一、堆的概念及其介绍
堆(Heap)是计算机科学中一类特殊的数据结构的统称,堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵完全二叉树的数组对象。如果有一个关键码的集合K = { , , ,…, },把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式存储 在一个一维数组中,并满足: <= 且 <= ( >= 且 >= ) i = 0,1, 2…,则称为小堆(或大堆)。将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
堆满足下列性质:
-
堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值。
- 每个结点的值都大于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆
- 每个结点的值都小于或等于具左石孩子结点 的值,称为小顶堆。
-
堆总是一棵完全二叉树。
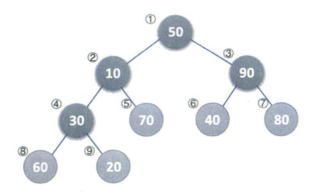
结构图示

二、如何使用无序序列构建一个堆?
如果有一组无序的数组,{50,10,90,30,70,40,80,60,20},我们将它抽象为逻辑结构,z这时怎么将无序序列变成一个大堆或者小堆呢?
向上调整法
从下标为1的位置开始,也就是图中10的位置,依次进行向上调整,每次将更小的换到上面,
题目中有个小问题,如何找到父节点?
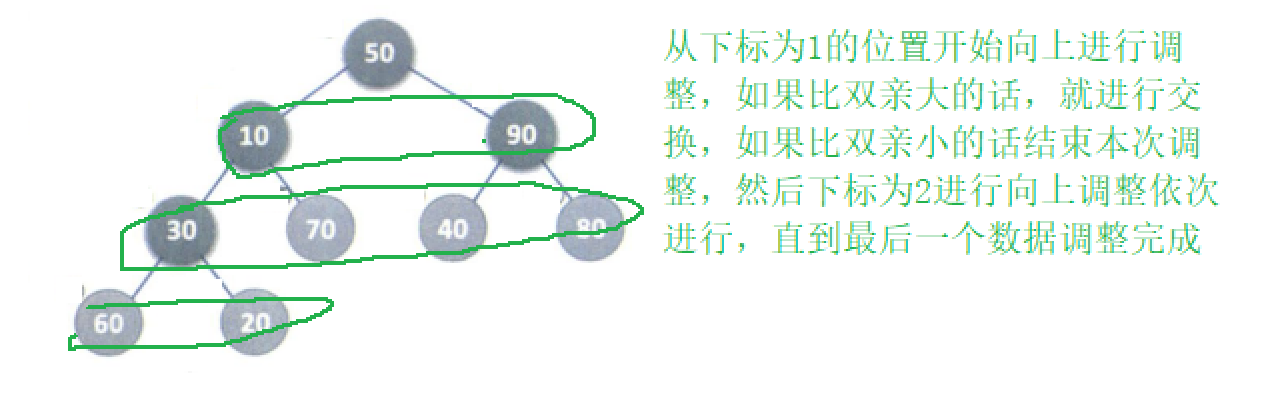
- 父节点 = (子结点-1)/2
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int HeapDataType;
void swap(HeapDataType* a, HeapDataType* b) //交换
{
HeapDataType temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void Adjustup(HeapDataType* arr, int child) //向上调整函数
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void CreateHeap(int* a, int n) //使用无序数组创建堆
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
Adjustup(a, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 50,10,90,30,70,40,80,60,20 };
CreateHeap(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
}
向下调整法(更优)
从非叶节点的最后一个数据的下标开始,每次取出孩子中较大或较小的数(看是大堆还是小堆)向下进行调整,由于每多一层,下层是上层的二倍,这种办法直接可以省略掉最后一层,也可以达到建堆的目的,所以这种办法为更优的办法。
由于需要向下调整,所以这种办法需要找到子节点,我们已经知道父结点的运算了,子结点就是父节点的逆运算。
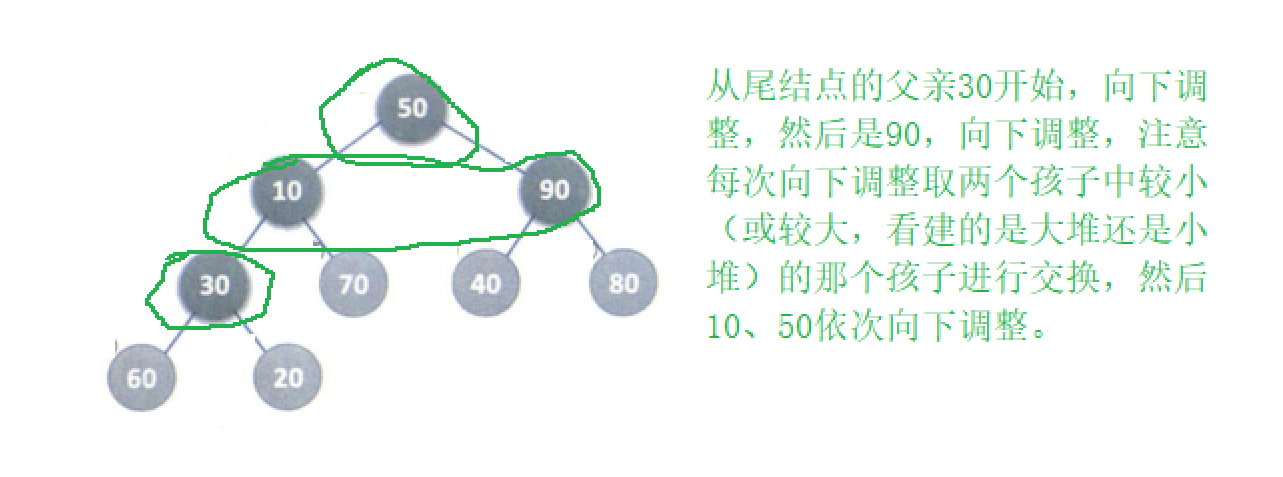
- 子节点:父节点*2+1
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int HeapDataType;
void swap(HeapDataType* a, HeapDataType* b) //交换
{
HeapDataType temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void AdjustDown(HeapDataType* arr, int n, int parent) //向下调整
{
assert(arr);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < n)
{
if (child<n - 1 && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
child = child + 1;
}
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
}
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
}
void CreateHeap(int* a, int n) //使用无序数组创建堆
{
for (int i = (n - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 50,10,90,30,70,40,80,60,20 };
CreateHeap(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
}
三、C语言实现堆的基本操作
结构体创建与销毁
顺序存储方式实现堆采用顺序表进行存储。
typedef int HeapDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
HeapDataType* arr;
int size; //当前大小
int capacity; //当前容量上限
}Heap;
void HeapDestroy(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
free(ph->arr);
ph->arr = NULL;
ph->capacity = 0;
ph->size = 0;
free(ph); //由于顺序表空间是申请堆空间的内存所以需要进行释放
}
获取堆顶数据与个数及堆的判空
HeapDataType HeapTop(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->arr[0];
}
int HeapSize(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->size;
}
int HeapEmpty(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->size == 0;
}
堆的插入与删除
插入时需要注意空间不足问题,如果空间不足,需要进行二次开辟空间,插入时直接插入到堆尾,然后利用上面写好的向上调整函数。
删除时删掉堆顶数据,将堆底数据拿到堆顶,在进行向下调整,即可保证堆性质不变,依然保持原有的大/小堆。
void HeapPush(Heap* ph, HeapDataType x)
{
assert(ph);
if (ph->size == ph->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ph->capacity == 0 ? 5 : ph->capacity * 2;
HeapDataType* temp = (HeapDataType*)realloc(ph->arr, sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc: error");
