一、DevCloud注册
注册链接 https://idzcn.com/devcloud.htm
接下来按照提示激活账户,然后会跳转至如下页面:
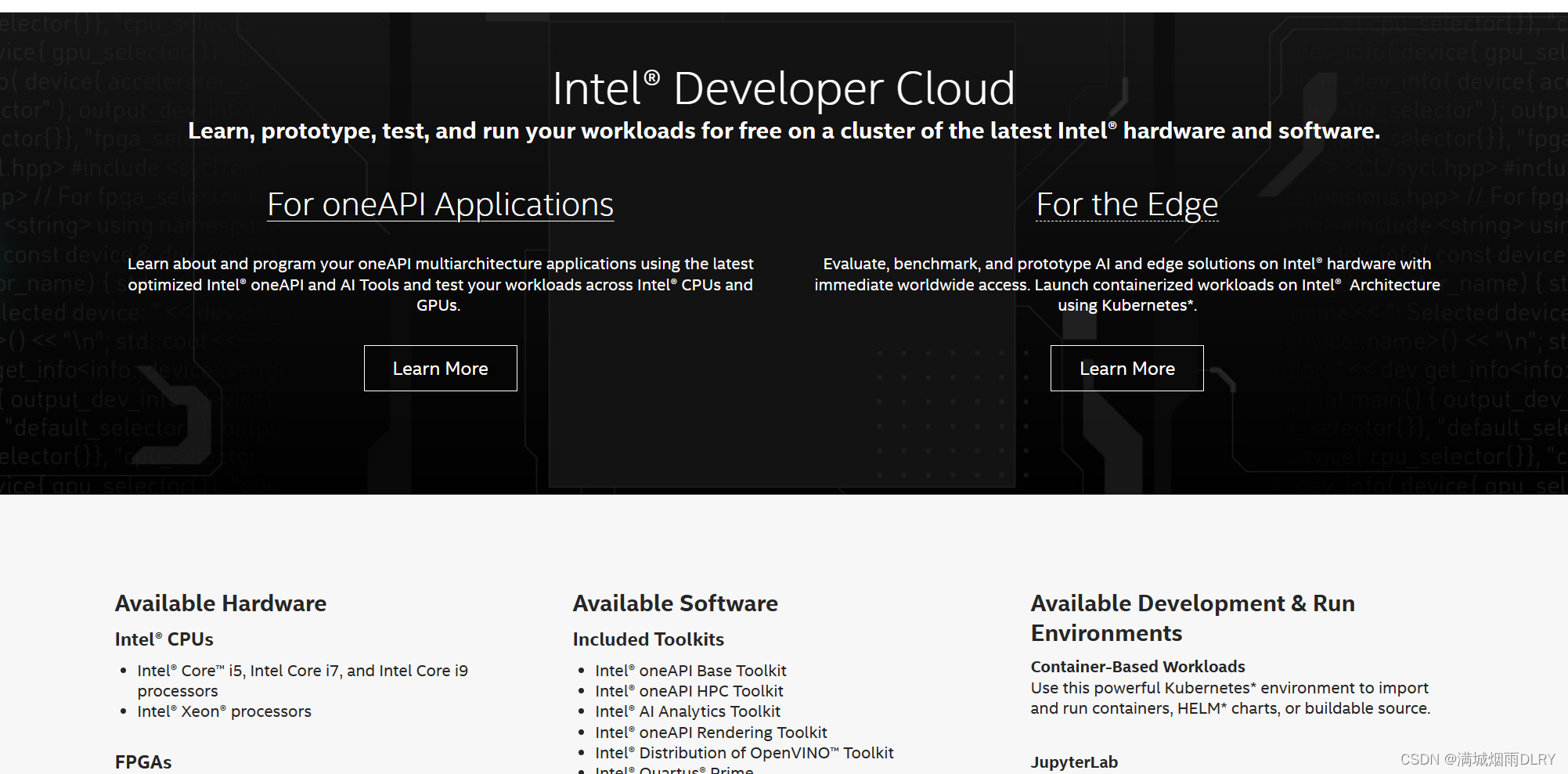
二、实践
点击For oneAPI Applications进入如下页面:
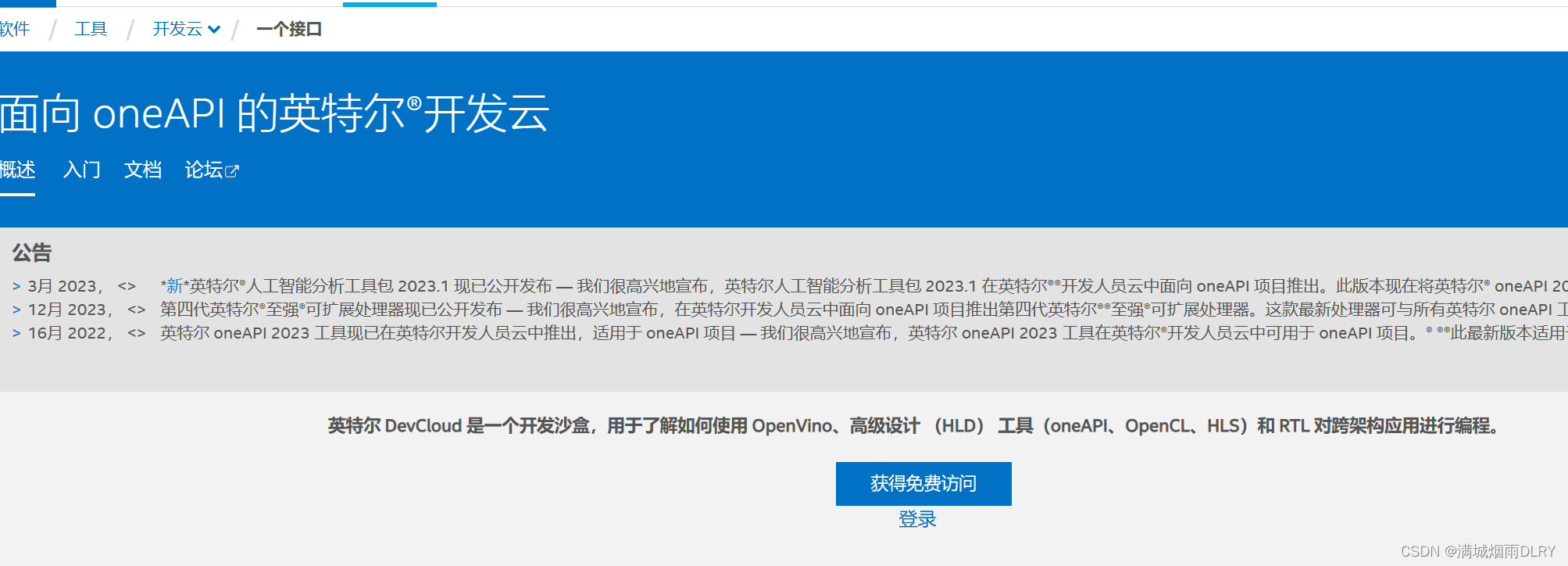 点击:登录进入如下页面
点击:登录进入如下页面
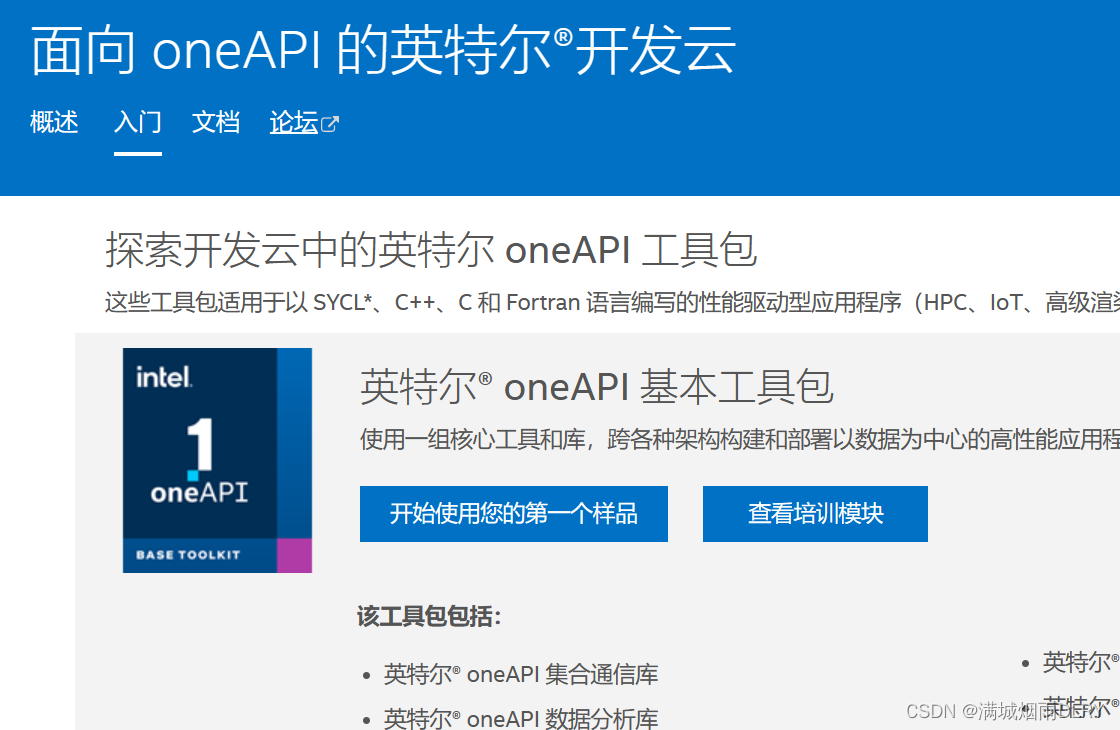
在这个页面的最下面有:
点击启动JupyterLab*进入这个页面:可能要等一会
接下来创建一个笔记本:
内核选择Python3
接下来我们在这里实现hello world:这是一helloworld输出代码,放在刚才创建的笔记本里
%%writefile lab/hello.cpp
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace sycl;
const std::string secret {
"Ifmmp-!xpsme\"\012J(n!tpssz-!Ebwf/!"
"J(n!bgsbje!J!dbo(u!ep!uibu/!.!IBM\01"};
const auto sz = secret.size();
int main() {
queue Q;
char *result = malloc_shared<char>(sz, Q);
std::memcpy(result, secret.data(), sz);
Q.parallel_for(sz, [=] (auto &i) {
result[i] -= 1;
}).wait();
std::cout << result << “\n”;
return 0;
}接下来我们创建一个hello.cpp,我创建在了:oneAPI_Essentials下:

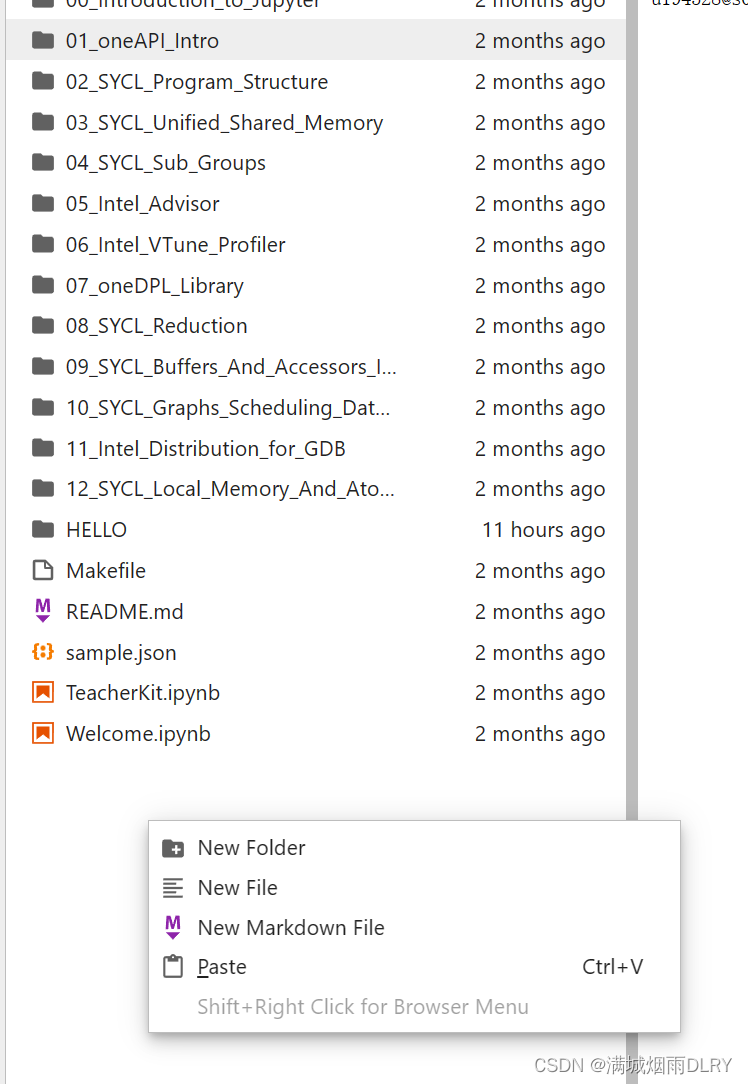
然后右键点击new Folder创建一个HELLO 文件夹,我们在里面再右键,点击new file创建一个hello.cpp

在heiio.cpp里面使用c语言写一个helloworld。
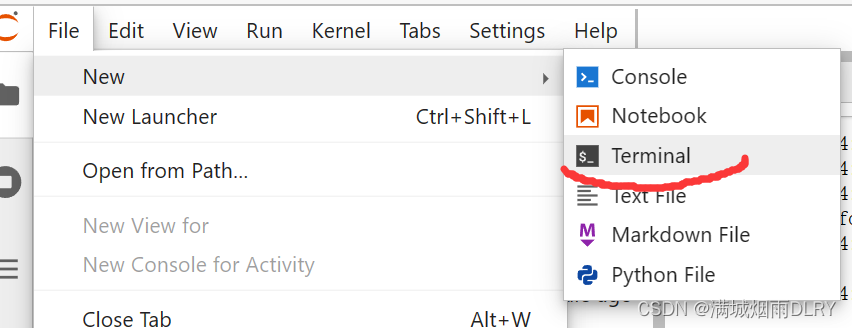
接下来如图创建一个终端,之后我们会在这里进行操作,我们需要使用命令行移动到HELLO文件夹,编译,运行。
命令行操作:
cd oneAPI_Essentials
cd HELLO
icpx -fsycl hello.cpp -o hello//生成可执行文件
./hello//运行结果如下:

三、depc++
创建如图的.cppwenjian
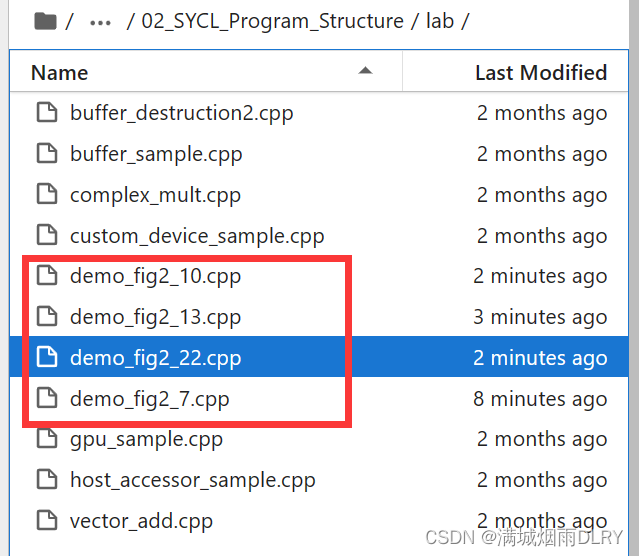
(1)demo_fig2_7.cpp
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace sycl;
int main(){
queue Q;
std::cout << "Select device: "<<
Q.get_device().get_info<info::device::name>() << "\n";
return 0;
}(2)demo_fig2_10.cpp
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace sycl;
int main(){
queue Q ( cpu_selector_v );
