RabbitMQ消息模型
RabbitMQ官方提供了5个不同的Demo示例,对应了不同的消息模型:
- 简单模型:一个消费者,一个发布者
- Work模型:多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
- 广播模型:Fanout交换机将消息路由给每一个与之绑定的队列
- 路由模型:Direct交换机根据RoutingKey判断路由给哪个队列
- 主题模型:Topic交换机接收的消息RoutingKey必须是多个单词,以 `**.**` 分割
导依赖
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>改配置
spring: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.150.101 # 主机名,mq所在服务器 port: 5672 # 端口 virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机 username: itcast # 用户名 password: 123321 # 密码
Queue 简单队列模型
发布者端
@Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Test public void testSimpleQueue() { // 队列名称 String queueName = "simple.queue"; // 消息 String message = "hello, spring amqp!"; // 发送消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message); }消费者端
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class SpringRabbitListener { @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")//指定队列名监听 public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) { System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】"); } }
WorkQueue工作队列
Work queue,工作队列模型,可以提高消息处理速度,避免队列消息堆积
发布者端
@Test public void testWorkQueue() throws InterruptedException { // 队列名称 String queueName = "simple.queue"; // 消息 String message = "hello, message_"; // 发送消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message + i); }消费者端
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException { System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now()); Thread.sleep(20); } @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException { System.err.println("消费者2........接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now()); Thread.sleep(200); }因为默认是均分的,如果一个服务器很慢,则会影响整个系统执行效率,做到能者多劳,在spring中有一个简单的配置,可以解决这个问题。我们修改consumer服务的application.yml文件,添加配置:
spring: rabbitmq: listener: simple: prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息
发布/订阅模型
发布订阅模式与之前案例的区别就是允许将同一消息发送给多个消费者。
模型
在consumer消费者中创建一个类,声明队列和交换机:
@Configuration public class FanoutConfig { //声明这是一个广播类型的交换机 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("exchange.fanout");//广播Fanout类型交换机 } //第1个队列 @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue1(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue1"); } //绑定队列和交换机 @Bean public Binding bindingQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange); } //第2个队列 @Bean public Queue fanoutQueue2(){ return new Queue("fanout.queue2"); } //绑定队列和交换机 @Bean public Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange); } }发布者端
@Test public void testFanoutExchange() { // 队列名称 String exchangeName = "exchange.fanout"; // 消息 String message = "hello, everyone!"; rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "", message); }消费者端
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1") public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) { System.out.println("消费者1接收到Fanout消息:【" + msg + "】"); } @RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2") public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) { System.out.println("消费者2接收到Fanout消息:【" + msg + "】"); }
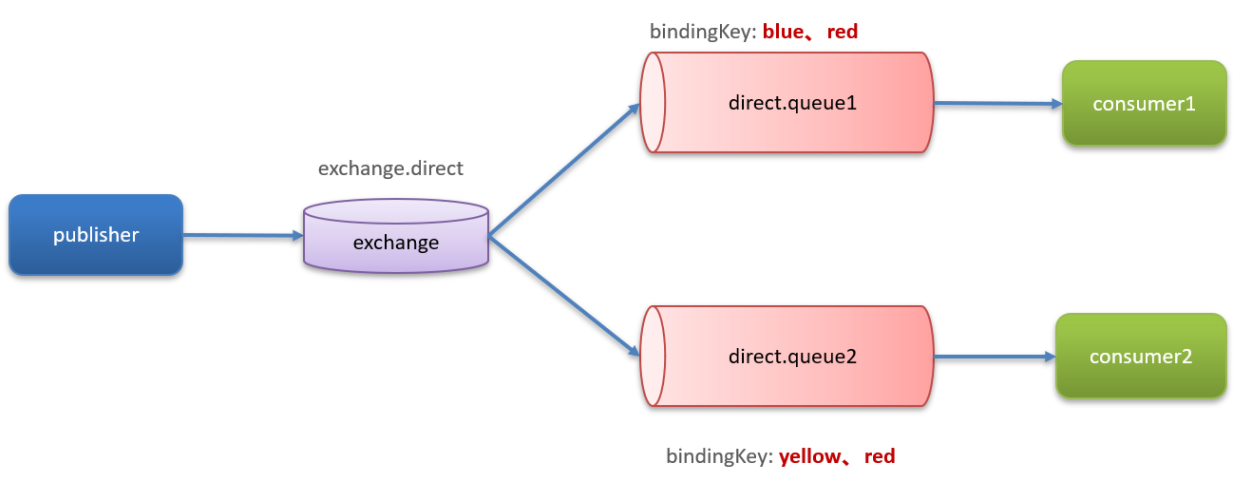
路由模型
我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费,这时就要用到Direct类型的Exchange。
基于注解声明队列和交换机
发布者端
@Test public void testSendDirectExchange() { // 交换机名称 String exchangeName = "exchange.direct"; // 消息 String message = "红色警报!日本乱排核废水,导致海洋生物变异,惊现哥斯拉!"; // 发送消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "red", message); }消费者端
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT), key = {"red", "blue"}//只消费带有,red或者blue的消息 )) public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】"); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT), key = {"red", "yellow"}//只消费带有,red或者yellow的消息 )) public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】"); }
主题模型
发布者端
@Test public void testSendTopicExchange() { // 交换机名称 String exchangeName = "exchange.topic"; // 消息 String message = "喜报!孙悟空大战哥斯拉,胜!"; // 发送消息 rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", message); }消费者端
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC), key = "china.#" )) public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】"); } @RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"), exchange = @Exchange(name = "exchange.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC), key = "#.news" )) public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){ System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】"); }消息转换器
默认实现是SimpleMessageConverter,基于JDK的ObjectOutputStream完成序列化。发送对象类型时,会乱码,如果要修改只需要定义一个MessageConverter 类型的Bean即可。推荐用JSON方式序列化,步骤如下:
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId> <version>2.9.10</ version > </dependency>在配置类声明转换器
@Bean public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter(){ return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter(); }




























 3351
3351

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








