1 数字三角形
1.1 题目
写一个程序来查找从最高点到底部任意处结束的路径,使路径经过数字的和最大。每一步可以走到左下方的点也可以到达右下方的点。
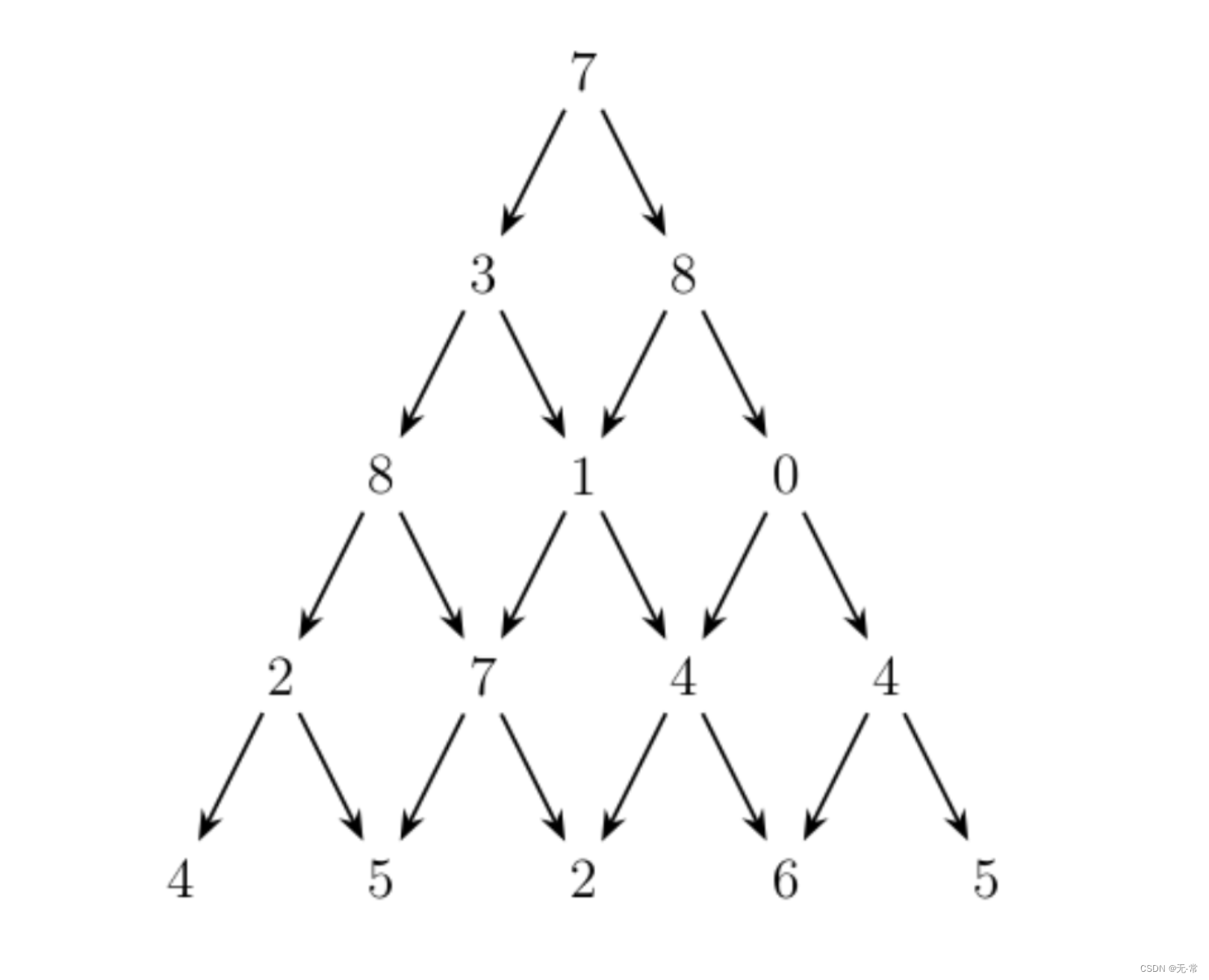
在上面的样例中,从 7→3→8→7→57→3→8→7→5 的路径产生了最大权值。
输入格式
第一个行一个正整数 N ,表示行的数目。
后面每行为这个数字金字塔特定行包含的整数。
输出格式
单独的一行,包含那个可能得到的最大的和。
1.2 代码
public static int N;
public static int d[][];
public static Scanner scanner;
public static void main(String[] args) {
scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scanner.nextInt();
d = new int[N + 2][N + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(d[i], -0x3f3f3f);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
d[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
d[i][j] = Math.max(d[i - 1][j], d[i - 1][j - 1]) + d[i][j];
}
}
int res = -0x3f3f3f;
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, d[N][i]);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
1.2.1 时空复杂度
1.2.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
1.2.1.2空间复杂度: n^2
2 数字三角形变形
2.1 题目
从三角形的顶部到底部有很多条不同的路径。对于每条路径,把路径上面的数加起来可以得到一个和,你的任务就是找到最大的和。路径上的每一步只能从一个数走到下一层和它最近的左边的那个数或者右 边的那个数。此外,向左下走的次数与向右下走的次数相差不能超过 1。
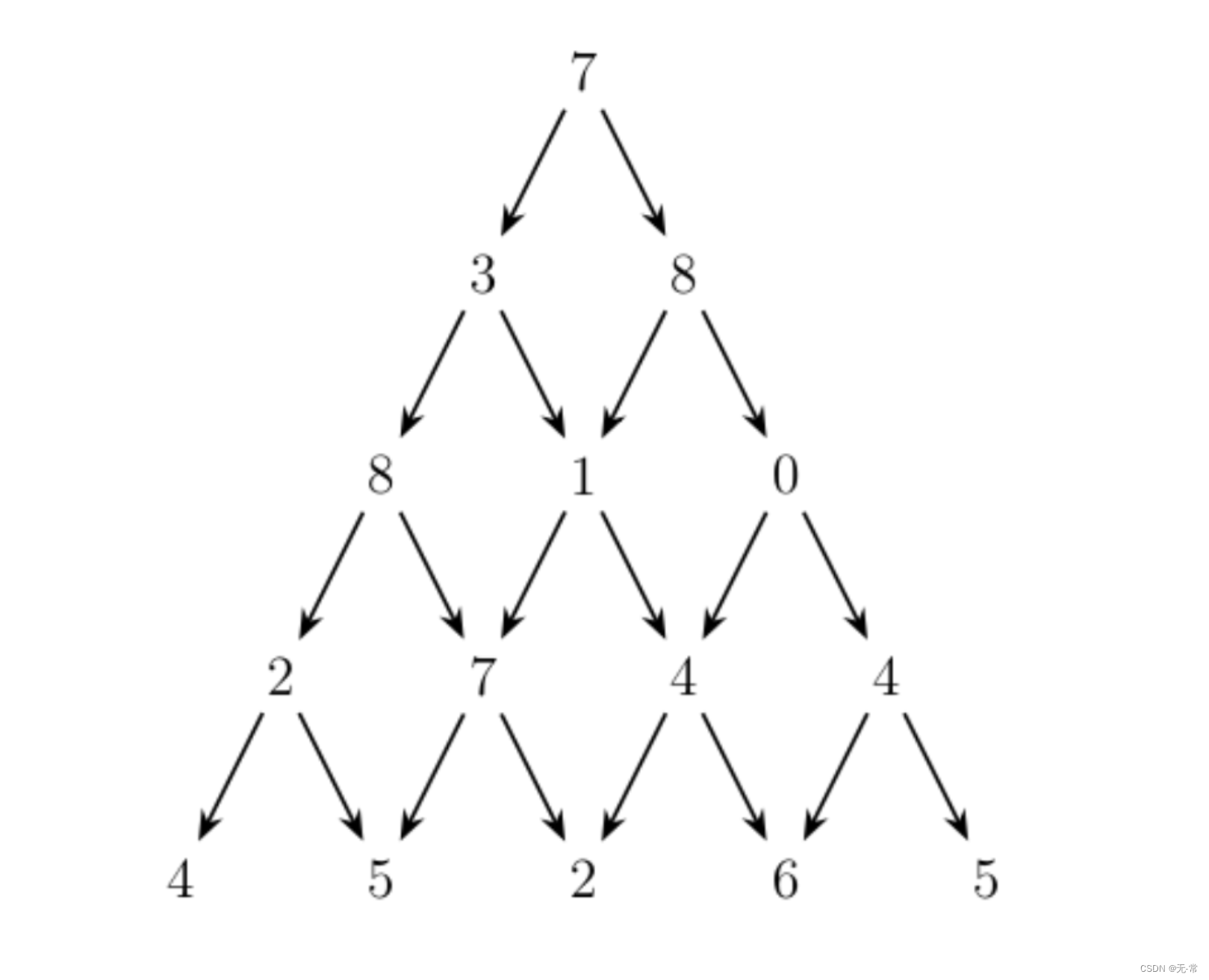
输入描述
输入的第一行包含一个整数,下面的 N 行给出数字三角形。数字三角形上的数都是 0 至 100 之间的整数。
输入描述
输出最大值
2.2 代码
public static int N;
public static int d[][];
public static Scanner scanner;
public static void main(String[] args) {
scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scanner.nextInt();
d = new int[N + 2][N + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) {
Arrays.fill(d[i], -0x3f3f3f);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
d[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
d[i][j] = Math.max(d[i - 1][j], d[i - 1][j - 1]) + d[i][j];
}
}
if (N % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println(Math.max(d[N][N / 2], d[N][N / 2 + 1]));
} else {
System.out.println(d[N][N / 2 + 1]);
}
}
2.2.1 时空复杂度
