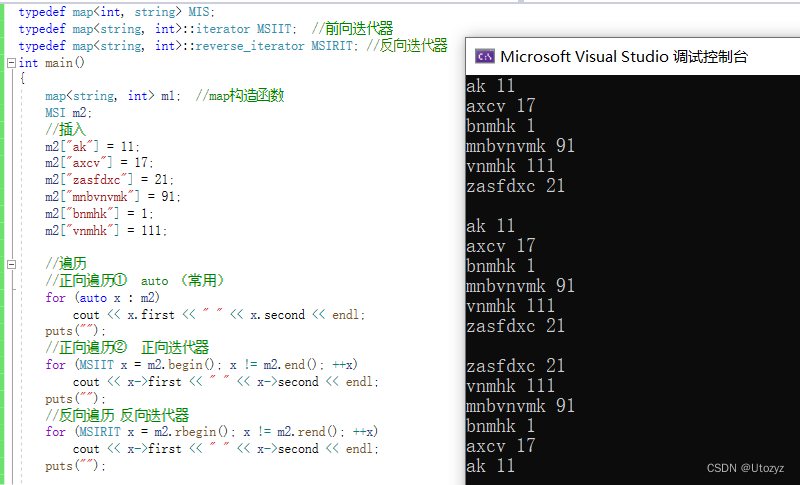
3.遍历 [正向、反向、数组方法遍历]
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT; //前向迭代器
typedef map<string, int>::reverse_iterator MSIRIT; //反向迭代器
int main()
{
map<string, int> m1; //map构造函数
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//遍历
//正向遍历① auto (常用)
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//正向遍历② 正向迭代器
for (MSIIT x = m2.begin(); x != m2.end(); ++x)
cout << x->first << " " << x->second << endl;
puts("");
//反向遍历 反向迭代器
for (MSIRIT x = m2.rbegin(); x != m2.rend(); ++x)
cout << x->first << " " << x->second << endl;
puts("");
//Specially 当 map<int,...> 时,可以用数组遍历
puts("");
MIS m3;
//插入
m3[1] = "mvbc";
m3[4] = "cvb";
//对于MIS,不存在key的value默认为"" 空
if (m3[2] == "") puts("none!");
if (m3[78] == "") puts("none!");
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i)
cout << i <<" "<< m3[i] << endl;
return 0;
}

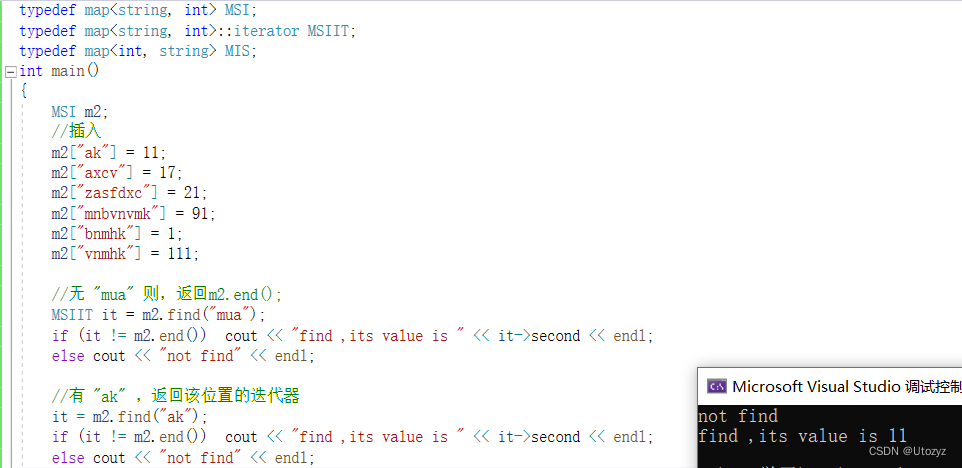
4.查找
①查找并返回key的迭代器 [find()]
备注:此处迭代器为pair对象,所以用first ,second访问
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//无 "mua" 则,返回m2.end();
MSIIT it = m2.find("mua");
if (it != m2.end()) cout << "find ,its value is " << it->second << endl;
else cout << "not find" << endl;
//有 "ak" ,返回该位置的迭代器
it = m2.find("ak");
