首先,我们回顾的知识点是RDD的五大特性:
1,一系列的分区。
2,一个函数作用于分区上。
3,RDD之间有一系列的依赖。
4,分区器。
5,最佳位置。
Spark属于链式计算,rdd之间有着依赖关系:窄依赖,宽依赖。
RDD执行的时候会将计算链条分为很多task,rdd的task分为:ResultTask和ShuffleMapTask。
1.Partitioner简介
书归正传,RDD之间的依赖如果是宽依赖,那么上游RDD该如何确定每个分区的输出将交由下游RDD的哪些分区呢?Spark提供了分区计算器来解决这个问题。ShuffleDependency的partitioner属性的类型是partitioner,抽象类Partitioner定义了分区计算器的接口规范,ShuffleDependency的分区取决于Partitioner的具体实现。Partitioner的定义如下:
abstract class Partitioner extends Serializable {
def numPartitions: Int
def getPartition(key: Any): Int
}Partitioner的numPartitions方法用于获取分区数量。Partitioner的getPartition方法用于将输入的key映射到下游的RDD的从0到numPartitions-1这个范围中的某一个分区中去。
Partitioner根据不同的需求有着具体的实现类,在idea打开源码,在该抽象类上按下F4键,可以看到继承关系,如下图:
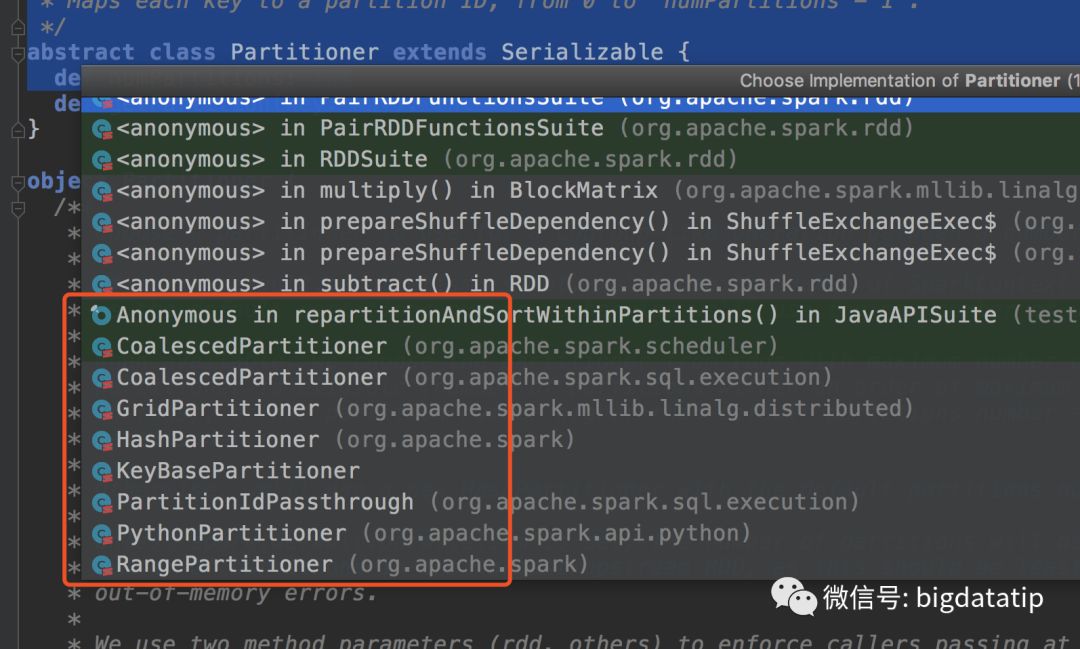
本分区系列,会将CoalescedPartitioner,GridPartitioner,HashPartitioner,RangePartitioner及自定义分区器逐个介绍。本文重点在hashPartitioner。
2.HashPartitioner
首先,我们先看HashPartitioner的源码实现。
class HashPartitioner(partitions: Int) extends Partitioner {
require(partitions >= 0, s"Number of partitions ($partitions) cannot be negative.")
