来看看struts2的doFilter方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try {
prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response);
prepare.createActionContext(request, response);
prepare.assignDispatcherToThread();
if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
request = prepare.wrapRequest(request);
ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true);
if (mapping == null) {
boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response);
if (!handled) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
} else {
execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);
}
}
} finally {
prepare.cleanupRequest(request);
}
}在分析之前先看一下prepare.findActionMapping()方法
public ActionMapping findActionMapping(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, boolean forceLookup) {
ActionMapping mapping = (ActionMapping) request.getAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY);
if (mapping == null || forceLookup) {
try {
mapping = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ActionMapper.class).getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
if (mapping != null) {
request.setAttribute(STRUTS_ACTION_MAPPING_KEY, mapping);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
}
}
return mapping;
}如果从请求中获取不到ActionMapping,则从新生成
看这条代码
mapping = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ActionMapper.class).getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
public ActionMapping getMapping(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigurationManager configManager) {
ActionMapping mapping = new ActionMapping();
String uri = getUri(request);
int indexOfSemicolon = uri.indexOf(";");
uri = (indexOfSemicolon > -1) ? uri.substring(0, indexOfSemicolon) : uri;
uri = dropExtension(uri, mapping);
if (uri == null) {
return null;
}
parseNameAndNamespace(uri, mapping, configManager);
handleSpecialParameters(request, mapping);
return parseActionName(mapping);
}从里就是从uri中取数据从而为mapping赋值。
下面我们继续开始doFilter()中方法的讲解。
来看一下execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping);这个方法
public void executeAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
}继续跟
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
if (nullStack) {
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
proxy.execute();
}
// If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
if (!nullStack) {
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
// WW-2874 Only log error if in devMode
if (devMode) {
String reqStr = request.getRequestURI();
if (request.getQueryString() != null) {
reqStr = reqStr + "?" + request.getQueryString();
}
LOG.error("Could not find action or result\n" + reqStr, e);
} else {
if (LOG.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOG.warn("Could not find action or result", e);
}
}
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (handleException || devMode) {
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} else {
throw new ServletException(e);
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();String name = mapping.getName(); String method = mapping.getMethod();这里三条代码就用到最一开始的mapping,就是从uri中获取的数据。紧接着是创建ActionProxy,然后proxy.execute()方法。这里先去看看创建ActionProxy的过程。
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
ActionInvocation inv = new DefaultActionInvocation(extraContext, true);
container.inject(inv);
return createActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
}跟createActionProxy
创建DefaultActionInvocation将extraContext赋值给成员变量extraContext
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(ActionInvocation inv, String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
DefaultActionProxy proxy = new DefaultActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
container.inject(proxy);
proxy.prepare();
return proxy;
}创建DefaultActionProxy对象,将invocaiton,namespace,actionName,methodName,executeResult,cleanupContext,赋值给proxy ,然后我们去查看一下proxy.prepare()方法
protected void prepare() {
String profileKey = "create DefaultActionProxy: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
config = configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration().getActionConfig(namespace, actionName);
if (config == null && unknownHandlerManager.hasUnknownHandlers()) {
config = unknownHandlerManager.handleUnknownAction(namespace, actionName);
}
if (config == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException(getErrorMessage());
}
resolveMethod();
if (!config.isAllowedMethod(method)) {
throw new ConfigurationException("Invalid method: " + method + " for action " + actionName);
}
invocation.init(this);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
}在这个方法对config成员变量实例化了,ActionConfig
先来看一下configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration()
protected synchronized RuntimeConfiguration buildRuntimeConfiguration() throws ConfigurationException {
Map<String, Map<String, ActionConfig>> namespaceActionConfigs = new LinkedHashMap<String, Map<String, ActionConfig>>();
Map<String, String> namespaceConfigs = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
for (PackageConfig packageConfig : packageContexts.values()) {
if (!packageConfig.isAbstract()) {
String namespace = packageConfig.getNamespace();
Map<String, ActionConfig> configs = namespaceActionConfigs.get(namespace);
if (configs == null) {
configs = new LinkedHashMap<String, ActionConfig>();
}
