注:数据结构与算法各大讲师的讲解或许各有千秋,但本质基本上是一样的,这篇博客取自比特的数据结构算法课程。之前我们出的一篇数据结构的博客是小甲鱼的,这一篇是对前文的补充与升级
前言:学习之途路漫漫,我们必须怀有“知命不惧,日日自新”的精神才能越走越远,大学生活的安逸使得很多人迷失了自我,这是一种无形的堕落。做学问需要的是一种态度,一种热爱的态度,而不是为了学习而去学习。今天,我们终于正式步入了数据结构与算法的大关,数据结构与算法初阶是由C语言实现的,进阶是由C++实现的。我们相信只要每天坚持下去,总有一天会成为我们想成为的模样。
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用 的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的, 线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。案例:蔬菜分为绿叶类、瓜类、菌菇类。线性表指的是具有部分相同特性的一类数据结构的集合
顺序表
顺序表的底层结构是数组,对数组的封装,实现了常用的增删改查等接口
由于是数组封装,所以在物理结构上是连续的
静态顺序表
概念:使用定长数组存储元素
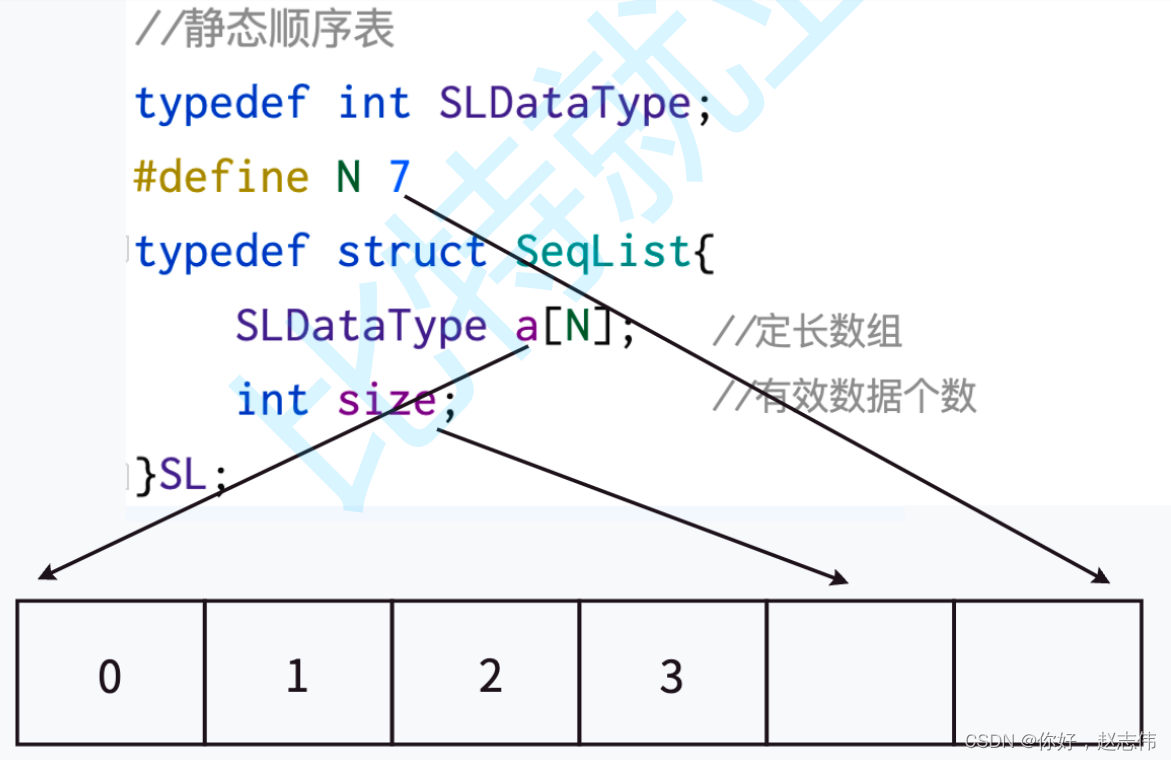
静态顺序表缺陷:空间给少了不够用,给多了造成空间浪费
注:具体的实现可以看我们上一篇博客
动态顺序表
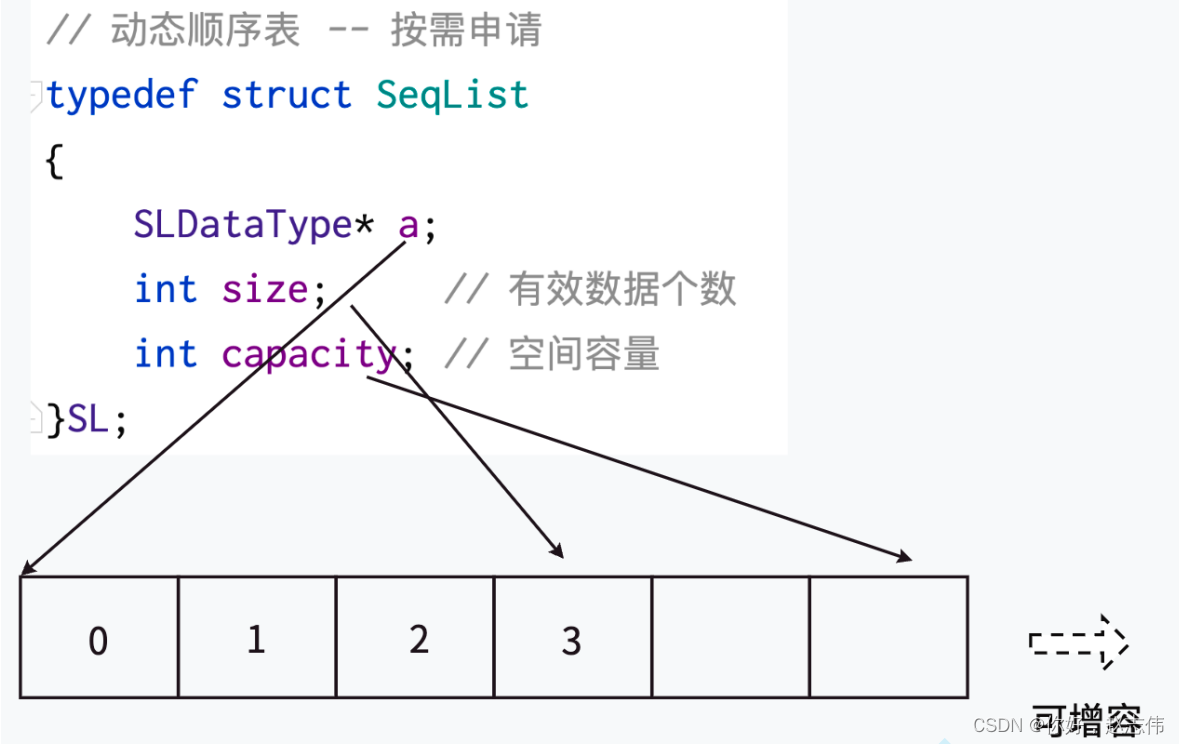
具体模拟与实现如下:
SeqList.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//动态顺序表
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size; //顺序表中有效的数据个数
int capacity; //顺序表当前的空间大小
}SL;
//typedef struct SeqList SL;
//对顺序表进行初始化与销毁
void SLInit(SL* ps);//初始化
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);//销毁
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//判断空间是否充足,不足则增加或者扩大
//头部/尾部 插入/删除
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//头删
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);//在指定的位置之前插入数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//删除指定位置的数据
bool SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//查找顺序表中某个值
void SLPrint(SL* ps);//打印
bool SLIsEmpty(SL* ps);//判断有效长度是否为0SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁顺序表
void SLDestroy(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
if(ps->a)
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//判断空间是否充足,不足则增加或者扩大
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) {
if (ps->size == ps->capacity) {
//空间不足以再额外插入一个数据
//扩容
int newCapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapcity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail!\n");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapcity;
}
}
//尾插(从尾部插入一个数据)
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
//assert(ps != NULL);
//暴力的方式
assert(ps);
//柔和方式
//if (ps == NULL) {
// return;
//}
//1)空间足够,直接尾插
//2)空间不够,扩容
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//直接插入数据
ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
