需求提出
在开发无人机定位模块时,为了复现测试过程,需要记录图像传感器(相机)传给机器的无损照片,这对于普通的sd卡压力是很大的(720*720的灰度图就需要15m/s左右的带宽),可能会出现由于写文件速度不够而带来的丢帧问题,于是乎就需要一个可以实时压缩的模块来缓解写文件线程的压力。
哈夫曼编码
算法实现
大致过程就是:
统计文本中字符出现的次数
按照频次排序
将频数最小的两个叶子节点组合成树,看成一个整体,整体的频数是叶子节点的频数和
把这个树当成整体和别的一起排序
重复上述过程指导生成整课树
生成码表
编码文件
写入码表和编码后的文件
实现代码
huffman.h
/**
* huffman.h
*/
#ifndef _huffman_h
#define _huffman_h
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 720*720
#define WRITE_BUFF_SIZE 100
#define PSEUDO_EOF 256
struct Huffman_node
{
int id; // 使用int类型,因为要插入值为256的pseudo-EOF
unsigned int freq;
string code;
Huffman_node* left,
* right,
* parent;
};
typedef Huffman_node* Node_ptr;
class Huffman
{
private:
Node_ptr* node_array = new Node_ptr[MAX_SIZE]; // 叶子节点数组
Node_ptr root; // 根节点
int size; // 叶子节点数
fstream in_file, out_file; // 输入、输出文件流
map<int, string> table; // 字符->huffman编码映射表
class Compare
{
public:
bool operator()(const Node_ptr& c1, const Node_ptr& c2) const
{
return (*c1).freq > (*c2).freq;
}
};
// 用于比较优先队列中元素间的顺序
priority_queue< Node_ptr, vector<Node_ptr>, Compare > pq;
// 根据输入文件构造包含字符及其频率的数组
void create_node_array();
// 根据构造好的Huffman树建立Huffman映射表
void create_map_table(const Node_ptr node, bool left);
// 构造优先队列
void create_pq();
// 构造Huffman树
void create_huffman_tree();
// 计算Huffman编码
void calculate_huffman_codes();
// 开始压缩过程
void do_compress();
// 从huffman编码文件中重建huffman树
void rebuid_huffman_tree();
// 根据重建好的huffman树解码文件
void decode_huffman();
public:
// 根据输入和输出流初始化对象
Huffman(string in_file_name, string out_file_name);
// 析构函数
~Huffman();
// 压缩文件
void compress();
// 解压文件
void decompress();
};
#endif
huffman.cpp
/**
* huffman.cpp
*/
#include "huffman.h"
void Huffman::create_node_array()
{
int i, count;
int* freq = new int[MAX_SIZE](); // 频数统计数组
char in_char;
// 依次读入字符,统计数据
while (!in_file.eof())
{
in_file.get(in_char);
// 消除最后一行的影响
if (in_file.eof())
break;
// char是有符号的,数组下标是unsigned 所以要换成unsigned char
freq[(unsigned char)in_char]++;
}
count = 0;
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE; ++i)
{
if (freq[i] <= 0)
continue;
Node_ptr node = new Huffman_node();
node->id = i;
node->freq = freq[i];
node->code = "";
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->parent = NULL;
node_array[count++] = node;
}
// 插入频率为1的pseudo-EOF
Node_ptr node = new Huffman_node();
node->id = PSEUDO_EOF;
node->freq = 1;
node->code = "";
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->parent = NULL;
node_array[count++] = node;
size = count;
delete[] freq;
}
void Huffman::create_map_table(const Node_ptr node, bool left)
{
if (left)
node->code = node->parent->code + "0";
else
node->code = node->parent->code + "1";