2.2.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
2.2.1.2空间复杂度: n^2
3 最大公共子序列
3.1 题目
给定一个长度为N的数组A,请你找到最长上升子序列。
2.1 不要路径代码
public static int arr[];
public static int dp[];
public static int path[];
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
arr = new int[n];
dp = new int[n + 10];
path = new int[n + 10];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
Arrays.fill(dp, 0x3f3f3f);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
path[i] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && dp[i] < dp[j] + 1) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
path[i] = j;
}
res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (dp[k] < dp[i]) {
k = i;
}
}
System.out.println("最大长度为: " + dp[k]);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < res; i++) {
stack.add(arr[k]);
k = path[k];
}
System.out.print("最长上升子序列为: ");
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
}
3.2.1 时空复杂度
3.2.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
3.2.1.2空间复杂度: n
3.3 要路径代码
public static int arr[];
public static int dp[];
public static int path[];
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
arr = new int[n];
dp = new int[n + 10];
path = new int[n + 10];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
Arrays.fill(dp, 0x3f3f3f);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
path[i] = i;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j] && dp[i] < dp[j] + 1) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
path[i] = j;
}
res = Math.max(res, dp[i]);
}
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (dp[k] < dp[i]) {
k = i;
}
}
System.out.println("最大长度为: " + dp[k]);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < res; i++) {
stack.add(arr[k]);
k = path[k];
}
System.out.print("最长上升子序列为: ");
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
}
3.3.1 时空复杂度