Map<String, ActionConfig> actionConfigs = packageConfig.getAllActionConfigs();
for (Object o : actionConfigs.keySet()) {
String actionName = (String) o;
ActionConfig baseConfig = actionConfigs.get(actionName);
configs.put(actionName, buildFullActionConfig(packageConfig, baseConfig));
}
namespaceActionConfigs.put(namespace, configs);
if (packageConfig.getFullDefaultActionRef() != null) {
namespaceConfigs.put(namespace, packageConfig.getFullDefaultActionRef());
}
}
}
PatternMatcher<int[]> matcher = container.getInstance(PatternMatcher.class);
return new RuntimeConfigurationImpl(Collections.unmodifiableMap(namespaceActionConfigs),
Collections.unmodifiableMap(namespaceConfigs), matcher);
}将从packageConfig中获取actionConfigs,然后将actionconfig放入到namespaceConfigs中。
接下来看一下getActionConfig()方法
public ActionConfig getActionConfig(String namespace, String name) {
ActionConfig config = findActionConfigInNamespace(namespace, name);
// try wildcarded namespaces
if (config == null) {
NamespaceMatch match = namespaceMatcher.match(namespace);
if (match != null) {
config = findActionConfigInNamespace(match.getPattern(), name);
// If config found, place all the matches found in the namespace processing in the action's parameters
if (config != null) {
config = new ActionConfig.Builder(config)
.addParams(match.getVariables())
.build();
}
}
}
// fail over to empty namespace
if ((config == null) && (namespace != null) && (!"".equals(namespace.trim()))) {
config = findActionConfigInNamespace("", name);
}
return config;
}在加載配置信息的時候,就把配置文件中信息加載到InterceptorStackConfig,resultTypeConfig等等中最終是放到PackageConfig对象中了,这个PackageConfig对象被放到DefaultConfiguration的packageContexts中。而findActionConfigInNamespace是DefaultConfiguration类中内部类的方法
private ActionConfig findActionConfigInNamespace(String namespace, String name) {
ActionConfig config = null;
if (namespace == null) {
namespace = "";
}
Map<String, ActionConfig> actions = namespaceActionConfigs.get(namespace);
if (actions != null) {
config = actions.get(name);
// Check wildcards
if (config == null) {
config = namespaceActionConfigMatchers.get(namespace).match(name);
// fail over to default action
if (config == null) {
String defaultActionRef = namespaceConfigs.get(namespace);
if (defaultActionRef != null) {
config = actions.get(defaultActionRef);
}
}
}
}
return config;
}这里的namespaceActionConfigs其实是configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration()这个方法调用创建一个RuntimeConfiguration对象,传递进来,也就是说,这里的findActionConfigInNamespace也就在在PackageConfig中寻找。
看一下 prepare方法中的invocation.init(this);方法
public void init(ActionProxy proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
Map<String, Object> contextMap = createContextMap();
// Setting this so that other classes, like object factories, can use the ActionProxy and other
// contextual information to operate
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (actionContext != null) {
actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
}
createAction(contextMap);
if (pushAction) {
stack.push(action);
contextMap.put("action", action);
}
invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
// get a new List so we don't get problems with the iterator if someone changes the list
List<InterceptorMapping> interceptorList = new ArrayList<InterceptorMapping>(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();
}this.proxy = proxy;这一条代码是将代理对象赋值给invocation对象。然后方法中创建action,并且将action放入根栈中最后。最后为拦截器映射得迭代器对象。
proxy.getConfig()里面就是配置信息里面的数据,所以这里可以拿到interceptorsmappings。
下面讲解一下proxy.execute()方法
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext nestedContext = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext());
String retCode = null;
String profileKey = "execute: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
retCode = invocation.invoke();
} finally {
if (cleanupContext) {
ActionContext.setContext(nestedContext);
}
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
return retCode;
}执行到invocation.invoke()方法
public String invoke() throws Exception {
String profileKey = "invoke: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
if (executed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed");
}
if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = interceptors.next();
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else {
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
// this is needed because the result will be executed, then control will return to the Interceptor, which will
// return above and flow through again
if (!executed) {
if (preResultListeners != null) {
for (Object preResultListener : preResultListeners) {
PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) preResultListener;
String _profileKey = "preResultListener: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey);
listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey);
}
}
}
// now execute the result, if we're supposed to
if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) {
executeResult();
}
executed = true;
}
return resultCode;
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
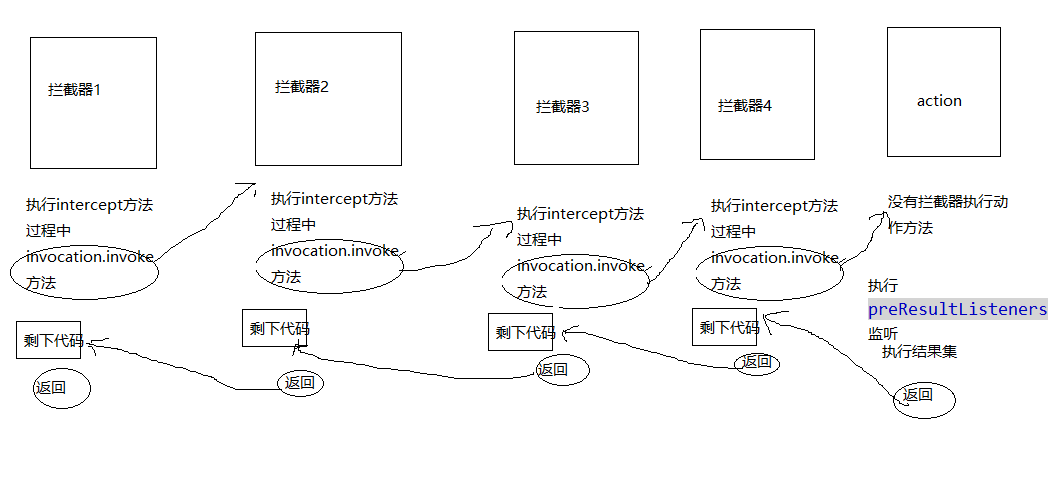
}在这个方法中拦截器会执行intercept方法,当然拦截器执行过程中会调用invocation.invoke()方法,从而形成拦截器链,当然当拦截器遍历完毕时就会执行到action的动作方法,然后action会返回,执行result结果集,第一次执行标识为true,执行玩改变标识,以后不再执行,执行完结果集返回,然后回到最后一个拦截器执行剩下的代码,然后一次往上执行拦截器剩下的代码。
到此完毕






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








