下面再介绍STL中与堆相关的4个函数——建立堆make_heap(),在堆中添加数据push_heap(),在堆中删除数据pop_heap()和堆排序sort_heap():
头文件 #include <algorithm>
下面的_First与_Last为可以随机访问的迭代器(指针),_Comp为比较函数(仿函数),其规则——如果函数的第一个参数小于第二个参数应返回true,否则返回false。
建立堆
make_heap(_First, _Last, _Comp)
默认是建立最大堆的。对int类型,可以在第三个参数传入greater<int>()得到最小堆。
在堆中添加数据
push_heap (_First, _Last)
要先在容器中加入数据,再调用push_heap ()
在堆中删除数据
pop_heap(_First, _Last)
要先调用pop_heap()再在容器中删除数据
堆排序
sort_heap(_First, _Last)
排序之后就不再是一个合法的heap了
有关堆与堆排序的更详细介绍请参阅——《白话经典算法系列之七 堆与堆排序》
下面给出STL中heap相关函数的使用范例:
- //by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <vector>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <functional>
- using namespace std;
- void PrintfVectorInt(vector<int> &vet)
- {
- for (vector<int>::iterator pos = vet.begin(); pos != vet.end(); pos++)
- printf("%d ", *pos);
- putchar('\n');
- }
- int main()
- {
- const int MAXN = 20;
- int a[MAXN];
- int i;
- for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
- a[i] = rand() % (MAXN * 2);
- //动态申请vector 并对vector建堆
- vector<int> *pvet = new vector<int>(40);
- pvet->assign(a, a + MAXN);
- //建堆
- make_heap(pvet->begin(), pvet->end());
- PrintfVectorInt(*pvet);
- //加入新数据 先在容器中加入,再调用push_heap()
- pvet->push_back(25);
- push_heap(pvet->begin(), pvet->end());
- PrintfVectorInt(*pvet);
- //删除数据 要先调用pop_heap(),再在容器中删除
- pop_heap(pvet->begin(), pvet->end());
- pvet->pop_back();
- pop_heap(pvet->begin(), pvet->end());
- pvet->pop_back();
- PrintfVectorInt(*pvet);
- //堆排序
- sort_heap(pvet->begin(), pvet->end());
- PrintfVectorInt(*pvet);
- delete pvet;
- return 0;
- }
掌握其基本用法后,我们用这个堆排序和《白话经典算法系列》中的堆排序、快速排序,归并排序来进行个性能测试(Win7 + VS2008 Release下),测试代码如下:
- // by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <ctime>
- using namespace std;
- //------------------------快速排序----------------------------
- void quick_sort(int s[], int l, int r)
- {
- if (l < r)
- {
- int i = l, j = r, x = s[l];
- while (i < j)
- {
- while(i < j && s[j] >= x) // 从右向左找第一个小于x的数
- j--;
- if(i < j)
- s[i++] = s[j];
- while(i < j && s[i] < x) // 从左向右找第一个大于等于x的数
- i++;
- if(i < j)
- s[j--] = s[i];
- }
- s[i] = x;
- quick_sort(s, l, i - 1); // 递归调用
- quick_sort(s, i + 1, r);
- }
- }
- //------------------------归并排序----------------------------
- //将有二个有序数列a[first...mid]和a[mid...last]合并。
- void mergearray(int a[], int first, int mid, int last, int temp[])
- {
- int i = first, j = mid + 1;
- int m = mid, n = last;
- int k = 0;
- while (i <= m && j <= n)
- {
- if (a[i] < a[j])
- temp[k++] = a[i++];
- else
- temp[k++] = a[j++];
- }
- while (i <= m)
- temp[k++] = a[i++];
- while (j <= n)
- temp[k++] = a[j++];
- for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
- a[first + i] = temp[i];
- }
- void mergesort(int a[], int first, int last, int temp[])
