
我在《Linux 中每个 TCP 连接最少占用多少内存?》一文中绘制了 Linux 内核现在(4.x)使用的文件描述符表(file descriptor table)的数据结构。本篇文章做一些代码考古工作,还原这个数据结构的五个版本的来龙去脉。英文提纲:File Descriptor Table - Shuo Chen's Notes
Table of Contents
Linux 内核版本历史
从 1991 年9 月发布的 Linux 0.01 起,Linux 已经走过了 1/4 世纪。下图是陈硕根据《Linux kernel "historical" git repository with full history》整理的内核版本简史。Linux 2.6 之前,内核采用的版本命名规则是“奇数开发、偶数稳定”。据此 1.0、1.2、2.0、2.2、2.4、2.6 是稳定版,而 1.1.x、1.3.x、2.1.x、2.3.x、2.5.x 则是开发版。2.6 之后不再单独设置“开发版”,而是直接在当前稳定版上滚动开发。更详细的介绍可参考 2. How the development process works 和 https://bootlin.com/doc/training/linux-kernel/linux-kernel-slides.pdf 第 401 页起的 “Linux versioning scheme and development process”一节。

Linux 从诞生以来,一直用 struct task_struct 来表示进程/线程,用 struct file 表示打开的文件,用 struct inode 表示文件本身。struct file 和 struct inode 的区别在于,如果两次 open 同一个文件(比方说 web server 写 access log,你用 less 看这个 assess log 文件),会有两个 struct file 对象,指向同一个 struct inode 对象。容易想到,打开文件的偏移量(offset)应该放在 struct file 里(web server 打开的 access log 的偏移量在文件末尾,你用 less 打开的 access log 的偏移量在文件开头),而文件本身的长度应该放在 struct inode 里(web server 往 access log 里继续写入内容,你不需要重新打开文件就能看到)。换句话说,你用 ls -l 命令看到的信息(除了文件名本身)都存在 struct inode 里;(f)stat(2) 返回的内容也都存在 struct inode 里。在过去的很长时间里,更新 struct file 中偏移量的代码有多线程安全方面的 bug,直到 2014 年 3 月底发布的 Linux 3.14 才修复,也就是说 Ubuntu 14.04 里的 write(2) 系统调用不是线程安全的。Bugs - Shuo Chen's Notes
本文着眼于 struct task_struct 与 struct file 关系的演变。
版本 A:从 0.01 到 1.1.10
最早的 Linux 内核直接把元素为 struct file* 的定长数组放在 struct task_struct 里。
// include/linux/sched.h of linux-1.1.10
struct task_struct {
// ...
struct file * filp[NR_OPEN];
fd_set close_on_exec;
// ...
}从 int fd 取到 struct file* fp 的写法是:
struct file* fp = current->filp[fd];而 struct file 和 struct inode 也是位于各自的定长数组中。
// fs/file_table.c of linux-0.99
struct file file_table[NR_FILE];
// fs/inode.c of linux-0.99
static struct inode inode_table[NR_INODE];NR_OPEN、NR_FILE、NR_INODE 这几个宏的值决定了上述数组的大小,它们的值逐渐增大。修改 NR_OPEN 会影响 sizeof (struct task_struct),也会直接影响每个进程占用的物理内存的大小,因为 task_struct 对象是不会 swap to disk 的。
| Version | NR_OPEN | NR_FILE | NR_INODE |
| ------- | ------- | ------- | -------- |
| 0.01 | 20 | 64 | 32 |
| 0.12 | 20 | 64 | 64 |
| 0.95 | 20 | 64 | 128 |
| 0.96a-3 | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| 0.96c-1 | 32 | 128 | 128 |
| 0.96pre | 32 | 64 | 128 |
| 0.97 | 32 | 128 | 128 |
| 0.98.4 | 256 | 128 | 128 |
| 0.99.10 | 256 | 1024 | 2048 |在 0.99.10 中,struct file 和 struct inode 改成了动态分配,这样整个系统能同时打开的文件数大大增加,但每个进程能打开的文件数还是 NR_OPEN。
// fs/file_table.c of linux-0.99.10
-struct file file_table[NR_FILE];
+struct file * first_file;版本 B:1.1.11 到 1.3.21
1.1.11 从 task_struct 中分离出了 fs_struct、files_struct、mm_struct。
// include/linux/sched.h of linux-1.3.21
/* Open file table structure */
struct files_struct {
int count;
fd_set close_on_exec;
struct file * fd[NR_OPEN];
};
struct task_struct {
// ...
/* filesystem information */
struct fs_struct fs[1];
/* open file information */
struct files_struct files[1];
/* memory management info */
struct mm_struct mm[1];
// ...
};这样做没有改变程序的功能,只是更好地组织了数据结构,让紧密相关的数据成员位于同一个结构体中,体现了封装的思想。修改 NR_OPEN 也会直接影响 sizeof (struct task_struct)。
从 int fd 取到 struct file* fp 的写法变成:
struct file* fp = current->files->fd[fd];这里为什么要用长度为 1 的 struct 数组,而不直接放 struct,我猜是为了将来改成指针时不必修改客户代码。
file descriptor flag 与 file status flag
在 man 2 fcntl 中提到,文件的标志分为 file descriptor flag 与 file status flag 两类,分别用 F_GETFD/F_SETFD 和 F_GETFL/F_SETFL 来存取(例见 muduo/net/SocketsOps.cc )。file descriptor flag 只有一个:close-on-exec;file status flags 包含 O_NONBLOCK、 O_APPEND、O_DIRECT 等等。因此 files_struct 要有 fd_set close_on_exec 成员,用于存储 file descriptor flag,而 file status flag 则是放在 struct file 的 f_flags 成员中。这两类标志(flags)的区别体现在 dup(2) 系统调用上,后面还会讲到。
版本 C:1.3.22 到 2.1.89
1.3.22 把 task_struct 的 files、fs、mm 等成员变成了指针,让 sizeof(struct task_struct) 瘦身了很多。这么做是为了支持多线程。
// include/linux/sched.h of linux-2.0.2
struct task_struct {
// ...
/* filesystem information */
- struct fs_struct fs[1];
+ struct fs_struct *fs;
/* open file information */
- struct files_struct files[1];
+ struct files_struct *files;
/* memory management info */
- struct mm_struct mm[1];
+ struct mm_struct *mm;
// ...
};从 int fd 取到 struct file* fp 的写法不变,还是 current->files->fd[fd]。
Linux 2.0 开始支持多线程。(最早是 LinuxThreads 实现,2.6 改成了更符合 POSIX 语义的 NPTL 实现。)把 files_struct 成员从 task_struct 里移出来,让同一进程内的多个线程可以共享一个 files_struct 对象,这样线程 1 打开的文件自然就能被线程 2 看到了。

