Let's define 𝑓(𝑥)f(x) for a positive integer 𝑥x as the length of the base-10 representation of 𝑥x without leading zeros. I like to call it a digital logarithm. Similar to a digital root, if you are familiar with that.
You are given two arrays 𝑎a and 𝑏b, each containing 𝑛n positive integers. In one operation, you do the following:
- pick some integer i from 1 to n;
- assign eitherf(ai) to 𝑎𝑖ai or 𝑓(𝑏𝑖)f(bi) to 𝑏𝑖bi.
Two arrays are considered similar to each other if you can rearrange the elements in both of them, so that they are equal (e. g. 𝑎𝑖=𝑏𝑖ai=bi for all 𝑖i from 11 to 𝑛n).
What's the smallest number of operations required to make 𝑎a and 𝑏b similar to each other?
Input
The first line contains a single integer 𝑡t (1≤𝑡≤1041≤t≤104) — the number of testcases.
The first line of the testcase contains a single integer 𝑛n (1≤𝑛≤2⋅1051≤n≤2⋅105) — the number of elements in each of the arrays.
The second line contains 𝑛n integers 𝑎1,𝑎2,…,𝑎𝑛a1,a2,…,an (1≤𝑎𝑖<1091≤ai<109).
The third line contains 𝑛n integers 𝑏1,𝑏2,…,𝑏𝑛b1,b2,…,bn (1≤𝑏𝑗<1091≤bj<109).
The sum of 𝑛n over all testcases doesn't exceed 2⋅1052⋅105.
Output
For each testcase, print the smallest number of operations required to make 𝑎a and 𝑏b similar to each other.
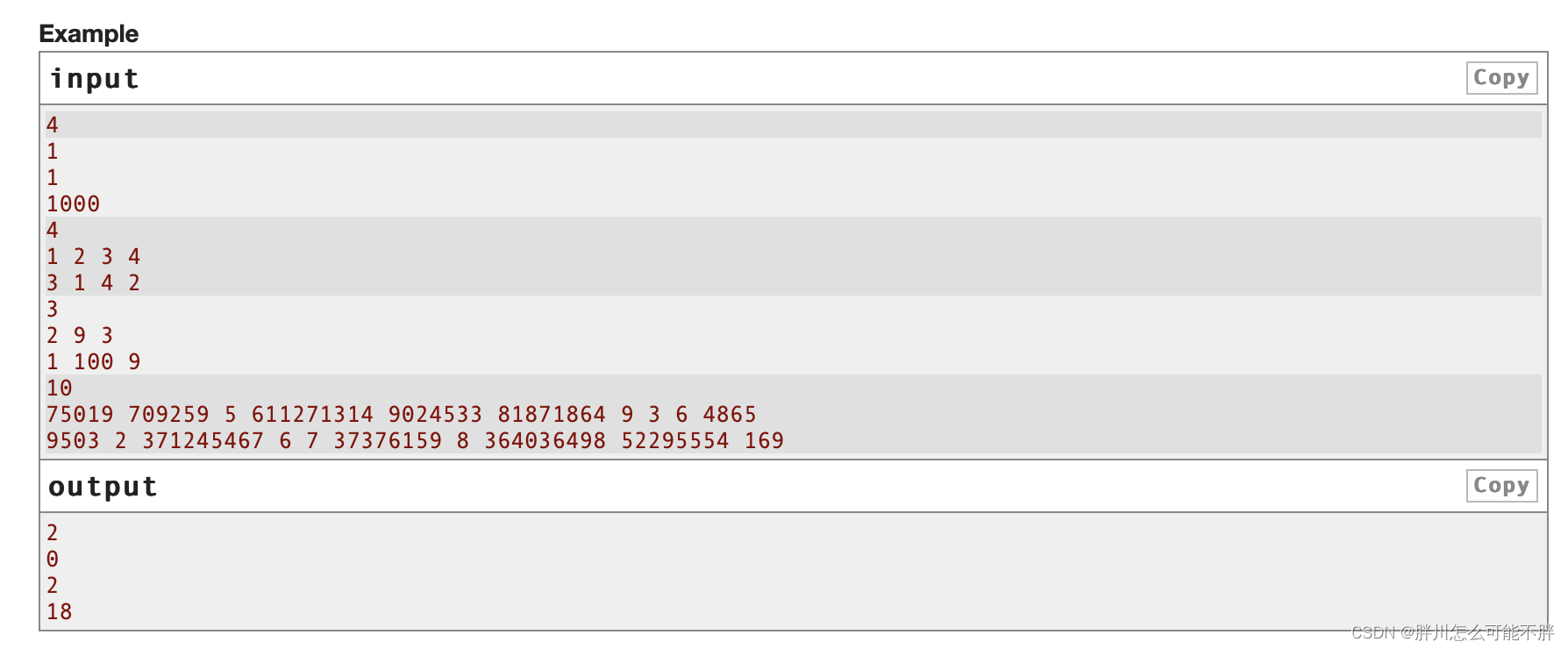
In the first testcase, you can apply the digital logarithm to 𝑏1b1 twice.
In the second testcase, the arrays are already similar to each other.
In the third testcase, you can first apply the digital logarithm to 𝑎1a1, then to 𝑏2b2.
解析:
求操作多少次可以使得俩个数组相等, 操作方法是选择一个i将ai或者bi便成自身数的长度,不如1000操作之后会变成4;直接优先队列暴力实现实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define dbug cout<<"hear!"<<endl;
#define rep(a,b) for(ll i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define rrep(a,b) for(ll j=a;j<=b;j++)
#define per(a,b) for(ll i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define pper(a,b) for(ll j=a;j>=b;j--)
#define no cout<<"NO"<<endl;
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<endl;
//priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> >q;
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
const int N = 2e5 + 100;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
ll gcdd(ll a, ll b)
{
if (b) while ((a %= b) && (b %= a));
return a + b;
}
// ll h[N],ne[N],w[N],to[N],idx;
// void add(int a,int b,int c)
// {
// to[idx]=b,w[idx]=c,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
// }
const ll mod =998244353;
ll t, n, m, a, b, c,d, x,y, k, cnt, ans, ant, sum,q, p;
ll arr[N], brr[N], crr[N];
ll len(ll x)
{
sum=0;
while(x)
{
x/=10;
sum++;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n;
priority_queue<ll>akk,bkk;
rep(1,n)
{
cin>>x;
akk.push(x);
}
rep(1,n)
{
cin>>x;
bkk.push(x);
}
ans=0;
while(!akk.empty() )
{
ant=akk.top();
cnt=bkk.top();
if(ant==cnt)
{
akk.pop();
bkk.pop();
}else if(ant>cnt)
{
akk.pop();
ant=len(ant);
akk.push(ant);
ans++;
}else{
bkk.pop();
cnt=len(cnt);
bkk.push(cnt);
ans++;
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}




















 518
518











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