//头插(从头部插入一个数据)
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
//判断空间是否足够,不够则扩容
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//空间足够,历史数据后移一位
for (size_t i = ps->size; i > 0 ; i--)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删(从尾部删除一个数据)
void SLPopBack(SL* ps) {
//判断顺序表是否为空
assert(ps);
assert(!SLIsEmpty(ps));//断言有效长度是否为0
ps->size--;
}
//头删(从头部删除一个数据)
void SLPopFront(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
assert(!SLIsEmpty(ps));//断言有效长度是否为0
//让后面的数据往前挪动一位
for (size_t i = 0; i < ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//在指定的位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//扩容
//for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
//{
//
// ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];//pos->a[pos+1] = ps->a[pos]
//}
for (int i = ps->size-1; i > pos-1 ; i--)
{
ps->a[i + 1] = ps->a[i];//ps->a[pos+1] = ps->a[pos]
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//删除指定位置的数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) {
assert(ps);
assert(!SLIsEmpty(ps));
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size-1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];//ps->a[ps->size-2] = ps->a[ps->size-1]
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找顺序表中某个值
bool SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x) {
//找到了
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
for (size_t i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//判断有效长度是否为0
bool SLIsEmpty(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->size == 0;
}text.c
#include"SeqList.h"
void menu() {
printf("************************动态顺序表********************************\n");
printf("******1、尾插 2、头插**********************\n");
printf("******3、尾删 4、头删**********************\n");
printf("******5、在指定的位置之前插入数据 6、删除指定位置的数据********\n");
printf("******7、查找顺序表中某个值 8、打印**********************\n");
printf("******************************************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
SL s1;
int op;
SLDataType x; int pos;
SLInit(&s1);
do {
menu();
printf("请选择您的操作:\n");
scanf("%d", &op);
switch (op)
{
case 1:
printf("请输入插入的数据\n");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPushBack(&s1, x);
break;
case 2:
