文章目录
Promise原理探究
基本原理
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
constructor(fn){
fn(this._resolve.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled){
this.callbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}
_resolve(val){
this.callbacks.forEach(onFulfilled => onFulfilled(val));
}
}
new Promise(function(resolve){
const data = "hello";
resolve(data);
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
});
new Promise(function(resolve){
setTimeout(function(){
const data = "hello";
resolve(data);
})
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
})

针对以上问题,有以下两种解决方式。
- 第一种:延时机制
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
constructor(fn){
fn(this._resolve.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled){
this.callbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}
_resolve(val){
setTimeout(function(self){
self.callbacks.forEach(onFulfilled => onFulfilled(val));
},0,this);
}
}
加入延时机制后,即使new Promise()里的代码是同步的,也能保证then()里的事件处理程序先完成注册,再resolve(val),所以最后输出了"hello"。
- 第二种:状态管理机制
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
state = "pending";
value = null;
constructor(fn){
fn(this._resolve.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled){
if(this.state==="pending"){
this.callbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}else{
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
}
_resolve(val){
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = val;
this.callbacks.forEach(onFulfilled => onFulfilled(val));
}
}
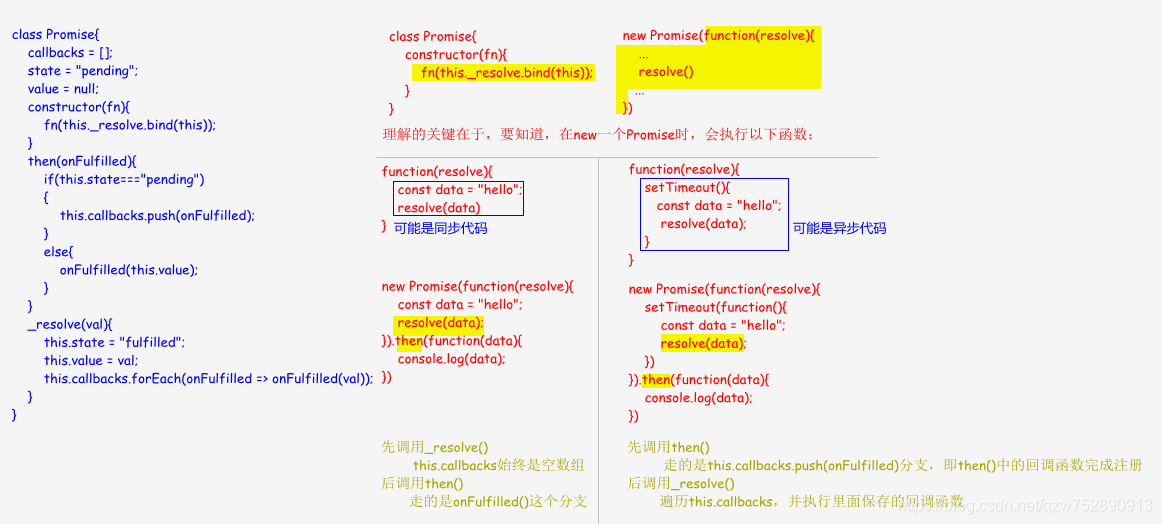
链式调用
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
state = "pending";
value = null;
constructor(fn){
fn(this._resolve.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled){
if(this.state==="pending"){
this.callbacks.push(onFulfilled);
}else{
onFulfilled(this.value);
}
return this;
}
_resolve(val){
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = val;
this.callbacks.forEach(onFulfilled => onFulfilled(val));
}
}
要实现链式调用,在then()返回this,即当前Promise实例,就好。
new Promise(function(resolve){
const data = "hello";
resolve(data);
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
})
确实,依次输出了"hello" "hello",与预期相符。
但是,看下面,不论new Promise()里的代码是同步还是异步,输出的都是"hello" "hello",都不符预期:"hello" "hello world"。
new Promise(function(resolve){
const data = "hello";
resolve(data);
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return data+" world";
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
})
new Promise(function(resolve){
setTimeout(function(){
const data = "hello";
resolve(data);
})
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
return data+" world";
}).then(function(data){
console.log(data);
})
这是因为then()里应该返回一个新的Promise实例,而不是this。
- 状态机制
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
state = "pending";
value = null;
constructor(fn){
fn(this._resolve.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled){
return new Promise(function(resolve){
this._handle({
resolve,
onFulfilled
})
}.bind(this));
}
_handle(callback){
if(this.state==="pending"){
this.callbacks.push(callback);
}else{
const {resolve,onFulfilled} = callback;
const newValue = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolve(newValue);
}
}
_resolve(val){
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = val;
this.callbacks.forEach(callback => this._handle(callback));
}
}