同一进程内的两个线程共享 files_struct 对象
fs_struct 和 mm_struct 也是同理。
版本 D:2.1.90 到 2.6.13
2.1.90 把 files_struct 的 fd 成员从定长数组改成了动态数组,这样每个进程就能同时打开很多文件了,为编写高并发的网络服务扫清了一大障碍。
// include/linux/sched.h of linux-2.2.0
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
atomic_t count;
+ int max_fds;
+ struct file ** fd; /* current fd array */
fd_set close_on_exec; // changed to fd_set* in 2.2.12
fd_set open_fds;
- struct file * fd[NR_OPEN];
};数据结构示意图:

动态大小的文件描述符表
从 int fd 取到 struct file* fp 的写法不变,还是 current->files->fd[fd]。
至此,文件描述符表的功能已经完善,下一个版本是性能的改进。
版本 E:2.6.14 至今
2.6.14 引入了 struct fdtable 作为 files_struct 的间接成员,把 fd、max_fds、close_on_exec 等成员移入 fdtable。这么做是为了方便采用 RCU,让 fdtable 可以整体替换。Read-Copy Update (RCU) 是 Paul E. McKenney 的杰作,是内核广泛采用的一种伸缩性更好的读写同步机制,他还写了著名的《Is Parallel Programming Hard, And If So, What Can You Do About It?》一书。
// include/linux/fdtable.h of linux-2.6.37
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */
fd_set *close_on_exec;
fd_set *open_fds;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct fdtable *next;
};
/*
* Open file table structure
*/
struct files_struct {
/*
* read mostly part
*/
atomic_t count;
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
struct fdtable fdtab;
/*
* written part on a separate cache line in SMP
*/
spinlock_t file_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
int next_fd;
struct embedded_fd_set close_on_exec_init;
struct embedded_fd_set open_fds_init;
struct file __rcu * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];
};数据结构示意图如下:
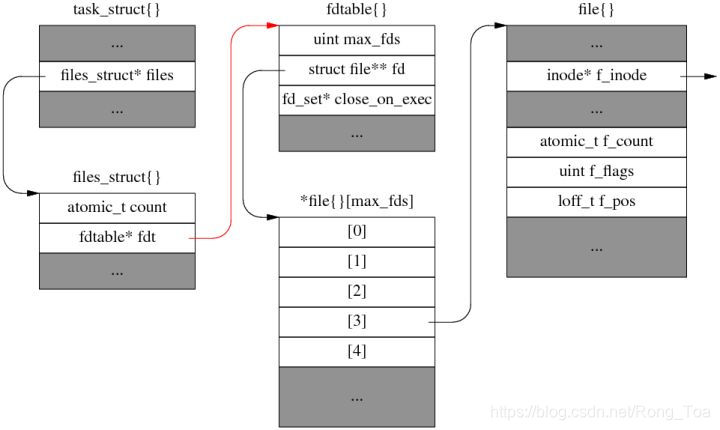
采用 RCU 之后的文件描述符表
从 int fd 取到 struct file* fp 的途径变成
current->files->fdt->fd[fd];实际的代码比这个要复杂,因为 files->fdt 这一步要用 rcu_dereference 来做(上图的红线)。
SO_REUSEPORT 和 dup(2)
将同一个listening socket加入多个epoll能否降低响应时间?有人提到可以对 listening socket 使用 dup(2) 来达到相同的效果,这是行不通的。原因在于 dup(2) 不会复制 struct file 本身,而只是复制 struct file 指针,并把 file 里的引用计数加一(f_count 成员)。对两个 fd 的读写操作还是通过同一个 file 对象进行,性能不会提高(见下图示意)。你把 3 和 4 两个 fd 分别加到两个 epoll 中,实际上是把同一个 file 加到了两个 epoll 中(file 的 f_ep_links 成员会把这两个 epoll 串起来),这跟 SO_REUSEPORT 有本质的区别。进一步可参考 《Linux 4.5/4.6 中对 SO_REUSEPORT 的改进》。