if (it != m2.end()) cout << "find ,its value is " << it->second << endl;
else cout << "not find" << endl;
return 0;
}
②仅判断是否存在key [count 、pair(lower_bound + upper_bound)]
方法1: count
map是一对一的映射关系,则count函数返回值 只可为 0 、1,即存在返回1,不存在返回0
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//无 "mua" 则
int cnt = m2.count("mua");
if (cnt) cout << "find" << endl;
else cout << "not find" << endl;
//有 "ak"
cnt = m2.count("ak");
if (cnt) cout << "find" << endl;
else cout << "not find" << endl;
return 0;
}
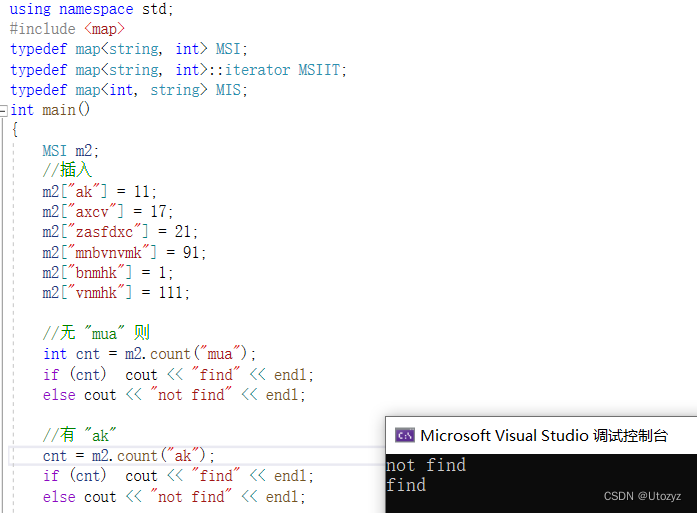
方法2:pair
前置知识:
1.equal_range() :
在[left , right)序列中表示一个数值的第一次出现与最后一次出现的后一位。得到相等元素的子范围,将两个迭代器以pair形式返回
2.lower_bound()、upper_bound()
lower_bound()返回一个 iterator 它指向在[first,last)标记的有序序列中可以插入value,而不会破坏容器顺序的第一个位置,而这个位置标记了一个不小于value 的值 即,找到>=value的位置并返回
同理,upper_bound()找到>value的位置并返回
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//当待查找的不存在时,lower_bound == upper_bound ,均返回 大于待查找的元素 的迭代器
pair<MSIIT, MSIIT> p = m2.equal_range("aka"); //两个迭代器,结合为pair形式返回
cout << p.first->first << " " << p.first -> second << endl;
cout << p.second->first << " " << p.second -> second << endl;
puts("");
//当 待查找的存在时, lower_bound != upper_bound
p = m2.equal_range("bnmhk");
cout << p.first->first << " " << p.first->second << endl;
cout << p.second->first << " " << p.second->second << endl;