std::cout << "Select device: "<<
Q.get_device().get_info<info::device::name>() << "\n";
std::cout <<" -> Device vendor: " <<
Q.get_device().get_info<info::device::vendor>() << "\n";
return 0;
}(3)demo_fig2_13.cpp
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace sycl;
int main(){
queue my_default_queue(default_selector_v);
queue my_accelerator_queue(accelerator_selector_v);
std::cout << "Selected device 1:" << my_default_queue.get_device().get_info<info::device::name>() << "\n";
std::cout << "Selected device 2:" << my_accelerator_queue.get_device().get_info<info::device::name>() << "\n";
return 0;
}(4)demo_fig2_22.cpp
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
using namespace sycl;
int main(){
constexpr int size = 16;
std::array<int,size> data;
buffer B {data};
queue Q{};
std::cout << "Selected device is : " << Q.get_device().get_info<info::device::name>() << "\n";
Q.submit([&](handler& h){
accessor acc{B,h};
h.parallel_for(size,[=](auto&idx){
acc[idx] = idx;
});
});
return 0;
}该代码使用 SYCL(Data Parallel C++)来执行并行计算。SYCL 是一种基于单一源码的编程模型,用于异构系统上的高性能并行计算。它允许开发人员使用单一的 C++ 代码编写并行计算任务,并在支持 SYCL 的设备上进行执行,如 GPU、FPGA 和多核 CPU。
上面代码的各部分用途如下:
- `CL/sycl.hpp`:SYCL 核心头文件。
- `array`:STL 标准库中的数组容器。
创建一个 `std::array` 容器 `data`,用于存储整型数据。 使用 `buffer` 类创建名为 `B` 的缓冲区对象,将 `data` 作为参数传递给缓冲区。缓冲区是 SYCL 中用于在主机和设备之间传递数据的抽象。 创建一个 SYCL `queue` 对象 `Q`,用于管理和提交并行计算任务。 使用 `Q.submit` 函数提交一个计算任务,该任务由一个 lambda 函数表示。lambda 函数接受一个 `handler` 对象 `h` 作为参数,用于配置并行计算任务的执行。 在 lambda 函数中,使用 `accessor` 类创建一个名为 `acc` 的访问器对象,并将缓冲区 `B` 和处理器对象 `h` 作为参数传递给访问器。访问器用于在并行计算中访问和操作缓冲区的元素。使用 `h.parallel_for` 函数指定一个并行计算任务,任务的迭代范围为 `size`,即数组的大小。lambda 函数作为参数传递给 `parallel_for`,并接受一个 `idx` 参数,用于访问迭代的索引。在 lambda 函数中,将索引值赋给访问器 `acc` 中对应的元素,实现并行计算任务。