异常处理
class Promise{
callbacks = [];
state = "pending";
value = null;
constructor(fn){
try{
fn(this._resolve.bind(this),this._reject.bind(this));
}catch(err){
console.log(err);
}
}
then(onFulfilled,onRejected){
return new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
this._handle({
resolve,
onFulfilled,
reject,
onRejected
})
}.bind(this));
}
_handle(callback){
if(this.state==="pending"){
this.callbacks.push(callback);
}else if(this.state === "fulfilled"){
const {onFulfilled,resolve} = callback;
if(onFulfilled){
const newValue = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolve(newValue);
}else{
return;
}
}else if(this.state === "rejected"){
const {onRejected,reject} = callback;
if(onRejected){
const newValue = onRejected(this.value);
reject(newValue);
}else{
return;
}
}
}
_resolve(val){
this.state = "fulfilled";
this.value = val;
this.callbacks.forEach(callback => this._handle(callback));
}
_reject(val){
this.state = "rejected";
this.value = val;
this.callbacks.forEach(callback => this._handle(callback));
}
}
new Promise(function(resolve,reject){
// const data = Math.floor(Math.random()*10+1);
// if(data%2===0){
// resolve(data);
// }else{
// reject(data);
// }
setTimeout(function(){
const data = Math.floor(Math.random()*10+1);
if(data%2===0){
resolve(data);
}else{
reject(data);
}
})
}).then(function(data){
console.log("got data success:",data);
},function(data){
console.log("got data failed:",data);
})
Promise的使用
Promise.prototype.catch
实际是Promise.then(null,onRejected),用于指定发生错误时的回调。
所以,通常会在catch里指定rejected时的回调函数。
new Promise(resolve => {
throw new Error("An error occurred");
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error);
})
虽然在then里也可以指定rejected时的回调函数,但是不太会这样写,可能是因为javascript里的try...catch...finally导致的习惯吧。
new Promise(resolve => {
throw new Error("An error occurred");
}).then(
value => {
console.log(value);
},
error => {
console.log(error);
}
)
catch之后的链式调用
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log("初始化");
resolve();
}).then(() => {
throw new Error("出错了");
console.log("执行[这个]");
}).catch(err => {
console.log("执行[那个]");
}).then(() => {
console.log("执行[这个],无论前面发生了什么!")
})
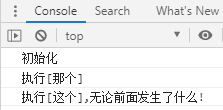
当然,上述过程可以使用javascript的try...catch...finally实现。
function test(){
console.log("初始化");
try{
throw new Error("出错了");
console.log("执行[这个]")
}catch(err){
console.log("执行[那个]");
}finally{
console.log("执行[那个],无论前面发生了什么!");
}
}
test();
回调函数与Promise混用带来的坑
new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
test();
})
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error);
})
function test(){
throw new Error("An error occurred");
return "hello world";
}
捕获不到错误,这个锅setTimeout得背。
解决方法:用Promise把setTimeout包裹起来,这样就不会直接调用setTimeout了。
const timeout = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve,ms));
timeout()
.then(() => {
return test();
}).then(value => {
console.log(value);
}).catch(error => {
console.log(error);
})
Promise.all()
Promise.all([promise1,promise2,promise3]).then([result1,result2,result3] => {})
Promise.all超讲义气。
所有兄弟一个个都resolve,才叫resolve;哪怕一个兄弟reject,最终都是reject。
function f1(){
return 1;
}
function f2(){
return 2;
}
function f3(){
return 3;
}
Promise.all([f1(),f2(),f3()])
.then(([res1,res2,res3]) => {
console.log(res1,res2,res3);//输出 1 2 3
})
const p1 = Promise.resolve(1);
const p2 = 2;
const p3 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve,1000,3));
Promise.all([p1,p2,p3]).then(values => {
const [val1,val2,val3] = values;
console.log(val1,val2,val3)//输出 1 2 3
})





















 2万+
2万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








