1. 地址空间划分
Start End Use
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
ffff8000 ffffffff copy_user_page/ clear_user_page use.
For SA11xx andXscale, this is used to
setup a minicachemapping.
ffff4000 ffffffff cachealiasing on ARMv6 and later CPUs.
ffff1000 ffff7fff Reserved.
Platforms must notuse this address range.
ffff0000 ffff0fff CPUvector page.
The CPU vectors aremapped here if the
CPU supports vectorrelocation (control
register V bit.)
>>异常向量地址。大小为1个PAGE,4KB。
fffe0000 fffeffff XScalecache flush area. This is used
in proc-xscale.S toflush the whole data
cache. (XScale doesnot have TCM.)
fffe8000 fffeffff DTCMmapping area for platforms with
DTCM mounted insidethe CPU.
fffe0000 fffe7fff ITCMmapping area for platforms with
ITCM mounted insidethe CPU.
fff00000 fffdffff Fixmapmapping region. Addresses provided
by fix_to_virt()will be located here.
ffc00000 ffefffff DMAmemory mapping region. Memory returned
by the dma_alloc_xxx functions will be
dynamically mappedhere.
>>一致性DMA映射地址。大小为3MByte。
ff000000 ffbfffff Reservedfor future expansion of DMA
mapping region.
VMALLOC_START VMALLOC_END-1 vmalloc()/ ioremap() space.
Memory returned byvmalloc/ioremap will
be dynamicallyplaced in this region.
Machine specificstatic mappings are also
located here throughiotable_init().
VMALLOC_START isbased upon the value
of the high_memoryvariable, and VMALLOC_END
is equal to0xff000000.
>>vmalloc/ioremap/iotable_init地址区。
Vmalloc – 非连续动态映射
Ioremap – 连续动态映射
Iotable_init – 静态映射
PAGE_OFFSET high_memory-1 Kernel direct-mapped RAM region.
This maps theplatforms RAM, and typically
maps all platformRAM in a 1:1 relationship.
>>直接地址映射区。
内核代码段/data段/bss段/kmalloc
PKMAP_BASE PAGE_OFFSET-1 Permanentkernel mappings
One way of mappingHIGHMEM pages into kernel
space.
>>高端内存映射区。内核访问高端内存的一种方式。
MODULES_VADDR MODULES_END-1 Kernelmodule space
Kernel modulesinserted via insmod are
placed here usingdynamic mappings.
>>内核模块区。
00001000 TASK_SIZE-1 Userspace mappings
Per-thread mappingsare placed here via
the mmap() systemcall.
00000000 00000fff CPUvector page / null pointer trap
CPUs which do notsupport vector remapping
place their vectorpage here. NULL pointer
dereferences by boththe kernel and user
space are alsocaught via this mapping.
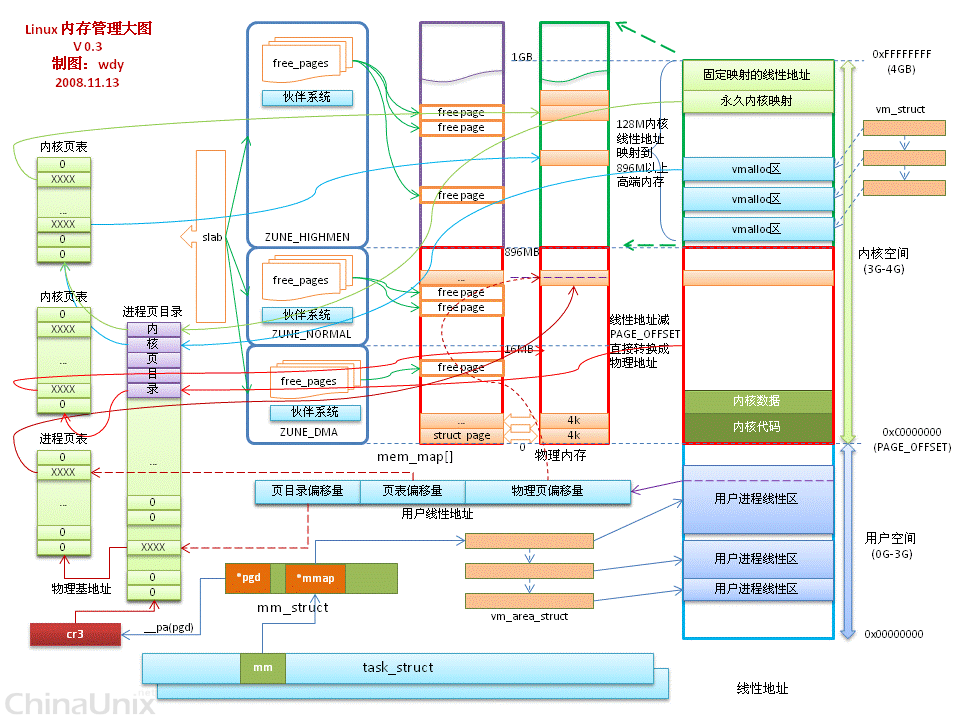
2. 网友Aryang 的图
l 我的一些理解:
从用户进程(地址空间为0-3G)的角度来看:
在linux系统中,进程用task_struct来描述。
进程使用的内存资源用mm_struct(task_struct->mm)来描述。
mm_struct中的pgd指示页目录基地址;mm_struct中的mmap为数个vm_area_struct的链表。因为一个进程可能由多个线性地址区组成。
vm_area_struct中的vm_start和vm_end指定了线性地址空间范围。
怎么由vm_area_struct找到其所对应物理地址呢?
每一个32位用户线性地址分为3部分:
页目录偏移(10位:31~22):根据该偏移找到页表物理地址。
页表偏移(10位:21~12):根据该偏移找到页物理地址。
页内偏移(12位:11~0):根据该偏移找到具体地址。
页表可分为进程页表和内核页表两种。页目录却只有一个(前面是内核目录项,后面是进程目录项)。
所有的物理内存通过free_pages管理起来了。
l 跟帖人回复:
内核地址空间的低896M为直接地址映射。将线性地址减去一个固定的偏移量即为物理地址。
>>我认为不是低896M的空间就是直接地址映射,而是要看给内核配置的系统内存大小。比如说配置为32M,可能就只有32M了。
进程地址空间所映射的物理内存可以映射到低端物理内存去,即896M物理内存下面。
一般来说系统空间不能映射到高端物理内存,但是内核可以把896 - 1G之间的128M用来映射高端物理内存。
3. Linux内存:内存管理的实质
http://bbs.chinaunix.net/thread-2055231-1-1.html






















 416
416

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








