目录
前言
如果你想快速了解一个下拉刷新,上拉加载更多框架的实现原理,这篇文章很适合你,欢迎参考!有什么好的建议,欢迎拍砖!
功能介绍
下来刷新,上拉加载更多几乎是每个Android应用必备的功能,多数情况下我们都是使用相对比较完善的第三方控件。
目前比较流行的第三方框架有:
大致列举这些,有精力的可以继续去github发掘。
但是当我们需要对下来刷新,上拉加载更多相关功能进行定制的话(如我们想定制header以及footer的动画效果等等),就需要理解此类控件的实现原理,so 这里以结构相对简单,实现相对清晰的XListView作为案例进行分析。
总体设计
组成
XListView的总体设计还是比较清晰的,控件的主体主要包含以下三个方面:
- XListView
- XListViewFooter
- XListViewHeader
还有一个测试Activity:XListViewActivity
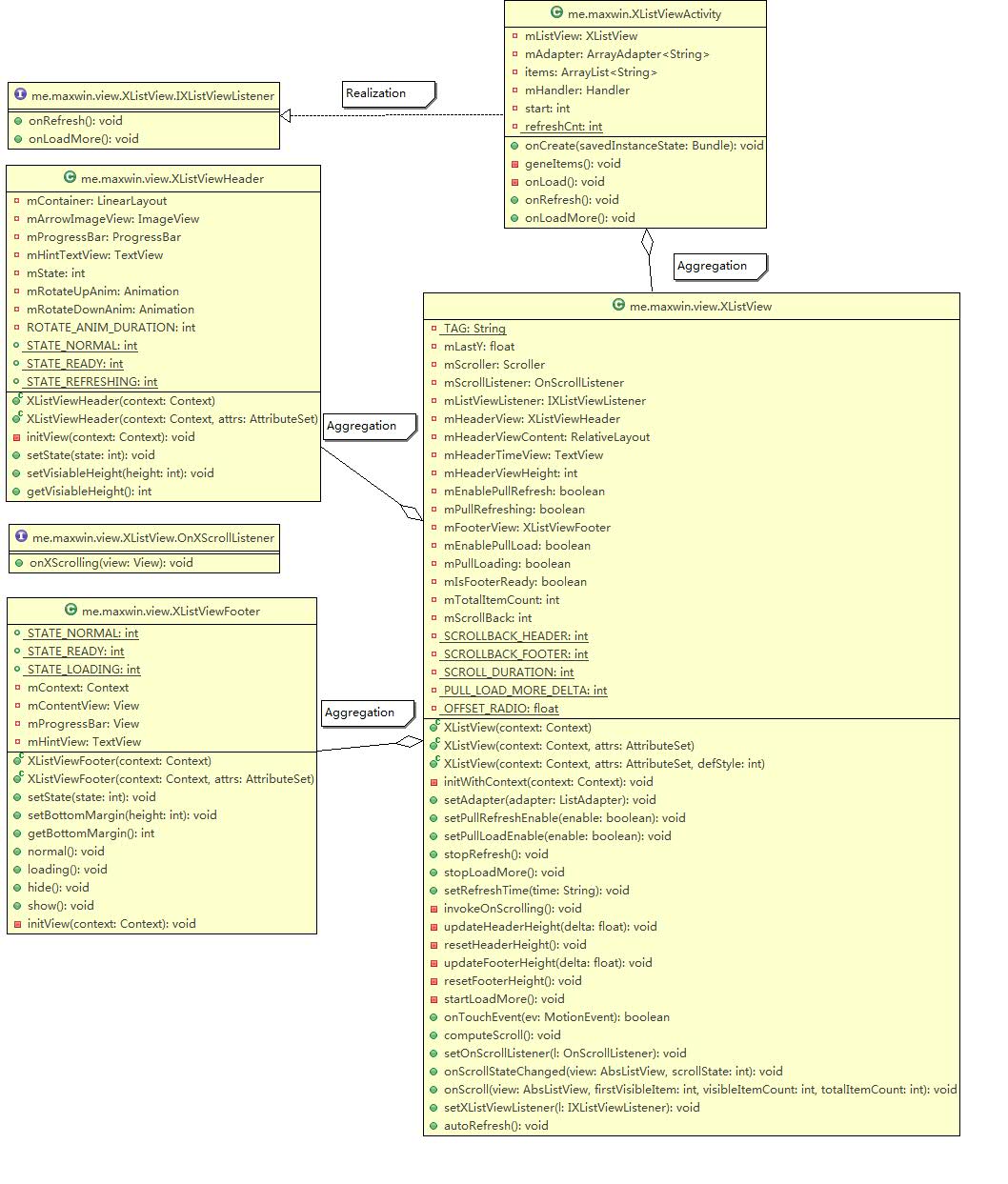
类关系图
它们之间的类关系图大致如下:
- XListView与XListViewFooter、XListView与XListViewHeader、 XListViewActivity与XListView之间都是聚合(Aggregation)关系,即has a关系
- XListViewActivity与IXListViewListener之间是实现(Realization)关系
详细设计
XlistViewHeader原理分析
涉及到view的,我们先从布局文件看起
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="bottom" >
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical" android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_text">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_hint_textview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/xlistview_header_hint_normal" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/xlistview_header_last_time"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_time"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_arrow"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/xlistview_header_text"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="-35dp"
android:src="@drawable/xlistview_arrow" />
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/xlistview_header_progressbar"
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:layout_alignLeft="@id/xlistview_header_text"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="-40dp"
android:visibility="invisible" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>这里我就不直接陈述了,直接顺着代码以注释的形式呈现更好。
//继承LinerLayout 实现下拉刷新的界面展示
public class XListViewHeader extends LinearLayout {
private LinearLayout mContainer;
//整个布局包含三部分控件
//随状态变化的可以朝上或者朝下的箭头
//说明文字(状态说明以及上次更新时间显示)
private ImageView mArrowImageView;
private ProgressBar mProgressBar;
private TextView mHintTextView;
private int mState = STATE_NORMAL;//默认为正常状态
//使箭头朝上或者朝下的动画
private Animation mRotateUpAnim;
private Animation mRotateDownAnim;
private final int ROTATE_ANIM_DURATION = 180;
//总共分为三个状态:正常、准备、正在刷新
public final static int STATE_NORMAL = 0;