该程序在 SYCL 中创建了一个并行计算任务,使用并行计算将索引值存储到数组中。此任务将在支持 SYCL 的设备上执行,并利用设备的并行计算能力加速计算。在任务执行期间,数据会在主机和设备之间自动传输,以实现数据的并行处理。
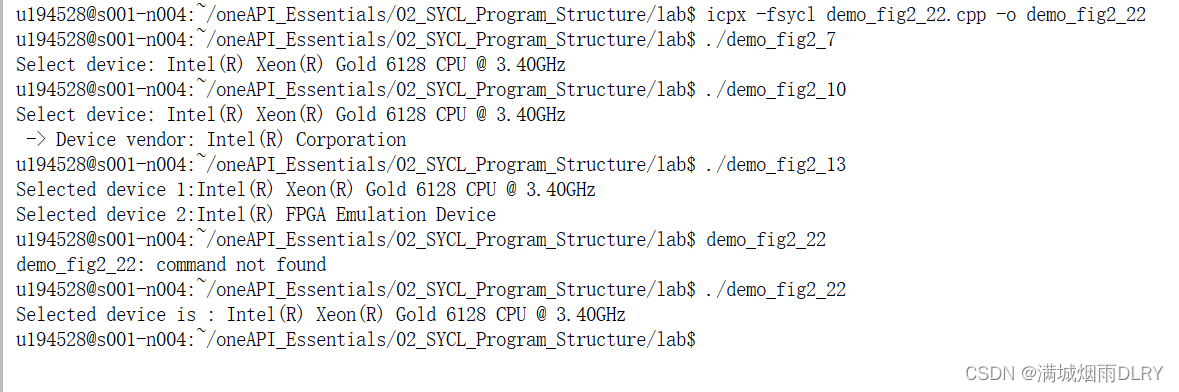
然后如下图输入命令进行编译,文件保存可能会延迟一会

结果:
有一个实验做不了,电脑不匹配。
实验课练习1:
修改程序输入数据的大小,设定M=N=K=2000
代码的目的是通过比较在GPU和CPU上执行矩阵乘法的性能来展示SYCL的用法
实验结果:
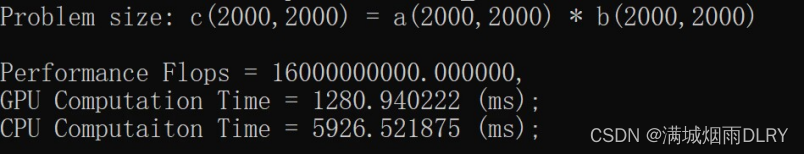
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#define random_float() (rand() / double(RAND_MAX))
using namespace std;
using namespace sycl;
// return execution time
double gpu_kernel(float *A, float *B, float *C, int M, int N, int K, int block_size, sycl::queue &q) {
// define the workgroup size and mapping
auto grid_rows = (M + block_size - 1) / block_size * block_size;
auto grid_cols = (N + block_size - 1) / block_size * block_size;
auto local_ndrange = range<2>(block_size, block_size);
auto global_ndrange = range<2>(grid_rows, grid_cols);
double duration = 0.0f;
auto e = q.submit([&](sycl::handler &h) {
h.parallel_for<class k_name_t>(
sycl::nd_range<2>(global_ndrange, local_ndrange), [=](sycl::nd_item<2> index) {
int row = index.get_global_id(0);
int col = index.get_global_id(1);
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < K; i++) {
sum += A[row * K + i] * B[i * N + col];
}
C[row * N + col] = sum;
});
});
e.wait();
duration += (e.get_profiling_info<info::event_profiling::command_end>() -
