set是python中一个无序且无重复元素的数据结构。无序,是因为set采用了hash技术进行元素的存储;无重复元素,本身就是set区别其他数据结构的一个重要特点,也是set之间能够进行并,交,差等各种集合运算的基础。set主要有两大类的操作。
(1)set本身的操作
1.初始化
s0 = {1, 2, 3}
s1 = set()
s2 = set('set')
s3 = set([1, 2, 3])
s4 = set((1, 2, 3))
print(s0, s1, s2, s3, s4, sep='\n')注意:set与dict一样使用{}来表示,但s={}创建的是空dict,不是创建空set。创建一个空set需要使用s=set()。输出结果:{1, 2, 3}set(){'s', 't', 'e'}{1, 2, 3}{1, 2, 3}
字符串str、列表list、元组tuple可以直接转换成set。
2.新增元素add和update
s = {1, 2, 'a', 5, 'b'}
s.add(7)
print(s)
s.add('a')
print(s)
s.add('ab')
print(s)
输出结果:{1, 2, 5, 'a', 7, 'b'}{1, 2, 5, 'a', 7, 'b'}{1, 2, 5, 'a', 7, 'ab', 'b'}
可以看出:1)如果新增的元素在原set已存在,则什么都不发生。2)add只是增加一个元素,所以即使一个字符串含有多个字符,也不会像初始化那样进行拆分。3)添加结果是无序的,并不一定是添加到尾部。
a = {1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'}
b = 'xyz'
c = {'xyz', 'abc'}
a.update(b)
print(a)
a.update(c)
print(a)
可以看出:1)update是批量的添加多个元素或集合;2)添加结果是无序的,并非是添加到尾部。输出结果:{'b', 1, 2, 3, 'a', 'x', 'z', 'y', 'c'}{'b', 1, 2, 3, 'xyz', 'a', 'abc', 'x', 'z', 'y', 'c'}
s = {1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b', 'c'}
s.remove(1)
print(s)
s.discard('a')
print(s)
s.pop()
print(s)
s.clear()
print(s)
删除元素有remove,discard,pop,clear操作。可以看出,clear是清空集合,使得集合重置为空;输出结果:{2, 3, 'c', 'a', 'b'}{2, 3, 'c', 'b'}{3, 'c', 'b'}set()
pop是任意选一个元素删除,并返回这个元素的值,clear和pop都没有输入参数;remove和discard都是删除一个指定的元素,区别是如果该元素不存在集合中,则remove会报错。
(2)set与set之间的操作:并集、交集、差集等
set是集合的数据结构,集合也是数学中的重要概念,并集、交集、差集等是集合的基本运算。
1.并集union
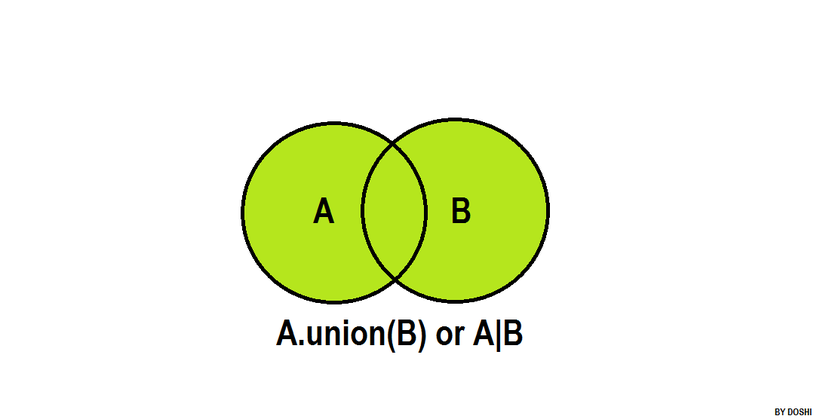
union()返回两个集合的并集。
s1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
print(s1.union(s2))
print(s2.union(s1))
print(s1 | s2)
可以看出:A.union(B)==B.union(A)==A|B==B|A输出结果:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
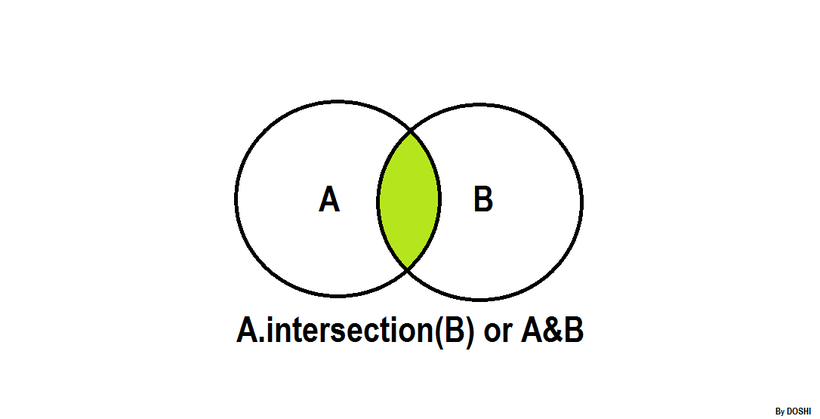
s1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
print(s1.intersection(s2))
print(s2.intersection(s1))
print(s1 & s2)
可以看出:A.intersection(B)==B.intersection(A)==A&B==B&A输出结果:{6, 7}{6, 7}{6, 7}