// 如果是叶子节点,则是一个“有效”节点,加入编码表
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
table[node->id] = node->code;
else
{
if (node->left != NULL)
create_map_table(node->left, true);
if (node->right != NULL)
create_map_table(node->right, false);
}
}
void Huffman::create_pq()
{
int i;
create_node_array();
for (i = 0; i < size; ++i)
pq.push(node_array[i]);
}
void Huffman::create_huffman_tree()
{
root = NULL;
while (!pq.empty())
{
Node_ptr first = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (pq.empty())
{
root = first;
break;
}
Node_ptr second = pq.top();
pq.pop();
Node_ptr new_node = new Huffman_node();
new_node->freq = first->freq + second->freq;
if (first->freq <= second->freq)
{
new_node->left = first;
new_node->right = second;
}
else
{
new_node->left = second;
new_node->right = first;
}
first->parent = new_node;
second->parent = new_node;
pq.push(new_node);
}
}
void Huffman::calculate_huffman_codes()
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("Build the huffman tree failed or no characters are counted\n");
exit(1);
}
if (root->left != NULL)
create_map_table(root->left, true);
if (root->right != NULL)
create_map_table(root->right, false);
}
void Huffman::do_compress()
{
int length, i, j, byte_count;
char in_char;
unsigned char out_c, tmp_c;
string code, out_string;
map<int, string>::iterator table_it;
// 按节点数(包括pseudo-EOF) + 哈夫曼树 + 哈夫曼编码来写入文件
// 第1行写入节点数(int)
out_file << size << endl;
// 第2~(size+1)行写入huffman树,即每行写入字符+huffman编码,如"43 00100"
for (table_it = table.begin(); table_it != table.end(); ++table_it)
{
out_file << table_it->first << " " << table_it->second << endl;
}
// 第size+2行写入huffman编码
in_file.clear();
in_file.seekg(ios::beg);
code.clear();
while (!in_file.eof())
{
in_file.get(in_char);
// 消除最后一行回车的影响
if (in_file.eof())
break;
// 找到每一个字符所对应的huffman编码
table_it = table.find((unsigned char)in_char);
if (table_it != table.end())
code += table_it->second;
else
{
printf("Can't find the huffman code of character %X\n", in_char);
exit(1);
}
// 当总编码的长度大于预设的WRITE_BUFF_SIZE时再写入文件
length = code.length();
if (length > WRITE_BUFF_SIZE)
{
out_string.clear();
//将huffman的01编码以二进制流写入到输出文件
for (i = 0; i + 7 < length; i += 8)
{
// 每八位01转化成一个unsigned char输出
// 不使用char,如果使用char,在移位操作的时候符号位会影响结果
// 另外char和unsigned char相互转化二进制位并不变
out_c = 0;
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
if ('0' == code[i + j])
tmp_c = 0;
else
tmp_c = 1;
out_c += tmp_c << (7 - j);
}
out_string += out_c;
}
out_file << out_string;
code = code.substr(i, length - i);
}
}
// 已读完所有文件,先插入pseudo-EOF
table_it = table.find(PSEUDO_EOF);
if (table_it != table.end())
code += table_it->second;