e.get_profiling_info<info::event_profiling::command_start>()) /1000.0f/1000.0f;
return(duration);
}
// return execution time
double cpu_kernel(float *cA, float *cB, float *cC, int M, int N, int K) {
double duration = 0.0;
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point s, e;
// Single Thread Computation in CPU
s = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
float sum = 0.0f;
for(int k = 0; k < K; k++) {
sum += cA[i * K + k] * cB[k * N + j];
}
cC[i * N + j] = sum;
}
}
e = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli>(e - s).count();
return(duration);
}
int verify(float *cpu_res, float *gpu_res, int length){
int err = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if( fabs(cpu_res[i] - gpu_res[i]) > 1e-3) {
err++;
printf("\n%lf, %lf", cpu_res[i], gpu_res[i]);
}
}
return(err);
}
int gemm(const int M,
const int N,
const int K,
const int block_size,
const int iterations,
sycl::queue &q) {
cout << "Problem size: c(" << M << "," << N << ") ="
<< " a(" << M << "," << K << ") *"
<< " b(" << K << "," << N << ")\n";
auto A = malloc_shared<float>(M * K, q);
auto B = malloc_shared<float>(K * N, q);
auto C = malloc_shared<float>(M * N, q);
auto C_host = malloc_host<float>(M * N, q);
// init the A/B/C
for(int i=0; i < M * K; i++) {
A[i] = random_float();
}
for(int i=0; i < K * N; i++) {
B[i] = random_float();
}
for(int i=0; i < M * N; i++) {
C[i] = 0.0f;
C_host[i] = 0.0f;
}
double flopsPerMatrixMul
= 2.0 * static_cast<double>(M) * static_cast<double>(N) * static_cast<double>(K);
double duration_gpu = 0.0f;
double duration_cpu = 0.0f;
// GPU compuation and timer