s1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
print(s1.difference(s2))
print(s2.difference(s1))
print(s1 - s2)
print(s2 - s1)
可以看出:1)A.difference(B) 不等于 B.difference(A),从上图中也可以看出来;2)difference可以使用“-”减号代替。输出结果:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}{8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}{8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
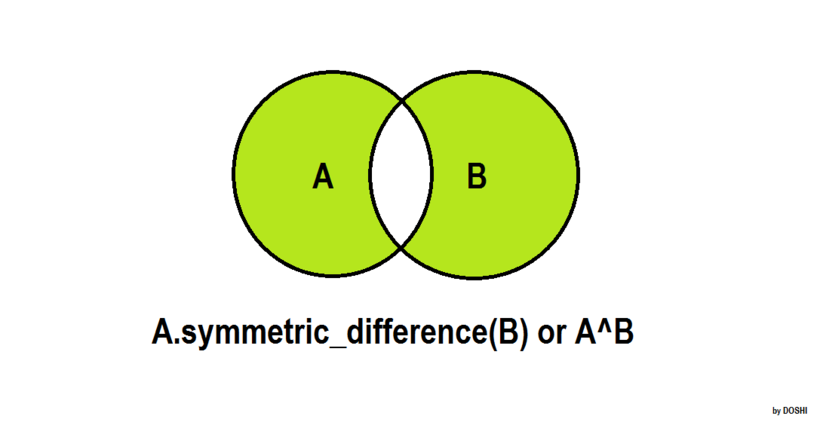
在集合A或集合B中,但又不同时在集合A和集合B中。
s1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
print(s1.symmetric_difference(s2))
print(s2.symmetric_difference(s1))
print(s1 ^ s2)
print(s2 ^ s1)
输出结果:{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
5.子集issubset,超集issuperset
判断一个集合是否是另一个集合的子集或超集,可以使用符号‘<=’,‘>’。
s1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12}
s3 = {1, 2, 3}
s4 = {1, 2, 3}
print(s1.issubset(s2))
print(s3.issubset(s1))
print(s1.issuperset(s3))
print(s4 <= s3)
print(s1 > s3)
输出结果:FalseTrueTrueTrueTrue
(3)set的一些重要特点
除了可以进行并、交、差等集合运算外,set还有一些其他特点。
1.初始化时的元素必须是hashable的类型
s = {1, 2, [3, 4, 5]}
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
初始化时,其中有一个列表[3,4,5],列表是unhashable type,因此报错。
s = {1, 2, (3, 4, 5), 'abc'}
print(s)
元组、字符串等hashable类型是可以的。{'abc', (3, 4, 5), 2, 1}
set是一个无序的数据结构,没有位置的概念,因此不支持通常的序列索引和切片操作。所有意图进行indexing和slice的操作都将报错。
3.可以用于去除重复元素
s = {1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5}
s = list(set(s))
print(s)
输出结果:[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
set使用hash技术进行元素的存储,因此其查询操作时间复杂度是O(1)的,远远高于列表的O(N)复杂度。
import time
st = time.clock()
N = 50000
arr = [i for i in range(N)]
A = [i for i in range(N) if i % 2 == 0]
B = [i for i in range(N) if i % 2 == 1]
count = 0
for x in arr:
if x in A:
count += 1
elif x in B:
count -= 1
print(count)
print(time.clock() - st)
耗时近24秒。如果把A、B转换成set,进行同样的运算:输出结果:023.8880947819304
import time
st = time.clock()
N = 50000
arr = [i for i in range(N)]
A = set([i for i in range(N) if i % 2 == 0])
B = set([i for i in range(N) if i % 2 == 1])
count = 0
for x in arr:
if x in A:
count += 1
elif x in B:
count -= 1
print(count)
print(time.clock() - st)
耗时0.03624秒,list是set耗时的660倍。因此,当需要对一个无重复元素数据集频繁进行查询操作时,使用set是一个很好的选择。输出结果:00.03624072844963256
























 1409
1409

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