else
{
printf("Can't find the huffman code of pseudo-EOF\n");
exit(1);
}
// 再处理尾部剩余的huffman编码
length = code.length();
out_c = 0;
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if ('0' == code[i])
tmp_c = 0;
else
tmp_c = 1;
out_c += tmp_c << (7 - (i % 8));
if (0 == (i + 1) % 8 || i == length - 1)
{
// 每8位写入一次文件
out_file << out_c;
out_c = 0;
}
}
}
void Huffman::rebuid_huffman_tree()
{
int i, j, id, length;
string code;
Node_ptr node, tmp, new_node;
root = new Huffman_node();
root->left = NULL;
root->right = NULL;
root->parent = NULL; //解码的时候parent没什么用了,可以不用赋值,但为了安全,还是赋值为空
in_file >> size;
if (size > MAX_SIZE)
{
printf("The number of nodes is not valid, maybe the compressed file has been broken.\n");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
in_file >> id;
in_file >> code;
length = code.length();
node = root;
for (j = 0; j < length; ++j)
{
if ('0' == code[j])
tmp = node->left;
else if ('1' == code[j])
tmp = node->right;
else
{
printf("Decode error, huffman code is not made up with 0 or 1\n");
exit(1);
}
// 如果到了空,则新建一个节点
if (tmp == NULL)
{
new_node = new Huffman_node();
new_node->left = NULL;
new_node->right = NULL;
new_node->parent = node;
// 如果是最后一个0或1,说明到了叶子节点,给叶子节点赋相关的值
if (j == length - 1)
{
new_node->id = id;
new_node->code = code;
}
if ('0' == code[j])
node->left = new_node;
else
node->right = new_node;
tmp = new_node;
}
// 如果不为空,且到了该huffman编码的最后一位,这里却已经存在了一个节点,就说明
// 原来的huffmaninman是有问题的
else if (j == length - 1)
{
printf("Huffman code is not valid, maybe the compressed file has been broken.\n");
exit(1);
}
// 如果不为空,但该节点却已经是叶子节点,说明寻路到了其他字符的编码处,huffman编码也不对
else if (tmp->left == NULL && tmp->right == NULL)
{
printf("Huffman code is not valid, maybe the compressed file has been broken.\n");
exit(1);
}
node = tmp;
}
}
}
void Huffman::decode_huffman()
{
bool pseudo_eof;
int i, id;
char in_char;
string out_string;
unsigned char u_char, flag;
Node_ptr node;
out_string.clear();
node = root;
pseudo_eof = false;
in_file.get(in_char);// 跳过最后一个回车
while (!in_file.eof())
{
in_file.get(in_char);
u_char = (unsigned char)in_char;
flag = 0x80;
for (i = 0; i < 8; ++i)
{
if (u_char & flag)
node = node->right;
else
node = node->left;
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
id = node->id;
if (id == PSEUDO_EOF)
{
pseudo_eof = true;
break;
}
else
{
// int to char是安全的,高位会被截断
out_string += (char)node->id;
node = root;
}
}
flag = flag >> 1;
}
if (pseudo_eof)
break;
if (WRITE_BUFF_SIZE < out_string.length())
{
out_file << out_string;
out_string.clear();
}
}
if (!out_string.empty())
out_file << out_string;
}
Huffman::Huffman(string in_file_name, string out_file_name)