int warmup = 10;
for (int run = 0; run < iterations + warmup; run++) {
float duration = gpu_kernel(A, B, C, M, N, K, block_size, q);
if(run >= warmup) duration_gpu += duration;
}
duration_gpu = duration_gpu / iterations;
// CPU compuation and timer
warmup = 2;
for(int run = 0; run < iterations/2 + warmup; run++) {
float duration = cpu_kernel(A, B, C_host, M, N, K);
if(run >= warmup) duration_cpu += duration;
}
duration_cpu = duration_cpu / iterations/2;
// Compare the resutls of CPU and GPU
int errCode = 0;
errCode = verify(C_host, C, M*N);
if(errCode > 0) printf("\nThere are %d errors\n", errCode);
printf("\nPerformance Flops = %lf, \n"
"GPU Computation Time = %lf (ms); \n"
"CPU Computaiton Time = %lf (ms); \n",
flopsPerMatrixMul, duration_gpu, duration_cpu);
free(A, q);
free(B, q);
free(C, q);
free(C_host, q);
return(errCode);
}
int main() {
auto propList = cl::sycl::property_list {cl::sycl::property::queue::enable_profiling()};
queue my_gpu_queue( cl::sycl::gpu_selector_v , propList);
int errCode = gemm(2000, 2000, 2000, 4, 10, my_gpu_queue);
return(errCode);
}
实验课练习2:
代码定义了一个 random_float() 宏,用于生成0到1之间的随机浮点数。
定义了 tileY 和 tileX 两个常量,表示矩阵乘法中每个工作组的大小。
gpu_kernel() 函数使用SYCL在GPU上执行矩阵乘法。它使用工作组和工作项的概念,并将计算任务分配给不同的工作项。函数接受输入矩阵 A、B 和输出矩阵 C,以及矩阵的尺寸和工作组大小等参数。
cpu_kernel() 函数在CPU上执行矩阵乘法。它使用双重循环遍历矩阵并进行计算。verify() 函数用于验证CPU和GPU计算结果之间的差异。它比较对应位置的元素,并计算不一致的个数。
gemm() 函数是主要的矩阵乘法函数。它初始化输入矩阵 A 和 B,调用 gpu_kernel() 和 cpu_kernel() 分别在GPU和CPU上执行计算,并比较结果。还计算了执行时间和浮点操作数。
main() 函数创建了一个SYCL队列,并调用 gemm() 函数执行矩阵乘法。