return 0;
}
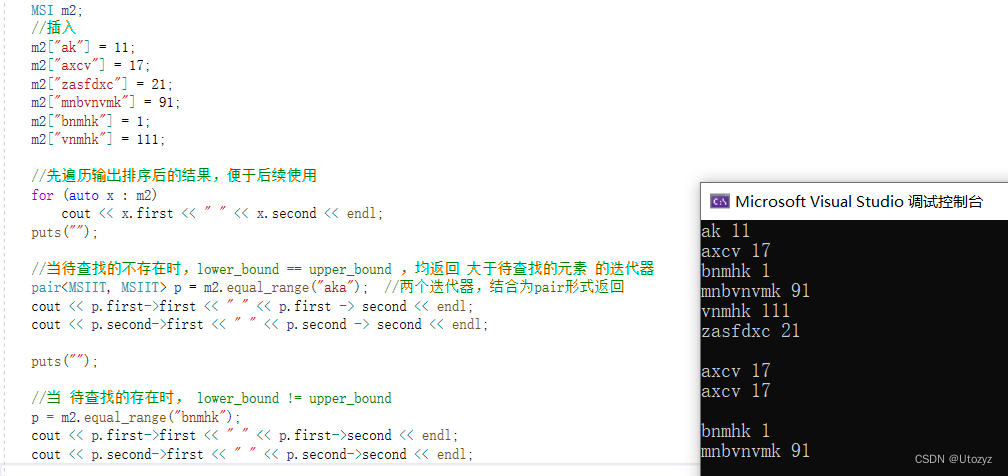
正文:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//当待查找的不存在时,lower_bound == upper_bound ,均返回 大于待查找的元素 的迭代器
pair<MSIIT, MSIIT> p = m2.equal_range("aka"); //两个迭代器,结合为pair形式返回
if (p.first != p.second) puts("find!");
else puts("not find");
puts("");
//当 待查找的存在时, lower_bound != upper_bound
p = m2.equal_range("bnmhk");
if (p.first != p.second) puts("find!");
else puts("not find");
return 0;
}
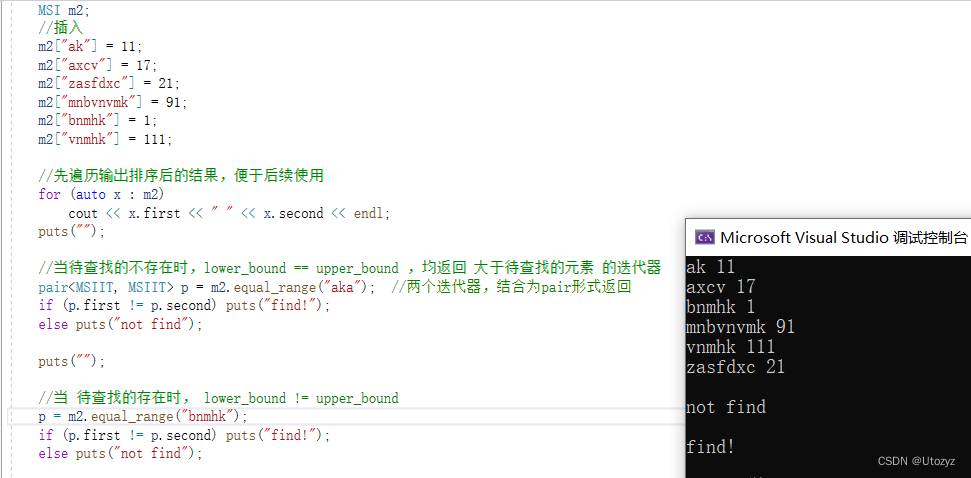
5.删除 [3种]
1.iterator erase(iterator it);//通过一个迭代器删除
2.iterator erase(iterator first,iterator last)//删除一个范围的元素
3.size_type erase(const Key&key); //通过关键字删除
clear()就相当于Map.erase(Map.begin(),Map.end());
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//1.迭代器 iterator
MSIIT it = m2.find("mnbvnvmk"); //找到位置
m2.erase(it);
//2.关键字
int t1=m2.erase("mnbvnvmk"); //已经被删除过了,则此次erase无效,返回0
int t2 = m2.erase("vnmhk"); //成功erase ,返回1
cout << t1 << " " << t2 << endl;
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
return 0;
}
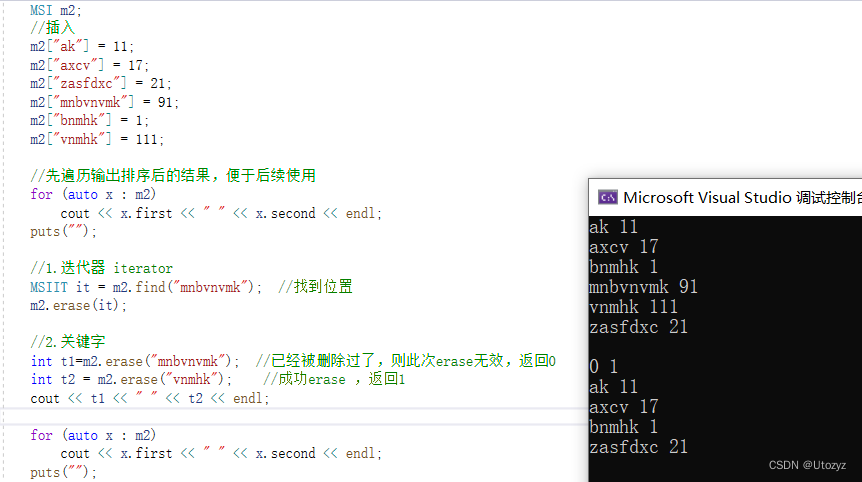
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m2;
//插入
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
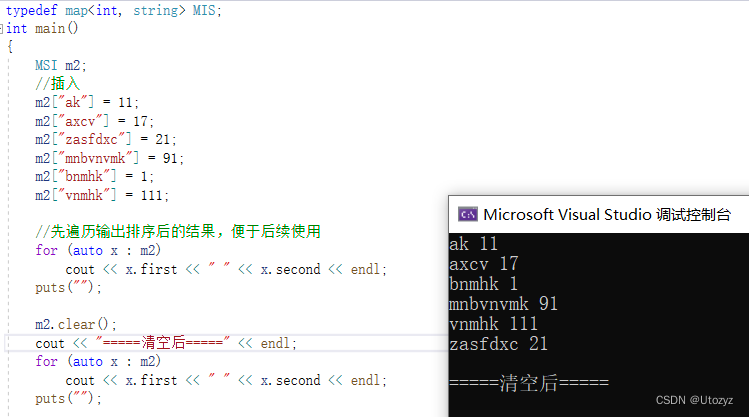
m2.clear();