public final static int STATE_READY = 1;
public final static int STATE_REFRESHING = 2;
public XListViewHeader(Context context) {
super(context);
initView(context);
}
/**
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public XListViewHeader(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context);
}
//构造函数中调用的视图初始化
private void initView(Context context) {
// 初始情况,设置下拉刷新view高度为0
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, 0);
mContainer = (LinearLayout) LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(
R.layout.xlistview_header, null);
addView(mContainer, lp);
setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM);
//箭头动画设置,完成箭头的旋转
mArrowImageView = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.xlistview_header_arrow);
mHintTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.xlistview_header_hint_textview);
mProgressBar = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.xlistview_header_progressbar);
mRotateUpAnim = new RotateAnimation(0.0f, -180.0f,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,
0.5f);
mRotateUpAnim.setDuration(ROTATE_ANIM_DURATION);
mRotateUpAnim.setFillAfter(true);
mRotateDownAnim = new RotateAnimation(-180.0f, 0.0f,
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,
0.5f);
mRotateDownAnim.setDuration(ROTATE_ANIM_DURATION);
mRotateDownAnim.setFillAfter(true);
}
//设置header状态,完成不同状态下控件的显示,主要在XListView中调用
public void setState(int state) {
if (state == mState) return ;
if (state == STATE_REFRESHING) { // 显示进度
mArrowImageView.clearAnimation();
mArrowImageView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
} else { // 显示箭头图片
mArrowImageView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
switch(state){
case STATE_NORMAL:
if (mState == STATE_READY) {
mArrowImageView.startAnimation(mRotateDownAnim);
}
if (mState == STATE_REFRESHING) {
mArrowImageView.clearAnimation();
}
mHintTextView.setText(R.string.xlistview_header_hint_normal);//下拉刷新
break;
case STATE_READY:
if (mState != STATE_READY) {
mArrowImageView.clearAnimation();
mArrowImageView.startAnimation(mRotateUpAnim);
mHintTextView.setText(R.string.xlistview_header_hint_ready);//松开刷新数据<
}
break;
case STATE_REFRESHING:
mHintTextView.setText(R.string.xlistview_header_hint_loading);//正在加载...
