一,双向链表
定义
typedef struct DoubleLinkedNode
{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkedNode* previous;
struct DoubleLinkedNode* next;
}DLNode,*DLNodePtr;
初始化
DLNodePtr initLinkList()
{
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}打印
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader)
{
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}删除
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader,char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p,q,r;
p=paraHeader;
while((p->next!=NULL)&&(p->next->data!=paraChar)){
p=p->next;
}
if(p->next==NULL){
printf("The char '%c' does not exist.\r\n",paraChar);
return;
}
q=p->next;
r=q->next;
p->next=r;
if(r!=NULL){
r->previous=p;
}
free(q);
}
添加
void insertDeleteTest(){
DLNedePtr templist=initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList,'H',0);
insertElement(tempList,'e',1);
insertElement(tempList,'l',2);
insertElement(tempList,'l',3);
insertElement(tempList,'o',4);
insertElement(tempList,'!',5);
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList,'e');
deleteElement(tempList,'a');
deleteElement(tempList,'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList,'o',1);
printList(tempList);
}
查找
int locateElement(DLNodePtr para Header,char paraValue){
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader;
for(int i=0;;i++){
if(p->data==paraValue){
retuen i;
}
p = p->next;
}
return 1;
}
图示
全部函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
//结构
typedef struct DoubleLinkedNode{
char data;
struct DoubleLinkedNode *previous;
struct DoubleLinkedNode *next;
} DLNode, *DLNodePtr;
//创建
DLNodePtr initLinkList(){
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}
//打印
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader){
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL){
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
//插入结点
void insertElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
//找到插入位置,并判断是否超出链表范围
p = paraHeader;
for (int i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++){
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL){
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
q = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
q->data = paraChar;
//插入链表
r = p->next;
q->next = p->next;
q->previous = p;
p->next = q;
//判断是否在链表尾部插入元素结点
if (r != NULL){
r->previous = q;
}
}
//删除
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
//查找
while((p->next != NULL) && (p->next->data != paraChar)){
p = p->next;
}
//判断是否找到
if (p->next == NULL){
printf("The char '%c' does not exist.\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
//删除
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
//判断在尾部删除结点
if (r != NULL){
r->previous = q;
}
free(q);
}
查找
int locateElemt(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar){
int paraPosition = -1;
DLNodePtr p;
p = paraHeader;
while(p != NULL && p->data != paraChar){
p = p->next;
paraPosition++;
}
if(p == NULL){
paraPosition = -1;
}
return paraPosition;
}
//插入、删除测试
void insertDeleteTest(){
//创建链表
DLNodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 5);
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 1);
printList(tempList);
}
void basicAddressTest(){
DLNode tempNode1, tempNode2;
tempNode1.data = 4;
tempNode1.next = NULL;
tempNode2.data = 6;
tempNode2.next = NULL;
printf("The first node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode1, &tempNode1.data, &tempNode1.next);
printf("The second node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode2, &tempNode2.data, &tempNode2.next);
tempNode1.next = &tempNode2;
}二,静态函数
结构体
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode{
char data;
int next;
}*NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
}*ListPtr;
初始化
ListPtr initLinkedList(){
ListPtr tempPtr=(ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
tempPtr->nodes=(NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode)*DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->nodes[0].data='\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next=-1;
tempPtr->used[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<DEFAULT_SIZE;i++){
tempPtr->used[i]=0;
}
return tempPtr;
}
打印
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr){
int p=0;
while(p!=-1){
printf("%c",paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p=paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
插入
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr,char paraChar,int paraPosition){
int p,q,i;
p=0;
for(i=0;i<paraPosition;i++){
p=paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if(p==-1){
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n",paraPosition);
return;
}
}
for(i=1;i<DEFAULT_SIZE;i++){
if(paraListPtr->used[i]==0){
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n",i);
paraListPtr->used[i]=1;
q=i;
break;
}
}
if(i==DEFAULT_SIZE){
printf("No space,\r\n");
return;
}
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data=paraChar;
printf("Linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next=paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next=q;
}删除
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr,char paraChar){
int p,q;
p=0;
while((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next!=-1)&&(paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data!=paraChar)){
p=paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}
if(paraListPtr->nodes[p].next==-1){
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n",paraChar);
return;
}
q=paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next=paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
paraListPtr->used[q]=0;
}
图示
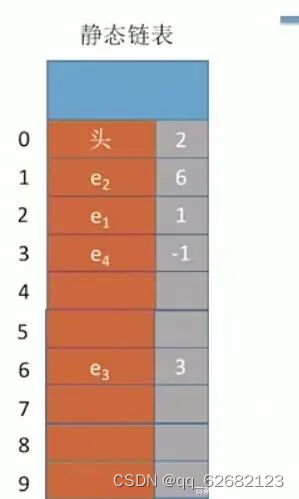
全部代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 6
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
} *ListPtr;
/**
* Initialize the list with a header.
* @return The pointer to the header.
*/
ListPtr initLinkedList(){
// The pointer to the whole list space.
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(StaticLinkedList));
// Allocate total space.
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
// The first node is the header.
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
// Only the first node is used.
tempPtr->used[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}// Of for i
return tempPtr;
}// Of initLinkedList
/**
* Print the list.
* @param paraListPtr The pointer to the list.
*/
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr){
int p = 0;
while (p != -1) {
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
printf("\r\n");
}// Of printList
/**
* Insert an element to the given position.
* @param paraListPtr The position of the list.
* @param paraChar The given char.
* @param paraPosition The given position.
*/
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition){
int p, q, i;
// Step 1. Search to the position.
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i ++) {
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}// Of if
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Construct a new node.
for (i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i ++){
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0){
// This is identical to malloc.
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}// Of if
}// Of for i
if (i == DEFAULT_SIZE){
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}// Of if
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
// Step 3. Now link.
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}// Of insertElement
/**
* Delete an element from the list.
* @param paraHeader The header of the list.
* @param paraChar The given char.
*/
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar){
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar)){
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1) {
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}// Of if
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
// This statement is identical to free(q)
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}// Of deleteElement
/**
* Unit test.
*/
void appendInsertDeleteTest(){
// Step 1. Initialize an empty list.
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
// Step 2. Add some characters.
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 4);
printList(tempList);
// Step 3. Delete some characters (the first occurrence).
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 3);
printList(tempList);
}// Of appendInsertDeleteTest
/**
* The entrance.
*/
void main(){
appendInsertDeleteTest();
}





















 978
978











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