3.3.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
3.3.1.2空间复杂度: n
4 最长公共子串
4.1 题目
求两个字符串的最长公共子串
4.2 代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String s1 = scanner.nextLine();
String s2 = scanner.nextLine();
int[][] dp = new int[s1.length() + 1][s2.length() + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < s2.length(); j++) {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = Math.max(dp[i][j + 1], dp[i + 1][j]);
if (s1.charAt(i) == s2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i + 1][j + 1] = dp[i][j] + 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[s1.length()-1][s2.length()-1]);
}
4.2.1 时空复杂度
4.2.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
4.2.1.2空间复杂度: n^2
5 合并最小代价
5.1题目
给出n个数,每次可以合并两个数,代价是两个数的和,求最小代价
5.2代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n + 10];
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
priorityQueue.add(scanner.nextInt());
}
while (priorityQueue.size() > 1) {
priorityQueue.add(priorityQueue.poll() + priorityQueue.poll());
}
System.out.println("max = " + priorityQueue.poll());
}
5.2.1 时空复杂度
5.2.1.1时间复杂度: n^2
5.2.1.2空间复杂度: n
6 合并石子
6.1 题目
每次可以合并相邻的石子,但合并是有代价的,合并相邻两堆石子需要相邻两堆石子之和的代价,求全部合并为一堆的最小代价
6.2 代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int[] s = new int[n + 10];
int[][] dp = new int[n + 10][n + 10];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
s[i] = scanner.nextInt();
s[i] += s[i - 1];
}
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len++) {
for (int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n; i++) {
int l = i;
int r = i + len - 1;
dp[l][r] = 0x3f3f3f;
for (int k = l; k < r; k++) {
dp[l][r]=Math.min(dp[l][k]+dp[k+1][r]+s[r]-s[l-1],dp[l][r]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[1][n]);
}






















 455
455

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