break;
default:
}
mState = state;
//设置Header中根布局文件高度属性
public void setVisiableHeight(int height) {
if (height < 0)
height = 0;
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) mContainer
.getLayoutParams();
lp.height = height;
mContainer.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
//获取Header中根文件高度属性,同setVisiableHeight()方法一起完成拉伸和收缩的效果
public int getVisiableHeight() {
//之前的代码
// return mContainer.height
//现在改为如下代码
//解决的问题:修复快速下拉无法回弹,或者UI线程繁忙的时候无法下拉刷新BUG
//原因:onTouch事件和UI线程属于同一个线程,所以得到的高度不是准确的。
return mContainer.getLayoutParams().height;
}
}
XListViewFooter原理分析
同样先看布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/xlistview_footer_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10dp" >
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/xlistview_footer_progressbar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:visibility="invisible" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/xlistview_footer_hint_textview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="@string/xlistview_footer_hint_normal" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>套路同上
public class XListViewFooter extends LinearLayout {
//与XListViewHeader的思路一致,分为正常、准备和加载三种状态
public final static int STATE_NORMAL = 0;
public final static int STATE_READY = 1;
public final static int STATE_LOADING = 2;
private Context mContext;
private View mContentView;
//两个控件
private View mProgressBar;
private TextView mHintView;
public XListViewFooter(Context context) {
super(context);
initView(context);
}
public XListViewFooter(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initView(context);
}
//设置footer的状态,主要在XListView中调用
public void setState(int state) {
mHintView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
mHintView.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
if (state == STATE_READY) {
mHintView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mHintView.setText(R.string.xlistview_footer_hint_ready);//松开载入更多
} else if (state == STATE_LOADING) {
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
} else {
mHintView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mHintView.setText(R.string.xlistview_footer_hint_normal);//查看更多
}
}
//区别于XListViewHeader通过设置可视高度完成拉伸以及收缩的视觉效果
//这里通过设置bottomMargin来完成
public void setBottomMargin(int height) {
if (height < 0) return ;
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)mContentView.getLayoutParams();
lp.bottomMargin = height;
mContentView.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
public int getBottomMargin() {
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)mContentView.getLayoutParams();
return lp.bottomMargin;
}
/**
* normal status
*/
public void normal() {
mHintView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
/**
* loading status
*/
public void loading() {
mHintView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mProgressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
/**
* hide footer when disable pull load more
*/
public void hide() {
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)mContentView.getLayoutParams();
lp.height = 0;
mContentView.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
/**
* show footer
*/
public void show() {
LinearLayout.LayoutParams lp = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams)mContentView.getLayoutParams();
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
mContentView.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
private void initView(Context context) {
mContext = context;
LinearLayout moreView = (LinearLayout)LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.xlistview_footer, null);
addView(moreView);
moreView.setLayoutParams(new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
mContentView = moreView.findViewById(R.id.xlistview_footer_content);
mProgressBar = moreView.findViewById(R.id.xlistview_footer_progressbar);
mHintView = (TextView)moreView.findViewById(R.id.xlistview_footer_hint_textview);
}
}XListView原理分析
这里在源码的基础上添加了大量注释以及增加了一个进入自动刷新的功能,详见autoRefresh方法
public class XListView extends ListView implements OnScrollListener {
private static final String TAG = "XListView";
private float mLastY = -1; // save event y
//Header是通过设置height,Footer是通过设置BottomMargin来模拟拉伸效果
//这里通过Scroller来实现模拟回弹效果
private Scroller mScroller; // used for scroll back
private OnScrollListener mScrollListener; // user's scroll listener
// the interface to trigger refresh and load more.
private IXListViewListener mListViewListener;
// -- header view
private XListViewHeader mHeaderView;
// header view content, use it to calculate the Header's height. And hide it
// when disable pull refresh.
private RelativeLayout mHeaderViewContent;
private TextView mHeaderTimeView;
private int mHeaderViewHeight; // header view's height
private boolean mEnablePullRefresh = true;
private boolean mPullRefreshing = false; // is refreashing.
