time limit per test
3 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
It costs a long time for CPUs to access data from memory, so most of CPUs have caches where requests for data can be served faster. To be cost-effective and to enable efficient use of data, caches must be relatively small. Therefore, we must use some policies to choose some data wisely and storage them in the cache. We divide the memory into many blocks which have the same size and index them from 1 to 109109, and every block has an unique index. A cache will have a capacity for KK blocks, which means it can storage at most KK blocks simultaneously. A cache hit occurs when the requested block is available in the cache, or we say a cache miss occurs. Now we introduce a LRU (Least Recently Used) placement policy on a fully associative cache.
- If the requested block is available in the cache, a cache hit occurs.
- If not, CPU can only access the block from the memory and write the block into the cache. If cache is not full, append the block into the cache.
- If the cache is full, cache is full, the block which haven't been visited for the longest time in the cache will be replaced by the new block.
An example for cache with capacity of 33 blocks is shown below.
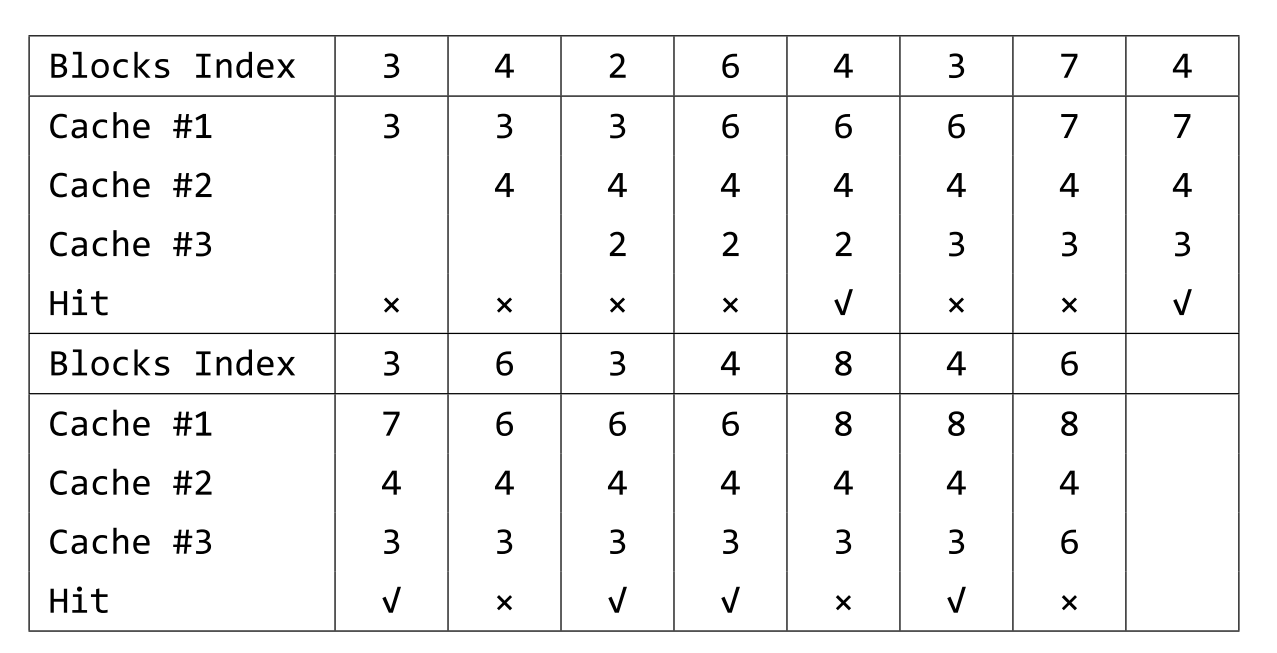
The 8th8th, 4th4th and 3rd3rd are in the cache when the 6th6th block is requested, so a cache miss occurs. At that time, the cache is full, and we must decide the block to be replaced. The most recent request of 8th8th block is the 13th13th request, the most recent request of 4th4th block is the 14th14th request and the most recent request of 3rd3rd block is the 11th11th request. The 3rd3rd block will be replaced by the 6th6th block because the 3rd3rd block hasn't been visited for longest time.
Now the sequence of requested blocks and the capacity of the cache are given, please determine the minimum capacity for the cache in order to ensure at least K requests to hit the cache.
Input
The first line contains two integers NN and K(1≤K≤N≤105)K(1≤K≤N≤105), denoting the length of sequence and the number of requests required to hit the cache. The second line contains NN integers and the ithith integers ai(1≤ai≤109)ai(1≤ai≤109) denoting the index of the block requested by the ithith request.
Output
The output contains only one line. If it is possible to ensure at least KK requests to hit the cache, then output a single integer denoting the smallest capacity in blocks, otherwise output "cbddl"(without quotes).
Examples
input
Copy
15 6 3 4 2 6 4 3 7 4 3 6 3 4 8 4 6
output
Copy
3
input
Copy
15 5 3 4 2 6 4 3 7 4 3 6 3 4 8 4 6
output
Copy
3
input
Copy
15 10 3 4 2 6 4 3 7 4 3 6 3 4 8 4 6
output
Copy
cbddl
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
unordered_map<int, int> ump, w;// 对于大数的桶直接用它
int n, k;
int a[N];
struct node
{
int value;
int time;
friend bool operator < (node x, node y)// 对优先队列的自定义排序,我只会在结构体中排,其他不会,背了就完事
{
return x.time > y.time;// time指的是代表的是优先级,越小越要被替换,还有这个优先队列的排序要和sort里的规则相反,不知道为什么,到时候再学
}
};
int check(int capacity)
{
w.clear();
set<int> s;
priority_queue<node> heap;// log(n)的复杂度
int ans = 0;
int time = 0;
node x;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
if (s.count(a[i]) == 0)// set里面没有找到,那就要进行插入操作
{
if (s.size() < capacity)
{
time++;
s.insert(a[i]);
x.time = time, x.value = a[i];
heap.push(x);
}
else if (s.size() == capacity)
{
node y = heap.top();
while (w[y.value])// 这一步很重要,利用桶的思想进行删除,典型的空间换时间
{
w[y.value]--;
heap.pop();
y = heap.top();
}
heap.pop();
s.erase(y.value);
time++;
s.insert(a[i]);
x.time = time, x.value = a[i];
heap.push(x);
}
}
else if (s.count(a[i]) == 1)
{
time++;
w[a[i]]++;// 找到了直接上桶,为的是要防止插入的时候影响其他值
x.time = time, x.value = a[i];
heap.push(x);
ans++;
}
}
if (ans >= k)// 说明符合条件的点比k多
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
IOS; cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
int sum = 0;
int different = 0;// 代表到底有几个数是不同的,确定二分区间
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
if (ump[num] == 0)
different++;
if (ump[num] != 0)
sum++;
ump[num]++;
a[i] = num;
}
if (sum < k)// 假设容量最大化都无法容纳完,那么肯定是不行的
cout << "cbddl" << endl;
else
{
int l = 1, r = different, mid;
while (l <= r)
{
mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (check(mid))
r = mid - 1;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
}
return 0;
}





















 280
280











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








