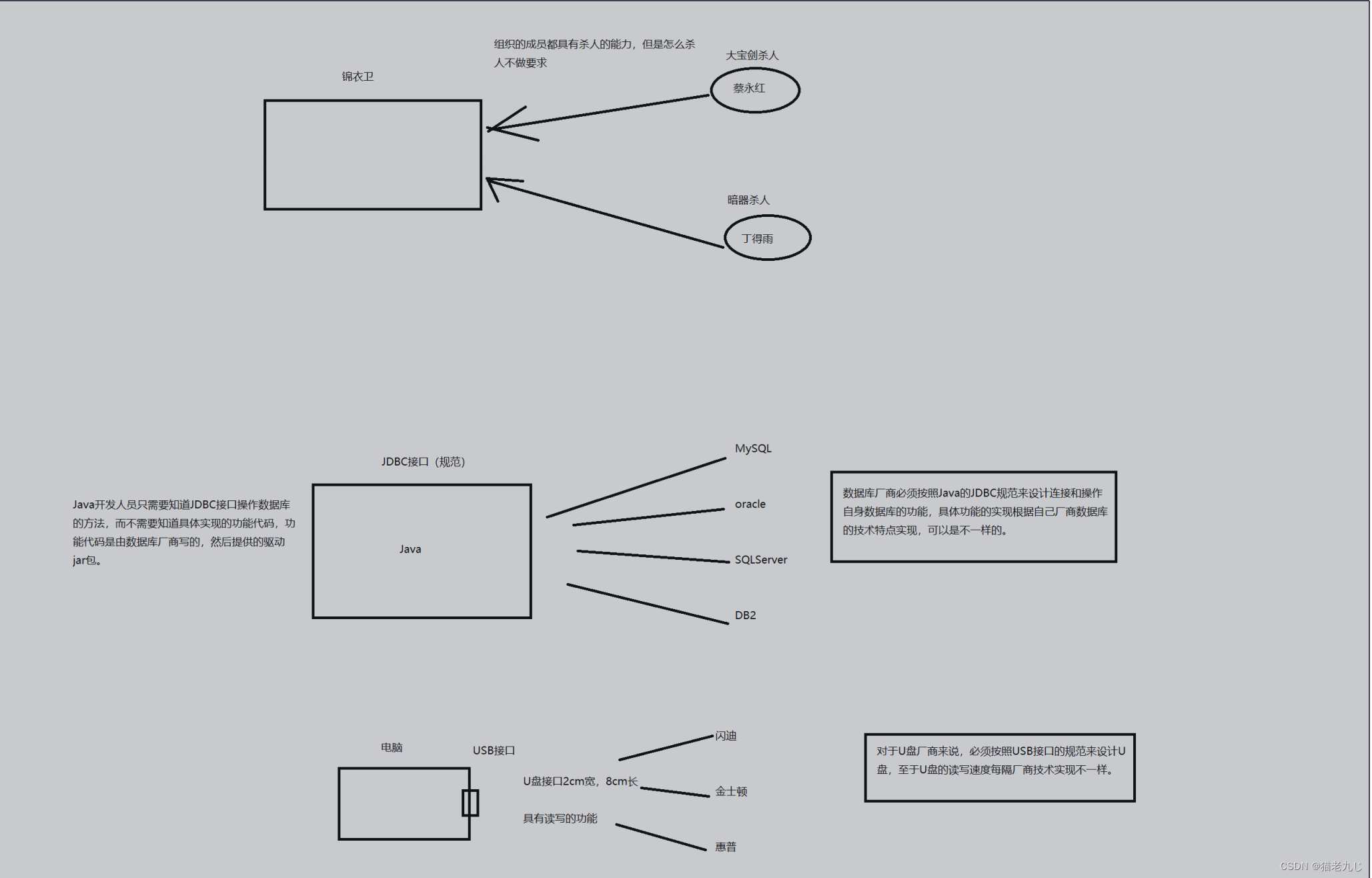
1.什么是JDBC
概念:
Java
数据库连接,(
Java Database Connectivity
,简称
JDBC
)是
Java
语言
中用来规范客户端程序
如何来访问数据库的
应用程序接口
,提供了诸如查询和更新数据库中数据的方法。
JDBC
也是
Sun
Microsystems
的商标。我们通常说的
JDBC
是面向关系型数据库的。
各数据库厂商根据
JDBC
的规范,实现自身数据库操作的功能代码,然后以
jar
包(数据库厂商提供的驱动
包)的形式提供给开发人员使用,开发人员使用反射的机制创建这些具体实现类,按照
JDBC
的规范来完
成数据库的操作。
接口和JDBC规范的理解
2.创建数据库
创建学生信息表
#设置数据的视图---使用数据库
use mydb;
#判断表存在就删除表
drop table if exists student;
#创建表
create table student (
stuId int primary key auto_increment,
stuName varchar(20),
stuSex varchar(2),
stuAge int,
stuAddr varchar(50)
);
#插入测试数据
insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values('张三','男',20,'河南');
insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values('小美','女',18,'山东');
insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values('Rose','女',19,'美国');
insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values('Jack','男',21,'英国');
#查询数据表
select * from student;3.JDBC进行数据库的操作
3.1
先在
IDEA
中创建实体类:类的名字对应数据库表的名字、类的属
性对应表的字段
public class Student {
//属性
private int stuId;
private String stuName;
private String stuSex;
private int stuAge;
private String stuAddr;
//IDEA自动构造代码快捷键:
alt + insert ...