// -- footer view
private XListViewFooter mFooterView;
private boolean mEnablePullLoad;
private boolean mPullLoading;
private boolean mIsFooterReady = false;
// total list items, used to detect is at the bottom of listview.
private int mTotalItemCount;
// for mScroller, scroll back from header or footer.
private int mScrollBack;
private final static int SCROLLBACK_HEADER = 0;//header回弹
private final static int SCROLLBACK_FOOTER = 1;//footer回弹
private final static int SCROLL_DURATION = 400; // scroll back duration
private final static int PULL_LOAD_MORE_DELTA = 50; // when pull up >= 50px
// at bottom, trigger
// load more.
private final static float OFFSET_RADIO = 1.8f; // support iOS like pull
// feature.
/**
* @param context
*/
public XListView(Context context) {
super(context);
initWithContext(context);
}
public XListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
initWithContext(context);
}
public XListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
initWithContext(context);
}
private void initWithContext(Context context) {
mScroller = new Scroller(context, new DecelerateInterpolator());
// XListView need the scroll event, and it will dispatch the event to
// user's listener (as a proxy).
super.setOnScrollListener(this);
// init header view
mHeaderView = new XListViewHeader(context);
mHeaderViewContent = (RelativeLayout) mHeaderView
.findViewById(R.id.xlistview_header_content);
mHeaderTimeView = (TextView) mHeaderView.findViewById(R.id.xlistview_header_time);
//Header和Footer通过addHeaderView和addFooterView【详情见setAdapter方法】添加上去
addHeaderView(mHeaderView);
// init footer view
mFooterView = new XListViewFooter(context);
mHeaderView.getHeight();
Log.d(TAG, "initWithContext() mHeaderView.getHeight()--->" + mHeaderView.getHeight());// 0
Log.d(TAG, "initWithContext() mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight()--->"
+ mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight());// 0
Log.d(TAG, "initWithContext() mHeaderViewContent.getHeight()--->"
+ mHeaderViewContent.getHeight());// 0
// init header height
// ViewTreeObserver监听很多不同的界面绘制事件。一般来说OnGlobalLayoutListener就是可以让我们获得到view的width和height的地方.
// 下面onGlobalLayout内的代码会在View完成Layout过程后调用
mHeaderView.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
mHeaderViewHeight = mHeaderViewContent.getHeight();
Log.d(TAG, "onGlobalLayout() mHeaderViewHeight--->" + mHeaderViewHeight);// 240
// 但是要注意这个方法在每次有些view的Layout发生变化的时候被调用(比如某个View被设置为Invisible),
// 所以在得到你想要的宽高后,记得移除onGlobleLayoutListener:
// 期间看到如下类似问题,有兴趣的可以看一下
// 附上相关问题链接
//http://stackoverflow.com/questions/15162821/why-does-removeongloballayoutlistener-throw-a-nosuchmethoderror
//http://stackoverflow.com/questions/12867760/fragment-removeglobalonlayoutlistener-illegalstateexception
getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(this);
}
});
}
@Override
public void setAdapter(ListAdapter adapter) {
// make sure XListViewFooter is the last footer view, and only add once.
if (mIsFooterReady == false) {
mIsFooterReady = true;
addFooterView(mFooterView);
}
super.setAdapter(adapter);
}
/**
* enable or disable pull down refresh feature.
*
* @param enable
*/
public void setPullRefreshEnable(boolean enable) {
mEnablePullRefresh = enable;
if (!mEnablePullRefresh) { // disable, hide the content
mHeaderViewContent.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
} else {
mHeaderViewContent.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
}
/**
* enable or disable pull up load more feature.
*
* @param enable
*/
public void setPullLoadEnable(boolean enable) {
mEnablePullLoad = enable;
if (!mEnablePullLoad) {
mFooterView.hide();
mFooterView.setOnClickListener(null);
// make sure "pull up" don't show a line in bottom when listview
// with one page
setFooterDividersEnabled(false);
} else {
mPullLoading = false;
mFooterView.show();
mFooterView.setState(XListViewFooter.STATE_NORMAL);
// make sure "pull up" don't show a line in bottom when listview
// with one page
setFooterDividersEnabled(true);
// both "pull up" and "click" will invoke load more.
mFooterView.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
startLoadMore();
}
});
}
}
/**
* stop refresh, reset header view.
*/
public void stopRefresh() {
if (mPullRefreshing == true) {
mPullRefreshing = false;
resetHeaderHeight();
}
}
/**
* stop load more, reset footer view.