return;
}
ph->arr = temp;
ph->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ph->arr[ph->size] = x;
Adjustup(ph->arr, ph->size - 1);
ph->size++;
}
void HeapPop(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
assert(ph->arr);
assert(!HeapEmpty(ph));
swap(&ph->arr[ph->size - 1], &ph->arr[0]);
ph->size--;
AdjustDown(ph->arr, ph->size, 0);
}
源代码分享
//heap.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int HeapDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{
int* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}Heap;
void HeapCreate(Heap* ph);
void HeapDestroy(Heap* ph);
void swap(HeapDataType* a, HeapDataType* b);
void Adjustup(HeapDataType* arr, int child);
void AdjustDown(HeapDataType* arr, int n, int parent);
void HeapPush(Heap* ph, HeapDataType x);
void HeapPop(Heap* ph);
HeapDataType HeapTop(Heap* ph);
int HeapSize(Heap* ph);
int HeapEmpty(Heap* ph);
//Heap.c
#include "Heap.h"
void HeapCreate(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
ph->arr = NULL;
ph->capacity = 0;
ph->size = 0;
}
void HeapDestroy(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
free(ph->arr);
ph->arr = NULL;
ph->capacity = 0;
ph->size = 0;
free(ph);
}
void swap(HeapDataType* a, HeapDataType* b)
{
HeapDataType temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void Adjustup(HeapDataType* arr, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustDown(HeapDataType* arr, int n, int parent)
{
assert(arr);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while(child<n)
{
if (child<n-1&&arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
child = child + 1;
}
if (arr[child] < arr[parent])
{
swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);
}
parent = child;
child = child * 2 + 1;
}
}
void HeapPush(Heap* ph, HeapDataType x)
{
assert(ph);
if (ph->size == ph->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ph->capacity == 0 ? 5 : ph->capacity * 2;
HeapDataType* temp = (HeapDataType*)realloc(ph->arr, sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc: error");
return;
}
ph->arr = temp;
ph->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ph->arr[ph->size] = x;
Adjustup(ph->arr, ph->size - 1);
ph->size++;
}
void HeapPop(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
assert(ph->arr);
assert(!HeapEmpty(ph));
swap(&ph->arr[ph->size - 1], &ph->arr[0]);
ph->size--;
AdjustDown(ph->arr, ph->size, 0);
}
HeapDataType HeapTop(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->arr[0];
}
int HeapSize(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->size;
}
int HeapEmpty(Heap* ph)
{
assert(ph);
return ph->size == 0;
}
//test.c
void CreateHeap(int* a, int n) //使用向上调整
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
Adjustup(a, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
}
void CreateHeap(int* a, int n) //使用向下调整
{
for (int i = (n - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 50,10,90,30,70,40,80,60,20 };
CreateHeap(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
}
✨本文收录于数据结构理解与实现
当你喜欢一篇文章时,点赞、收藏和关注是最好的支持方式。如果你喜欢我的文章,请不要吝啬你的支持,点赞👍、收藏⭐和关注都是对我最好的鼓励。感谢你们的支持!






















 3729
3729

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








