栈和队列理论基础
STL(standard template library标准模板库)
三个最为普遍的STL版本:
-
HP STL 其他版本的C++ STL,一般是以HP STL为蓝本实现出来的,HP STL是C++ STL的第一个实现版本,而且开放源代码。
-
P.J.Plauger STL 由P.J.Plauger参照HP STL实现出来的,被Visual C++编译器所采用,不是开源的。
-
SGI STL 由Silicon Graphics Computer Systems公司参照HP STL实现,被Linux的C++编译器GCC所采用,SGI STL是开源软件,源码可读性甚高。
STL六大组件简介
STL提供了六大组件,彼此之间可以组合套用,这六大组件分别是:容器、算法、迭代器、仿函数、适配器(配接器)、空间配置器。
容器:各种数据结构,如vector、list、deque、set、map等,用来存放数据,从实现角度来看,STL容器是一种class template。
算法:各种常用的算法,如sort、find、copy、for_each。从实现的角度来看,STL算法是一种function tempalte.
迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂,共有五种类型,从实现角度来看,迭代器是一种将operator* , operator-> , operator++,operator–等指针相关操作予以重载的class template. 所有STL容器都附带有自己专属的迭代器,只有容器的设计者才知道如何遍历自己的元素。原生指针(native pointer)也是一种迭代器。
仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略。从实现角度来看,仿函数是一种重载了operator()的class 或者class template
适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西。如queue、stack
空间配置器:负责空间的配置与管理。从实现角度看,配置器是一个实现了动态空间配置、空间管理、空间释放的class tempalte.
STL六大组件的交互关系,容器通过空间配置器取得数据存储空间,算法通过迭代器存储容器中的内容,仿函数可以协助算法完成不同的策略的变化,适配器可以修饰仿函数。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42322103/article/details/99685797
stack(container adapter)
栈提供push 和 pop 等等接口,所有元素必须符合先进后出规则,所以栈不提供走访功能,也不提供迭代器(iterator)。 不像是set 或者map 提供迭代器iterator来遍历所有元素。
栈是以底层容器完成其所有的工作,对外提供统一的接口,底层容器是可插拔的(也就是说我们可以控制使用哪种容器来实现栈的功能)。
所以STL中栈往往不被归类为容器,而被归类为container adapter(容器适配器)。
那么问题来了,STL 中栈是用什么容器实现的?
从下图中可以看出,栈的内部结构,栈的底层实现可以是vector,deque,list 都是可以的, 主要就是数组和链表的底层实现。
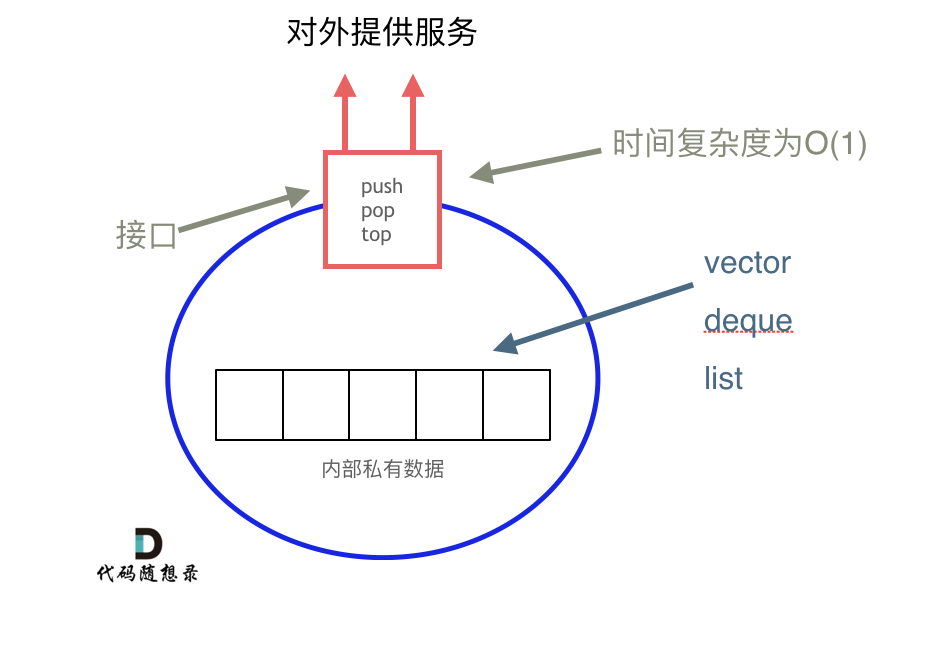
我们常用的SGI STL,如果没有指定底层实现的话,默认是以deque为缺省情况下栈的底层结构。
deque是一个双向队列,只要封住一段,只开通另一端就可以实现栈的逻辑了。
Queue(container adapter)
SGI STL中 队列底层实现缺省情况下一样使用deque实现的。
https://cplusplus.com/reference/stack/stack/
232. 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop()从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek()返回队列开头的元素boolean empty()如果队列为空,返回true;否则,返回false
思路:自己想的思路就是直接把stIn当成队列,需要pop或peek时借用来一个栈来找到队列开头
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
int pop() {
while(!stIn.empty()){
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
int res=stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
while(!stOut.empty()){
stIn.push(stOut.top());
stOut.pop();
}
return res;
}
int peek() {
while(!stIn.empty()){
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
int res=stOut.top();
while(!stOut.empty()){
stIn.push(stOut.top());
stOut.pop();
}
return res;
}
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/觉得下面这个解法更好一点,少掉了把stOut移回stIn的操作,同样能实现队列。且调用已实现的函数方便使用。

class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(stOut.empty()){
while(!stIn.empty()){
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
}
int res=stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return res;
}
int peek() {
int res=this->pop();
stOut.push(res);
return res;
}
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty()&&stOut.empty();
}
};- 时间复杂度: push和empty为O(1), pop和peek为O(n)
- 空间复杂度: O(n)
225. 用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x)将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop()移除并返回栈顶元素。int top()返回栈顶元素。boolean empty()如果栈是空的,返回true;否则,返回false。
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que1;
queue<int> que2;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
que2.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(que2.empty()){
queue<int> tmp=que1;
que1=que2;
que2=tmp;
}
while(que2.size()>1){
que1.push(que2.front());
que2.pop();
}
int res=que2.front();
que2.pop();
return res;
}
int top() {
int res=this->pop();
this->push(res);
return res;
}
bool empty() {
return que1.empty()&&que2.empty();
}
};进阶:使用一个队列实现
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
MyStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
int pop() {
int size=que.size()-1;
while(size--){
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int res=que.front();
que.pop();
return res;
}
int top() {
// int res=this->pop();
// this->push(res);
// return res;
return que.back();
}
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};





















 413
413











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