cout << "=====清空后=====" << endl;
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
return 0;
}
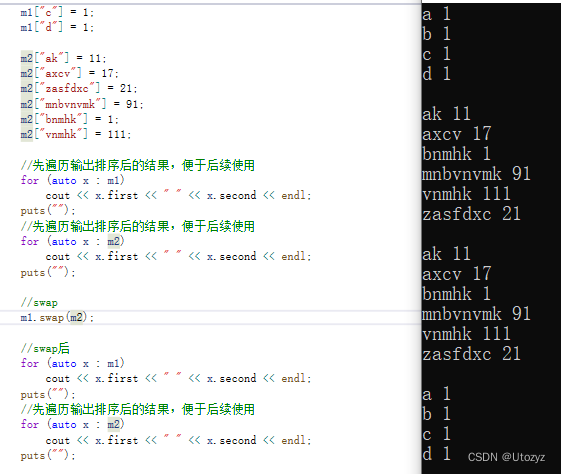
6.swap() [两种]
swap的作用是,交换两个容器内的所有元素
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
int main()
{
MSI m1,m2;
//插入
m1["a"] = 1;
m1["b"] = 1;
m1["c"] = 1;
m1["d"] = 1;
m2["ak"] = 11;
m2["axcv"] = 17;
m2["zasfdxc"] = 21;
m2["mnbvnvmk"] = 91;
m2["bnmhk"] = 1;
m2["vnmhk"] = 111;
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m1)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
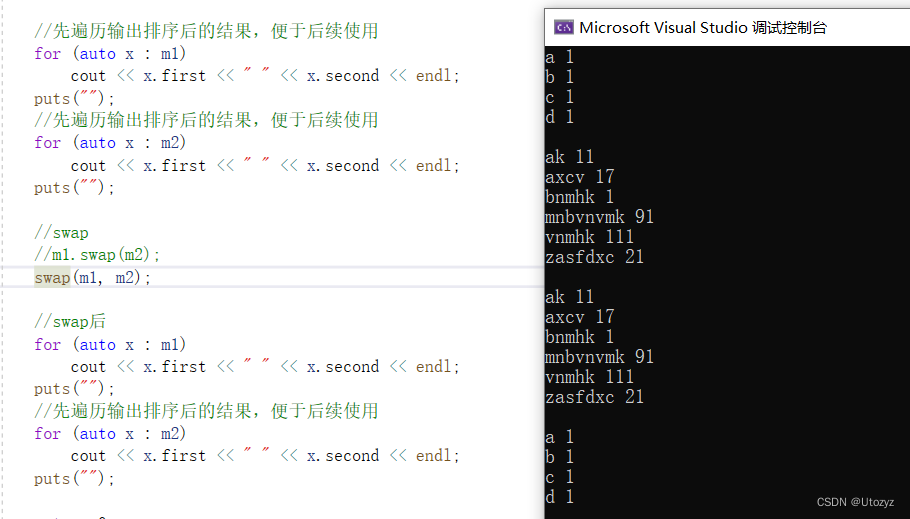
//swap
m1.swap(m2);
//也可以 : swap(m1, m2);
//swap后
for (auto x : m1)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
//先遍历输出排序后的结果,便于后续使用
for (auto x : m2)
cout << x.first << " " << x.second << endl;
puts("");
return 0;
}
其实直接用swap()是一样的
如果用map函数可以实现的功能,而STL Algorithm也可以完成该功能,建议用map自带函数,效率高一些。
7.排序
默认按key升序排序,不可使用sort
当,关键字为 结构体时,insert等会通不过, 此时要重载 < 号
如果不重载<号,VS2019会报以下错误:
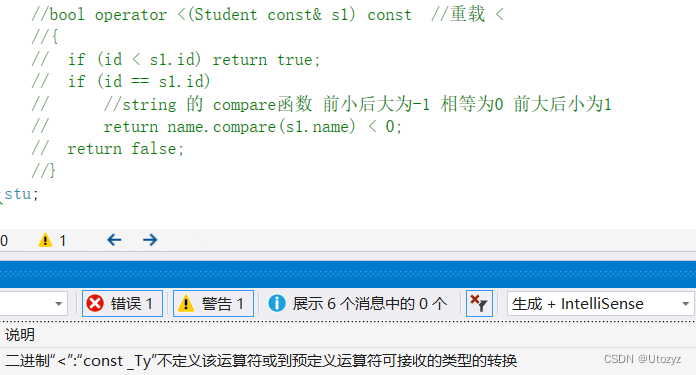
重载 <
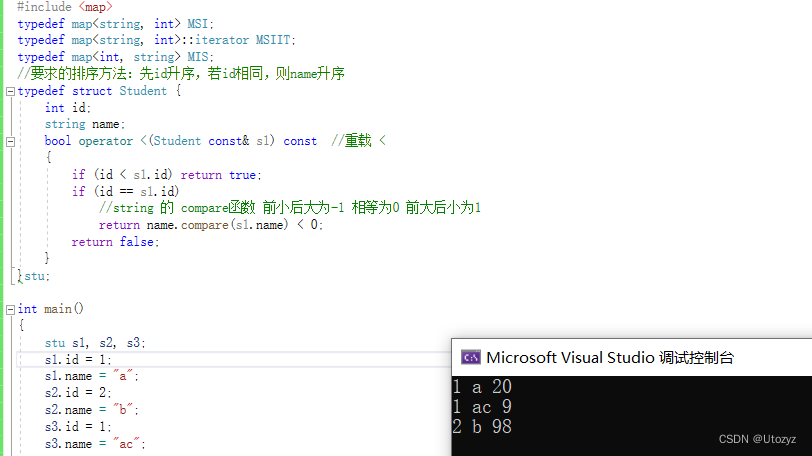
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <map>
typedef map<string, int> MSI;
typedef map<string, int>::iterator MSIIT;
typedef map<int, string> MIS;
//要求的排序方法:先id升序,若id相同,则name升序
typedef struct Student {
int id;