*/
public void stopLoadMore() {
if (mPullLoading == true) {
mPullLoading = false;
mFooterView.setState(XListViewFooter.STATE_NORMAL);
}
}
/**
* set last refresh time
*
* @param time
*/
public void setRefreshTime(String time) {
mHeaderTimeView.setText(time);
}
private void invokeOnScrolling() {
if (mScrollListener instanceof OnXScrollListener) {
OnXScrollListener l = (OnXScrollListener) mScrollListener;
l.onXScrolling(this);
}
}
private void updateHeaderHeight(float delta) {
mHeaderView.setVisiableHeight((int) delta + mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight());
if (mEnablePullRefresh && !mPullRefreshing) { // 未处于刷新状态,更新箭头
if (mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight() > mHeaderViewHeight) {
mHeaderView.setState(XListViewHeader.STATE_READY);
} else {
mHeaderView.setState(XListViewHeader.STATE_NORMAL);
}
}
setSelection(0); // scroll to top each time
}
/**
* reset header view's height.
*/
private void resetHeaderHeight() {
int height = mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight();
if (height == 0) // not visible.
return;
// refreshing and header isn't shown fully. do nothing.
if (mPullRefreshing && height <= mHeaderViewHeight) {
return;
}
int finalHeight = 0; // default: scroll back to dismiss header.
// is refreshing, just scroll back to show all the header.
if (mPullRefreshing && height > mHeaderViewHeight) {
finalHeight = mHeaderViewHeight;
}
mScrollBack = SCROLLBACK_HEADER;
//滚动操作实现,computeScroll会被调用
//startScroll这个方法可以这么理解 从height的间距变成height + finalHeight - height
//官方api的参数有时挺难理解
mScroller.startScroll(0, height, 0, finalHeight - height, SCROLL_DURATION);
// trigger computeScroll
invalidate();
}
private void updateFooterHeight(float delta) {
int height = mFooterView.getBottomMargin() + (int) delta;
if (mEnablePullLoad && !mPullLoading) {
if (height > PULL_LOAD_MORE_DELTA) { // height enough to invoke load
// more.
mFooterView.setState(XListViewFooter.STATE_READY);
} else {
mFooterView.setState(XListViewFooter.STATE_NORMAL);
}
}
mFooterView.setBottomMargin(height);
// setSelection(mTotalItemCount - 1); // scroll to bottom
}
private void resetFooterHeight() {
int bottomMargin = mFooterView.getBottomMargin();
Log.d(TAG, "resetFooterHeight() bottomMargin--->" + bottomMargin);
if (bottomMargin > 0) {
mScrollBack = SCROLLBACK_FOOTER;
//滚动操作实现,computeScroll会被调用
//startScroll这个方法可以这么理解 从height的间距变成bottomMargin -bottomMargin
mScroller.startScroll(0, bottomMargin, 0, -bottomMargin, SCROLL_DURATION);
invalidate();
}
}
private void startLoadMore() {
mPullLoading = true;
mFooterView.setState(XListViewFooter.STATE_LOADING);
if (mListViewListener != null) {
mListViewListener.onLoadMore();
}
}
//通过用户的手势和距离进行判断
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//如果adapter中有10个数据,其实listView当中是有12个item的
//mTotalItemCount = getAdapter().getCount();
if (mLastY == -1) {
//getRowY()是获取元Y坐标,即与Window和View坐标没有关系的坐标,代表在屏幕上的绝对位置
mLastY = ev.getRawY();
}
switch (ev.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mLastY = ev.getRawY();
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//move的过程会不断调用updateHeaderHeight()和updateFooterHeight()方法
final float deltaY = ev.getRawY() - mLastY;
//deltaY>0即为向下滑动,反之是向上滑动
mLastY = ev.getRawY();
//OFFSET_RADIO为一个移动比例,控制用户滑动的体验
//如果手指移动180px,按照这个比例,控件移动100px
if (getFirstVisiblePosition() == 0
&& (mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight() > 0 || deltaY > 0)) {
// the first item is showing, header has shown or pull down.