3.2 JDBC
的增删改查操作
junit
的用法补充
:junit
可以使方法脱离
main
方法直接执行,方便进行程序测试。
package com.hp.test2;
import org.junit.Test;
public class StudentTest {
/*
junit用法:
1.方法要定义为无参无返回值的。且测试类的名字不能是Test
2.在方法上使用 @Test 这个注解
3.光标放在后面,然后使用 alt + 回车 进行自动导包,选择---Add 'JUnit4' to classpath
4.这个方法就不需要依赖main方法就可以直接执行
*/
@Test
public void testSelectAll(){
System.out.println("testSelectAll执行...");
}
}
1 JDBC
的全查操作
查询获得的结果集
| stuld | stuName | stuSex | stuAge | stuAddr |
| 1 | 张三 | 男 | 20 | 河南 |
| 2 | 小美 | 女 | 18 | 山东 |
| 3 | Rose | 女 | 19 | 美国 |
| 4 | Jack | 男 | 21 | 英国 |
结果集的游标默认指向的是数据标题,需要使用
next()
方法移动游标,指向真正的数据。该方法
的返回值是
boolean
类型,如果向下移动有数据行返回
true
,否则返回
false
。
JDBC
全查的源代码如下:
public class StudentTest {
/**
* JDBC连接数据库,需要配置四大参数,同时需要导入数据库对应的驱动包
*/
private String driver="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
private String url="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mydb? useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"; private String username="root";
private String password="123";
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//JDBC操作数据库的步骤
//1.首先在项目根目录创建lib文件夹,放入jdbc驱动程序,然后Add As Library
//2.加载数据库驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//3.使用驱动管理器来获得连接---获得一个数据库连接对象Connection Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 生成方法调用返回值的快捷键:ctrl + alt + v
//4.使用Connection创建PreparedStatement预处理对象---PreparedStatement对象可以 执行带 ? 的sql语句
String sql="select * from student";
PreparedStatement pstm = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.使用PreparedStatement对象执行SQL语句,获得ResultSet结果集对象
ResultSet rs = pstm.executeQuery();
//6.操作判断--增删改返回的是影响的行数(返回值是int),只有查询获得结果集(返回值 ResultSet)
//让结果集的游标不断的往下移动,直到没有数据的时候结束循环
List<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<>();
//定义集合(大的容器),用来装 Student对象(小容器)
while(rs.next()){
//根据字段名称获取表中的数据
int stuId=rs.getInt("stuId");
String stuName=rs.getString("stuName");
String stuSex=rs.getString("stuSex");
int stuAge=rs.getInt("stuAge");
String stuAddr=rs.getString("stuAddr");
//把以上数据封装到Student对象中
Student student=new Student(); //一行数据就封装成了一个Student对象 student.setStuId(stuId);
student.setStuName(stuName);
student.setStuSex(stuSex);
student.setStuAge(stuAge);
student.setStuAddr(stuAddr);
//把当前行封装后的Student对象装载到 List集合中
studentList.add(student);
}
System.out.println(studentList);
//7.回收资源,先关闭rs结果集对象 再pstm预处理对象 最后con连接对象
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}if(pstm!=null){
pstm.close();
}
if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
}
}
2 JDBC
的添加操作
/**
* 添加操作
*/
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动包
//2.通过反射加载驱动程序
Class.forName(driver);
//3.通过驱动管理器获得数据库的连接对象
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4.通过连接对象,获取SQ预处理对象
String sql="insert into student(stuName,stuSex,stuAge,stuAddr) values(?,?,?,?)"; PreparedStatement pstm = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//实际开发是前端页面传递过来的数据,此处我们直接模拟一组数据
Student student=new Student();
student.setStuName("孔顺达");
student.setStuSex("男");
student.setStuAge(18);
student.setStuAddr("南阳");
//5.1预处理对象的sql语句有 ? 所以需要进行传参
pstm.setObject(1,student.getStuName());
pstm.setObject(2,student.getStuSex());
pstm.setObject(3,student.getStuAge());
pstm.setObject(4,student.getStuAddr());
//5.2执行更新(增删改都叫做数据库的更新,更新返回的是影响的行数)
int n = pstm.executeUpdate();
//6判断影响的行数 n > 0 表示插入成功,否则插入失败
if(n>0){
System.out.println("插入数据成功");
}else{
System.out.println("插入数据失败");
}//7释放资源
if(pstm!=null){
pstm.close();
}if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
}
3 JDBC
的删除操作
/**
* 删除操作
*/
@Test
public void testDel() throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动程序包
//2.通过反射加载驱动程序
Class.forName(driver);
//3.通过驱动管理器获得数据库的连接对象
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4.通过数据库连接对象获取sql预处理对象
String sql="delete from student where stuId=?";
PreparedStatement pstm = con.prepareStatement(sql);
//5.1预处理对象的sql语句有 ? ,所以需要传参
int stuId=3; //实际开发是从前端页面获取要删除的id
pstm.setObject(1,stuId);
//5.2执行更新操作(增删改都是更新操作,返回的结果是影响的行数)
int n=pstm.executeUpdate();
//6判断影响的行数 n>0 表示删除成功,否则删除失败
if(n>0){
System.out.println("删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
//7释放资源
if(pstm!=null){
pstm.close();
}if(con!=null){
con.close();
}
}





















 1417
1417











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