- {
- if (first < last)
- {
- int mid = (first + last) / 2;
- mergesort(a, first, mid, temp); //左边有序
- mergesort(a, mid + 1, last, temp); //右边有序
- mergearray(a, first, mid, last, temp); //再将二个有序数列合并
- }
- }
- bool MergeSort(int a[], int n)
- {
- int *p = new int[n];
- if (p == NULL)
- return false;
- mergesort(a, 0, n - 1, p);
- return true;
- }
- //------------------------堆排序---------------------------
- inline void Swap(int &a, int &b)
- {
- int c = a;
- a = b;
- b = c;
- }
- //建立最小堆
- // 从i节点开始调整,n为节点总数 从0开始计算 i节点的子节点为 2*i+1, 2*i+2
- void MinHeapFixdown(int a[], int i, int n)
- {
- int j, temp;
- temp = a[i];
- j = 2 * i + 1;
- while (j < n)
- {
- if (j + 1 < n && a[j + 1] < a[j]) //在左右孩子中找最小的
- j++;
- if (a[j] >= temp)
- break;
- a[i] = a[j]; //把较小的子结点往上移动,替换它的父结点
- i = j;
- j = 2 * i + 1;
- }
- a[i] = temp;
- }
- //建立最小堆
- void MakeMinHeap(int a[], int n)
- {
- for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
- MinHeapFixdown(a, i, n);
- }
- void MinheapsortTodescendarray(int a[], int n)
- {
- for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
- {
- Swap(a[i], a[0]);
- MinHeapFixdown(a, 0, i);
- }
- }
- const int MAXN = 5000000;
- int a[MAXN];
- int b[MAXN], c[MAXN], d[MAXN];
- int main()
- {
- int i;
- srand(time(NULL));
- for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
- a[i] = rand() * rand(); //注rand()产生的数在0到0x7FFF之间
- for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
- d[i] = c[i] = b[i] = a[i];
- clock_t ibegin, iend;
- printf("--当前数据量为%d--By MoreWindows(http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows)--\n", MAXN);
- //快速排序
- printf("快速排序: ");
- ibegin = clock();
- quick_sort(a, 0, MAXN - 1);
- iend = clock();
- printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
- //归并排序
- printf("归并排序: ");
- ibegin = clock();
- MergeSort(b, MAXN);
- iend = clock();
- printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
- //堆排序
- printf("堆排序: ");
- ibegin = clock();
- MakeMinHeap(c, MAXN);
- MinheapsortTodescendarray(c, MAXN);
- iend = clock();
- printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
- //STL中的堆排序
- printf("STL中的堆排序: ");
- ibegin = clock();
- make_heap(d, d + MAXN);
- sort_heap(d, d + MAXN);
- iend = clock();
- printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
- return 0;
- }
对100000(十万)个数据的测试结果:
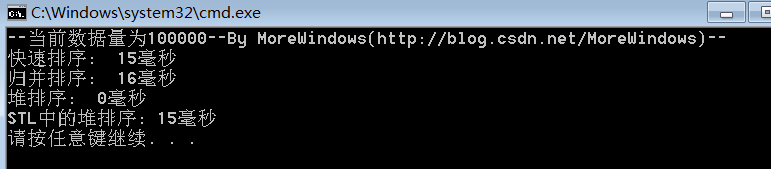
对500000(五十万)个数据的测试结果:
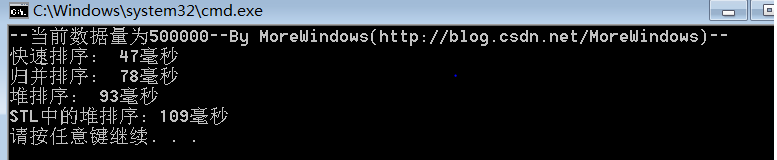
对1000000(一百万)个数据的测试结果:
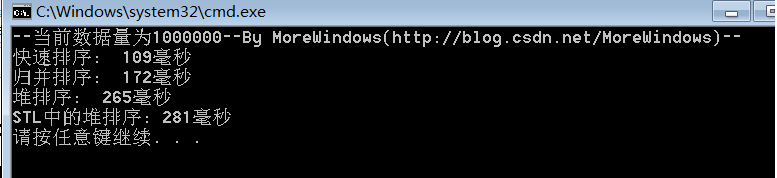
对5000000(五百万)个数据的测试结果:
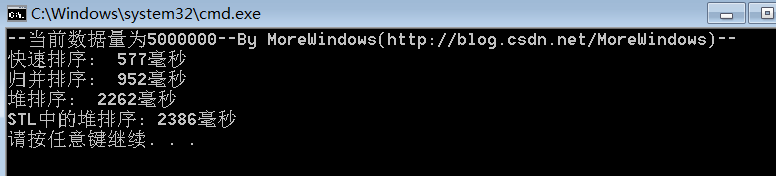
从中可以看出快速排序的效率确实要比其它同为O(N * logN)的排序算法要高,而STL中堆操作函数的性能与《白话经典算法系列之七 堆与堆排序》一文中堆操作函数的性能是相差无几的。






















 3026
3026

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