printf("请输入插入的数据\n");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLPushFront(&s1,x);
break;
case 3:
SLPopBack(&s1);
break;
case 4:
SLPopFront(&s1);
break;
case 5:
printf("请输入插入的数据\n");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("请输入指定的位置\n");
scanf("%d", &pos);
SLInsert(&s1, pos, x);
break;
case 6:
printf("请输入指定的位置\n");
scanf("%d", &pos);
SLErase(&s1, pos);
break;
case 7:
printf("请输入查找的值\n");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLFind(&s1, x);
if (SLFind(&s1, x) == 1)
printf("找到了\n");
else
printf("没找到\n");
break;
case 8:
SLPrint(&s1);
break;
case 0:
printf("goodbye~\n");
break;
default:
printf("您的输入有误,请重新输入\n");
break;
}
} while (op != 0);
SLDestroy(&s1);
return 0;
}通讯录的模拟与实现
结合静态顺序表和动态顺序表进而实现模拟
SeqList.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//动态顺序表
typedef struct ContactInfo SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size; //顺序表中有效的数据个数
int capacity; //顺序表当前的空间大小
}SL;
//typedef struct SeqList SL;
//对顺序表进行初始化与销毁
void SLInit(SL* ps);//初始化
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);//销毁
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//删除指定位置的数据
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//判断空间是否充足,不足则增加或者扩大
bool SLIsEmpty(SL* ps);//判断有效长度是否为0
Contact.h
#pragma once
//创建保存联系人数据的结构
#define NAME_MAX 100
#define SEX_MAX 10
#define TEL_MAX 15
#define ADDR_MAX 100
typedef struct ContactInfo
{
char name[NAME_MAX];//使用定长数组还是动态数组呢?,字符数组,数组名就是数组的地址
char sex[SEX_MAX];
int age;
char tel[TEL_MAX];
char addr[ADDR_MAX];
}CInfo;
//通讯录底层是顺序表来实现
typedef struct SeqList contact;
//通讯录的初始化和销毁
void ContactInit(contact* pcon);
void ContactDestroy(contact* pcon);
//添加联系人
void ContactAdd(contact* pcon);
//删除联系人
void ContactDel(contact* pcon);
//修改联系人
void ContactModify(contact* pcon);
//查看通讯录
void ContactShow(contact* pcon);
//查找指定联系人
void ContactFind(contact* pcon);
SeqList.c
#include"SeqList.h"
#include"Contact.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁顺序表
void SLDestroy(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
if (ps->a)
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//判断空间是否充足,不足则增加或者扩大
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps) {
if (ps->size == ps->capacity) {
//空间不足以再额外插入一个数据
//扩容