string name;
bool operator <(Student const& s1) const //重载 <
{
if (id < s1.id) return true;
if (id == s1.id)
//string 的 compare函数 前小后大为-1 相等为0 前大后小为1
return name.compare(s1.name) < 0;
return false;
}
}stu;
int main()
{
stu s1, s2, s3;
s1.id = 1;
s1.name = "a";
s2.id = 2;
s2.name = "b";
s3.id = 1;
s3.name = "ac";
map<stu, int> m1; //学生信息,以及分数
m1.insert({ s1,20 });
m1.insert({ s2,98 });
m1.insert({ s3,9 });
//x为pair类型变量 直接 . 访问
for (auto x : m1)
cout << x.first.id << " " <<x.first.name <<" "<< x.second << endl;
return 0;
}
3.总结
C++ maps是一种关联式容器,包含“关键字 key/值 value”对 [键值对]
map中由于它内部有序,是由红黑树保证,因此很多函数执行的时间复杂度都是log2N的
begin() 返回指向map头部的迭代器
end() 返回指向map末尾的迭代器
size() 返回map中元素的个数
clear() 删除所有元素
count() 返回指定元素出现的次数
empty() 判断map是否为空 [map为空则返回true]
insert() 插入元素
erase() 删除一个元素
find() 查找一个元素
rbegin() 返回一个指向map尾部的逆向迭代器
rend() 返回一个指向map头部的逆向迭代器
lower_bound() 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置
upper_bound() 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置
max_size() 返回可以容纳的最大元素个数
swap() 交换两个map
equal_range() 返回特殊条目的迭代器对
get_allocator() 返回map的配置器
key_comp() 返回比较元素key的函数
value_comp() 返回比较元素value的函数
4.更新日志
2022.8.7 整理
欢迎评论留言、指正~~

























 9375
9375











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