updateHeaderHeight(deltaY / OFFSET_RADIO);
invokeOnScrolling();
} else if (getLastVisiblePosition() == mTotalItemCount - 1
&& (mFooterView.getBottomMargin() > 0 || deltaY < 0)) {
// last item, already pulled up or want to pull up.
updateFooterHeight(-deltaY / OFFSET_RADIO);
}
break;
default:
//这里其实多数是指MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE
//手指移开会调用resetHeaderHeight()以及 resetFooterHeight()
mLastY = -1; // reset
if (getFirstVisiblePosition() == 0) {
// invoke refresh
if (mEnablePullRefresh && mHeaderView.getVisiableHeight() > mHeaderViewHeight) {
mPullRefreshing = true;
mHeaderView.setState(XListViewHeader.STATE_REFRESHING);
if (mListViewListener != null) {
mListViewListener.onRefresh();
}
}
resetHeaderHeight();
} else if (getLastVisiblePosition() == mTotalItemCount - 1) {
// invoke load more.
if (mEnablePullLoad && mFooterView.getBottomMargin() > PULL_LOAD_MORE_DELTA
&& !mPullLoading) {
startLoadMore();
}
resetFooterHeight();
}
break;
}
return super.onTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
if (mScrollBack == SCROLLBACK_HEADER) {
mHeaderView.setVisiableHeight(mScroller.getCurrY());
} else {
mFooterView.setBottomMargin(mScroller.getCurrY());
}
//Log.d(TAG, "computeScroll() mScroller.getCurrY()--->" + mScroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
invokeOnScrolling();
}
super.computeScroll();
}
//其实没用到
@Override
public void setOnScrollListener(OnScrollListener l) {
Log.d(TAG, "setOnScrollListener()--->");
mScrollListener = l;
}
// 在initWithContext中调用了super.setOnScrollListener(this),并且实现了onSrollerListener
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView view, int scrollState) {
//可以理解成从父类的回调,但是mScrollListener其实为空,下面的onScroll类似
Log.d(TAG, "onScrollStateChanged()--->");
if (mScrollListener != null) {
mScrollListener.onScrollStateChanged(view, scrollState);
}else{
Log.d(TAG, "onScrollStateChanged()---> mScrollListener is null");
}
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView view, int firstVisibleItem, int visibleItemCount,
int totalItemCount) {
Log.d(TAG, "onScroll()--->");
// send to user's listener
mTotalItemCount = totalItemCount;
if (mScrollListener != null) {
mScrollListener.onScroll(view, firstVisibleItem, visibleItemCount, totalItemCount);
}else{
Log.d(TAG, "onScroll()---> mScrollListener is null");
}
}
public void setXListViewListener(IXListViewListener l) {
mListViewListener = l;
}
//进入自动刷新
public void autoRefresh() {
mLastY = -1; // reset
// 判断是否在第一行,如果不是第一行,则不执行
if (getFirstVisiblePosition() == 0) {
// 判断是否可刷新和不处于刷新状态
if (mEnablePullRefresh && mPullRefreshing != true) {
mPullRefreshing = true;
mScrollBack = SCROLLBACK_HEADER;
if (mHeaderViewHeight == 0) {
int width = ((WindowManager) this.getContext()
.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE)).getDefaultDisplay()
.getWidth();
mHeaderViewContent.measure(
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(width, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST),
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec((1 << 30) - 1, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST));
mScroller.startScroll(0, 0, 0, mHeaderViewContent.getMeasuredHeight(),
SCROLL_DURATION);
invalidate();
} else {
mScroller.startScroll(0, 0, 0, mHeaderViewHeight, SCROLL_DURATION);
invalidate();
}
mHeaderView.setState(XListViewHeader.STATE_REFRESHING);
if (mListViewListener != null) {
mListViewListener.onRefresh();
}
}
resetHeaderHeight();
}
}
/**
* you can listen ListView.OnScrollListener or this one. it will invoke
* onXScrolling when header/footer scroll back.
*/
public interface OnXScrollListener extends OnScrollListener {
public void onXScrolling(View view);
}
/**
* implements this interface to get refresh/load more event.
*/
public interface IXListViewListener {
public void onRefresh();
public void onLoadMore();
}
}
代码(带注释)下载
源代码地址:click here























 697
697

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