{
in_file.open(in_file_name.c_str(), ios::in | ios::binary);
if (!in_file)
{
printf("Open file error, path is: %s\n", in_file_name.c_str());
exit(1);
}
out_file.open(out_file_name.c_str(), ios::out | ios::binary);
if (!out_file)
{
printf("Open file error, path is: %s\n", out_file_name.c_str());
exit(1);
}
}
Huffman::~Huffman()
{
in_file.close();
out_file.close();
delete[] node_array;
}
void Huffman::compress()
{
create_pq();
create_huffman_tree();
calculate_huffman_codes();
do_compress();
}
void Huffman::decompress()
{
rebuid_huffman_tree();
decode_huffman();
}
测试效果
不知道是不是因为代码过分简单,压缩效果非常差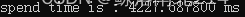
时间上肯定是达不到实时的(对于30秒的视频一帧大约33ms),那就跟不用说压缩比了,果断放弃
lzo
算法实现
不需要知道,只要会用官方给的代码就行。
代码地址
lzo-2.09.tar.gz下载地址
这里再给出一个lzo轻量库的地址,如果只是想简单使用到自己的项目里面用这个会很方便
minilzo地址
使用说明
搭配环境
对于lzo,解压缩文件后用makefile文件进行编译就可以了。但是不建议使用,很麻烦(虽然它的功能也更强大)。
对于minilzo就很简单了,只需要将lzoconf.h,lzodefs.h,minilzo.h,minilzo.c放到项目目录下就可以了。
简单使用
压缩
1.申请算法需要的缓冲区,就按照官方示例中申请的wrkmem这么大就可以了。
2.使用lzo_init()函数并判断返回值是否等于LZO_E_OK,如果相等进行下一步
3.使用lzo1x_1_compress(in, in_len, out, &out_len, wrkmem)函数进行压缩in是输入指针,in_len是舒服长度,out是压缩后数据指针,ou_len可以获得压缩后数据长度,wrkmem就是工作缓冲区,返回值为LZO_E_OK就可以了。
解压
解压不需要缓冲区
直接使用lzo1x_decompress(in, in_len, new, &new_len, NULL)。
如果使用的是lzo的话还可以调节压缩倍率,比如:
lzo1x_1_compress
lzo1x_1_11_compress
lzo1x_1_12_compress
lzo1x_1_15_compress
lzo1x_999_compress
对应的wrkmem申请的空间也要用不同的大小(用对应的宏确定大小就可以了)。
实际测试下来lzo1x后面的数字越大压缩比越大,压缩时间也越长,为了达到实时压缩的效果最终使用了lzo轻量库minilzo。
压缩效果
对于720*720的室内灰度图在pc上测试压缩比可以达到1.79,压缩时间在2.8ms上下,速度上是很快的。可以达到实时压缩的需求。
值得注意的是,lzo算法对复杂度不同的图片压缩效果也不同,对于一些纹理十分复杂的图片,甚至会反向压缩(但是压缩时间也更短),如下图(转为灰度图后)就会反向压缩
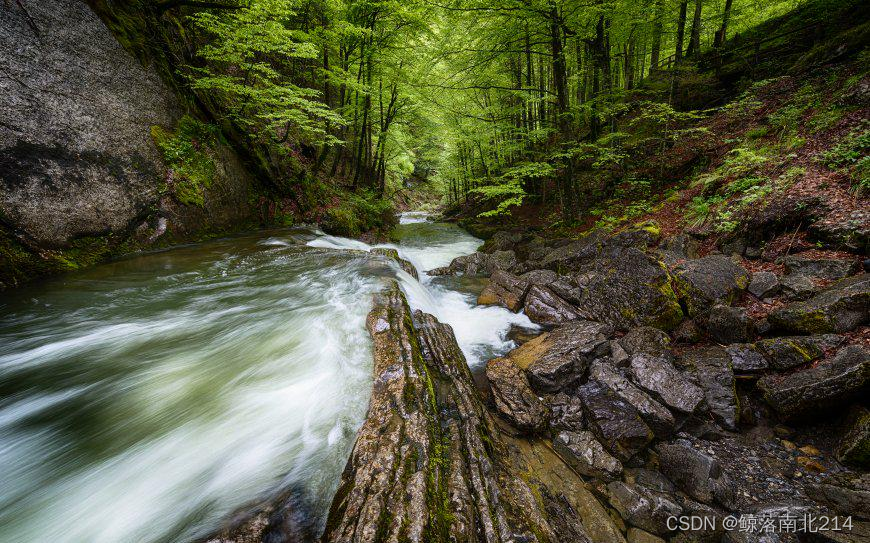

此外minilzo由纯c编码,可以自己再用类封装一下,咋样在一些c++项目里面使用更方便
下面代码仅供参考
lzo_compress.h
#include "minilzo.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#define IN_LEN (720*720ul)
#define OUT_LEN (IN_LEN + IN_LEN / 16 + 64 + 3)
class LzoCompress {
public:
LzoCompress();
~LzoCompress();
/*
* This function must be called before compression
* The data must have already applied for space
*/
void set_input(unsigned char* data);
int compress();
unsigned char* get_outcome();
int get_out_len();
double get_compress_proportion();
private:
int index_ = 0;
lzo_uint in_len_;
lzo_uint out_len_;
unsigned char* in;
unsigned char* out;
lzo_align_t* wrkmem;//压缩算法需要的空间
};
lzo_compress.cpp
#include "lzo_compress.h"
LzoCompress::LzoCompress() {
wrkmem = (lzo_align_t*)malloc(sizeof(lzo_align_t) * (((LZO1X_1_MEM_COMPRESS)+(sizeof(lzo_align_t) - 1)) / sizeof(lzo_align_t)));
in = NULL;
out = (unsigned char*)malloc(OUT_LEN);
if (lzo_init() != LZO_E_OK)
{
printf("internal error - lzo_init() failed !!!\n");