代码中的 gemm() 函数在给定的问题规模下执行矩阵乘法,并测量在GPU上执行的时间和在CPU上执行的时间。然后,它比较CPU和GPU计算的结果,并输出性能指标,如计算时间和浮点操作数。最后,main() 函数调用 gemm() 函数以进行示例运行。
这段代码的目的是展示如何使用SYCL编写矩阵乘法,并通过比较GPU和CPU的性能来说明GPU加速的优势。


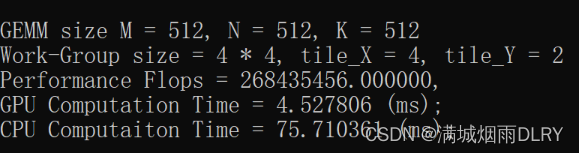

#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <CL/sycl.hpp>
#define random_float() (rand() / double(RAND_MAX))
using namespace std;
using namespace sycl;
#define tileY 2
#define tileX 2
// return execution time
double gpu_kernel(float *A, float *B, float *C,
int M, int N, int K,
int BLOCK, sycl::queue &q) {
// define the workgroup size and mapping
auto grid_rows = M / tileY;
auto grid_cols = N / tileX;
auto local_ndrange = range<2>(BLOCK, BLOCK);
auto global_ndrange = range<2>(grid_rows, grid_cols);
double duration = 0.0f;
auto e = q.submit([&](sycl::handler &h) {
h.parallel_for<class k_name_t>(
sycl::nd_range<2>(global_ndrange, local_ndrange), [=](sycl::nd_item<2> index) {
int row = tileY * index.get_global_id(0);
int col = tileX * index.get_global_id(1);
float sum[tileY][tileX] = {0.0f};
float subA[tileY] = {0.0f};
float subB[tileX] = {0.0f};
// core computation
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
// read data to register
for(int m = 0; m < tileY; m++) {
subA[m] = A[(row + m) * N + k];
}
for(int p = 0; p < tileX; p++) {
subB[p] = B[k * N + p + col];
}
for (int m = 0; m < tileY; m++) {
for (int p = 0; p < tileX; p++) {
sum[m][p] += subA[m] * subB[p];
}
}
} //end of K
// write results back
for (int m = 0; m < tileY; m++) {
for (int p = 0; p < tileX; p++) {
C[(row + m) * N + col + p] = sum[m][p];
}
}
});
});
e.wait();