def numPartitions: Int = partitions
def getPartition(key: Any): Int = key match {
case null => 0
case _ => Utils.nonNegativeMod(key.hashCode, numPartitions)
}
override def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match {
case h: HashPartitioner =>
h.numPartitions == numPartitions
case _ =>
false
}
override def hashCode: Int = numPartitions
}根据上面代码我们可以看到,其传入的参数partitions,决定总的分区数,重写的numPartitions方法也只是简单返回该值。重写的getPartition方法实际上是以key的hashcode和numPartitions作为参数调用了Utils工具类的nonNegativeMod方法,该方法的具体实现如下:
def nonNegativeMod(x: Int, mod: Int): Int = {
val rawMod = x % mod
rawMod + (if (rawMod < 0) mod else 0)
}nonNegativeMod方法将对key的hashCode和numPartitions进行取模运算,得到key对应的分区索引。使用哈希和取模的方式,可以方便地计算出下游RDD的各个分区将具体处理哪些key。由于上游RDD所处理的key的哈希值在取模后很可能产生数据倾斜,所以HashPartitioner并不是一个均衡的分区计算器。
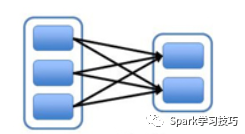
根据HashPartitioner的实现,我们知道ShuffleDependency中的分区依赖关系并不再是一对一的,而取决于key,并且当前RDD的某个分区将可能依赖于ShuffleDependcy的RDD的任何一个分区。我们分析的内容可以作图如下:
3.用HashPartitioner的RDD算子
举几个常见的使用HashPartitioner的例子。
Reducebykey
def reduceByKey(func: (V, V) => V): RDD[(K, V)] = self.withScope {
reduceByKey(defaultPartitioner(self), func)
}aggregateByKey
def aggregateByKey[U: ClassTag](zeroValue: U, numPartitions: Int)(seqOp: (U, V) => U,
combOp: (U, U) => U): RDD[(K, U)] = self.withScope {
aggregateByKey(zeroValue, new HashPartitioner(numPartitions))(seqOp, combOp)
}join
def join[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (V, W))] = self.withScope {
join(other, defaultPartitioner(self, other))
}4.简单介绍defaultPartitioner
简单看一一下,上面代码片段提到的defaultPartitioner方法,该方法的源码如下:
def defaultPartitioner(rdd: RDD[_], others: RDD[_]*): Partitioner = {
val rdds = (Seq(rdd) ++ others)
val hasPartitioner = rdds.filter(_.partitioner.exists(_.numPartitions > 0))
val hasMaxPartitioner: Option[RDD[_]] = if (hasPartitioner.nonEmpty) {
Some(hasPartitioner.maxBy(_.partitions.length))
} else {
None
}
val defaultNumPartitions = if (rdd.context.conf.contains("spark.default.parallelism")) {
rdd.context.defaultParallelism
} else {
rdds.map(_.partitions.length).max
}
// If the existing max partitioner is an eligible one, or its partitions number is larger
// than the default number of partitions, use the existing partitioner.
if (hasMaxPartitioner.nonEmpty && (isEligiblePartitioner(hasMaxPartitioner.get, rdds) ||
defaultNumPartitions < hasMaxPartitioner.get.getNumPartitions)) {
hasMaxPartitioner.get.partitioner.get
} else {
new HashPartitioner(defaultNumPartitions)
}
}该方法首先,会获取带分区数大于零的RDD,然后假如不为空,就采用分区数最大的RDD的分区器当做得到的分区器返回。
假如,都没有分区器,就会默认给定一个HashPartitioner分区器,前面我们也说到了HashPartitioner分区构建的时候要传入一个分区数的参数。这里获取分区数的方式,首先是判断是否设置了spark.default.parallelism参数,假如有的话,可以对rdd.context.defaultParallelism进行追述,最终假如是集群模式调用的是CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的下面方法:
override def defaultParallelism(): Int = {
conf.getInt("spark.default.parallelism", math.max(totalCoreCount.get(), 2))
}结果是假如设定了该参数,采用我们的设定值。没设定的话总core数和2取最大值作为分区数。
后续文章:
RangePartitioner,CoalescedPartitioner,HashPartitioner及自定义分区器
推荐阅读:
Spark源码系列之foreach和foreachPartition的区别























 1470
1470











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