printf("(this usually indicates a compiler bug - try recompiling\nwithout optimizations, and enable '-DLZO_DEBUG' for diagnostics)\n");
}
}
LzoCompress::~LzoCompress() {
free(wrkmem);
free(out);
}
void LzoCompress::set_input(unsigned char* data) {
in = data;
in_len_ = IN_LEN;
}
int LzoCompress::compress() {
int r = lzo1x_1_compress(in, in_len_, out, &out_len_, wrkmem);
index_++;
return r;
}
unsigned char* LzoCompress::get_outcome() {
return out;
}
int LzoCompress::get_out_len() {
return out_len_;
}
double LzoCompress::get_compress_proportion() {
return (double)in_len_ / out_len_;
}
lzo_decompress.h
#include "minilzo.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
class LzoDeCompress {
public:
LzoDeCompress();
~LzoDeCompress();
/*
* This function must be called before compression
* The data must have already applied for space
*/
void set_input(unsigned char* data, int in_len);
int decompress();
unsigned char* get_outcome();
int get_out_len();
private:
int index_ = 0;
lzo_uint in_len_;
lzo_uint out_len_;
lzo_uint new_len_;
unsigned char* in;
unsigned char* out;
lzo_align_t* wrkmem;//压缩算法需要的空间
};
lzo_decompress.cpp
#include "lzo_decompress.h"
LzoDeCompress::LzoDeCompress() {
wrkmem = (lzo_align_t*)malloc(sizeof(lzo_align_t) * (((LZO1X_1_MEM_COMPRESS)+(sizeof(lzo_align_t) - 1)) / sizeof(lzo_align_t)));
in = NULL;
out = (unsigned char*)malloc(720 * 720);
if (lzo_init() != LZO_E_OK){
printf("internal error - lzo_init() failed !!!\n");
printf("(this usually indicates a compiler bug - try recompiling\nwithout optimizations, and enable '-DLZO_DEBUG' for diagnostics)\n");
}
}
LzoDeCompress::~LzoDeCompress() {
free(wrkmem);
free(out);
}
void LzoDeCompress::set_input(unsigned char* data, int in_len) {
in = data;
in_len_ = in_len;
}
int LzoDeCompress::decompress() {
int r = lzo1x_decompress(in, in_len_, out, &out_len_, NULL);
if (r != LZO_E_OK || out_len_ != 720 * 720) {
std::cout << "the " << index_ << "th image decompress failed";
}
index_++;
return r;
}
unsigned char* LzoDeCompress::get_outcome() {
return out;
}
int LzoDeCompress::get_out_len() {
return out_len_;
}
以上就是本人关于huffman编码和lzo算法的一些拙见,希望对你的学习有所帮助,有错误的话也希望在评论区指出
最后发点牢骚,我觉得csdn作为一个专业IT社区,致力于为软件开发者提供知识传播、在线学习、职业发展等全生命周期服务的社区,这里的氛围应该是互相探讨知识交流知识的,而不是到处都是纯纯复制粘贴的文章,到处都是铜钱的恶臭,在这段学习时间里有很多不会的技术,我很希望csdn能给我带来一定的帮助,但是绝大部分博客都知识复制粘贴的流水账,甚至接连十几篇的文章连错都错的一模一样,不是说写的博客不可以有错但起码自己发出来的东西自己也读一遍吧。另外就是一些博主恶意在自己的博客里留问题,就比如我之前在一篇博客里发现博客有错误,就抱着交流心得的态度去和博主探讨探讨,结果得到的回复是《私人解决问题是收费的》,我反问那你博客有问题你自己也知道为啥不改,得到的回复是《我平时比较忙》。





















 1437
1437











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