duration += (e.get_profiling_info<info::event_profiling::command_end>() -
e.get_profiling_info<info::event_profiling::command_start>()) /1000.0f/1000.0f;
return(duration);
}
// return execution time
double cpu_kernel(float *cA, float *cB, float *cC, int M, int N, int K) {
double duration = 0.0;
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point s, e;
// Single Thread Computation in CPU
s = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
float sum = 0.0f;
for(int k = 0; k < K; k++) {
sum += cA[i * K + k] * cB[k * N + j];
}
cC[i * N + j] = sum;
}
}
e = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = std::chrono::duration<float, std::milli>(e - s).count();
return(duration);
}
int verify(float *cpu_res, float *gpu_res, int length){
int err = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if( fabs(cpu_res[i] - gpu_res[i]) > 1e-3) {
err++;
printf("\n%lf, %lf", cpu_res[i], gpu_res[i]);
}
}
return(err);
}
int gemm(const int M,
const int N,
const int K,
const int block_size,
const int iterations,
sycl::queue &q) {
cout << "Problem size: c(" << M << "," << N << ") ="
<< " a(" << M << "," << K << ") *"
<< " b(" << K << "," << N << ")\n";
auto A = malloc_shared<float>(M * K, q);
auto B = malloc_shared<float>(K * N, q);
auto C = malloc_shared<float>(M * N, q);
auto C_host = malloc_host<float>(M * N, q);
// init the A/B/C
for(int i=0; i < M * K; i++) {
A[i] = random_float();
}
for(int i=0; i < K * N; i++) {
B[i] = random_float();
}
for(int i=0; i < M * N; i++) {
C[i] = 0.0f;
C_host[i] = 0.0f;
}
double flopsPerMatrixMul