int newCapcity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapcity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL) {
perror("realloc fail!\n");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapcity;
}
}
//尾插(从尾部插入一个数据)
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x) {
//assert(ps != NULL);
//暴力的方式
assert(ps);
//柔和方式
//if (ps == NULL) {
// return;
//}
//1)空间足够,直接尾插
//2)空间不够,扩容
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//直接插入数据
ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
//删除指定位置的数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos) {
assert(ps);
assert(!SLIsEmpty(ps));
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];//ps->a[ps->size-2] = ps->a[ps->size-1]
}
ps->size--;
}
//判断有效长度是否为0
bool SLIsEmpty(SL* ps) {
assert(ps);
return ps->size == 0;
}Contact.c
#include"Contact.h"
#include"SeqList.h"
#include <string.h>
void ContactInit(contact* pcon) {
SLInit(pcon);
}
void ContactDestroy(contact* pcon) {
SLDestroy(pcon);
}
//添加联系人
void ContactAdd(contact* pcon) {
//接下来要获取的信息都是CInfo结构体里要求的数据
CInfo info;
printf("请输入联系人姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", info.name);
printf("请输入联系人的性别:\n");
scanf("%s", info.sex);
printf("请输入联系人的年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &info.age);
printf("请输入联系人的电话:\n");
scanf("%s", info.tel);
printf("请输入联系人的住址:\n");
scanf("%s", info.addr);
//联系人数据都获取到了,并保存到了结构体info中
//往通讯录(顺序表)中插入数据
SLPushBack(pcon, info);
}
//查找联系人
int FindByName(contact* pcon, char name[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < pcon->size; i++)
{
if (strcmp(pcon->a[i].name, name) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//删除联系人
void ContactDel(contact* pcon) {
//直接强制要求用户使用联系人名称来查找
printf("请输入要删除的用户名称:\n");
char name[NAME_MAX];
scanf("%s", name);
int findidex = FindByName(pcon, name);
if (findidex < 0) {
printf("要删除的联系人不存在!\n");
return;
}
//找到了,要删除findid




 此博客基于比特的数据结构算法课程,介绍线性表和链表知识。线性表包含顺序表,链表有单链表、双向循环链表等。还给出多个相关例题,如删除链表节点、反转链表等,并对快慢指针在链表环问题中的应用进行讨论和公式推导。
此博客基于比特的数据结构算法课程,介绍线性表和链表知识。线性表包含顺序表,链表有单链表、双向循环链表等。还给出多个相关例题,如删除链表节点、反转链表等,并对快慢指针在链表环问题中的应用进行讨论和公式推导。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 7672
7672

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