BSD 与 FreeBSD
最后,我们看看 BSD 与 FreeBSD 内核里是怎么做的。以下是 BSD 的版本简史。
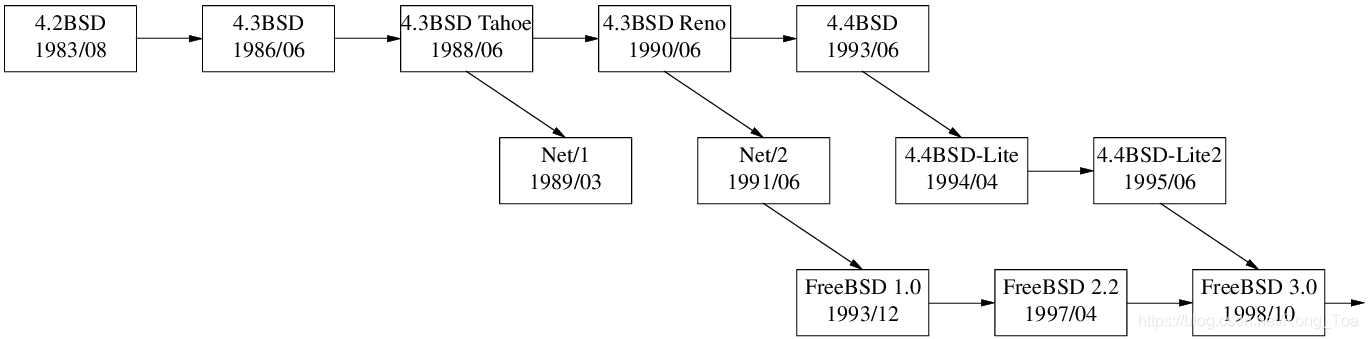
BSD 内核中文件描述符表的历史要简单得多。
4.3BSD-Reno 及以前的版本(上至 Unix V4)采用的是 Linux 版本 A 的做法,直接在进程的描述符里放 struct file* 的定长数组。
struct user {
// ...
struct file *u_ofile[NOFILE]; /* file structures for open files */
// ...
};Unix V7 的写法与此一模一样 http://minnie.tuhs.org/cgi-bin/utree.pl?file=V7/usr/sys/h/user.h 。
BSD Net/2 到 FreeBSD 9.3 采用的是 Linux 版本 D 的做法,其中 proc == task_struct, filedesc == files_struct, file == file。
// sys/proc.h
/*
* Process structure.
*/
struct proc {
// ...
struct filedesc *p_fd; /* (b) Open files. */
// ...
};
// sys/filedesc.h
struct filedesc {
struct file **fd_ofiles; /* file structures for open files */
char *fd_ofileflags; /* per-process open file flags */
struct vnode *fd_cdir; /* current directory */
struct vnode *fd_rdir; /* root directory */
struct vnode *fd_jdir; /* jail root directory */
int fd_nfiles; /* number of open files allocated */
NDSLOTTYPE *fd_map; /* bitmap of free fds */
int fd_lastfile; /* high-water mark of fd_ofiles */
int fd_freefile; /* approx. next free file */
u_short fd_cmask; /* mask for file creation */
u_short fd_refcnt; /* thread reference count */
u_short fd_holdcnt; /* hold count on structure + mutex */
struct sx fd_sx; /* protects members of this struct */
struct kqlist fd_kqlist; /* list of kqueues on this filedesc */
int fd_holdleaderscount; /* block fdfree() for shared close() */
int fd_holdleaderswakeup; /* fdfree() needs wakeup */
};
// sys/file.h
struct file {
void *f_data; /* file descriptor specific data */
struct fileops *f_ops; /* File operations */
struct ucred *f_cred; /* associated credentials. */
struct vnode *f_vnode; /* NULL or applicable vnode */
short f_type; /* descriptor type */
short f_vnread_flags; /* (f) Sleep lock for f_offset */
volatile u_int f_flag; /* see fcntl.h */
volatile u_int f_count; /* reference count */
// ...
off_t f_offset;
// ...
}; 可见 BSD 内核源码比 Linux 要工整得多,注释也很详尽。
























 2271
2271

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