= 2.0 * static_cast<double>(M) * static_cast<double>(N) * static_cast<double>(K);
double duration_gpu = 0.0f;
double duration_cpu = 0.0f;
// GPU compuation and timer
int warmup = 10;
for (int run = 0; run < iterations + warmup; run++) {
float duration = gpu_kernel(A, B, C, M, N, K, block_size, q);
if(run >= warmup) duration_gpu += duration;
}
duration_gpu = duration_gpu / iterations;
// CPU compuation and timer
warmup = 2;
for(int run = 0; run < iterations/2 + warmup; run++) {
float duration = cpu_kernel(A, B, C_host, M, N, K);
if(run >= warmup) duration_cpu += duration;
}
duration_cpu = duration_cpu / iterations/2;
// Compare the resutls of CPU and GPU
int errCode = 0;
errCode = verify(C_host, C, M*N);
if(errCode > 0) printf("\nThere are %d errors\n", errCode);
printf("\nGEMM size M = %d, N = %d, K = %d", M, N, K);
printf("\nWork-Group size = %d * %d, tile_X = %d, tile_Y = %d", block_size, block_size, tileX, tileY);
printf("\nPerformance Flops = %lf, \n"
"GPU Computation Time = %lf (ms); \n"
"CPU Computaiton Time = %lf (ms); \n",
flopsPerMatrixMul, duration_gpu, duration_cpu);
free(A, q);
free(B, q);
free(C, q);
free(C_host, q);
return(errCode);
}
int main() {
auto propList = cl::sycl::property_list {cl::sycl::property::queue::enable_profiling()};
queue my_gpu_queue( cl::sycl::gpu_selector_v , propList);
int errCode = gemm(512, 512, 512, /* GEMM size, M, N, K */
4, /* workgroup size */
10, /* repeat time */
my_gpu_queue);
return(errCode);
}























 9024
9024











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










