springboot启动一个项目代码例子如下
SpringApplication.run(xxxx.class, args);
跟踪进去如下
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource,
String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources,
String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
上面是创建了一个SpringApplication对象,然后调用其run方法
SpringApplication构造方法:
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
//上面传null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//上面传运行的主方法的类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//三种类型:REACTIVE|NONE|SERVLET;REACTIVE对应spring5新增的webflux;SERVLET是传统servlet
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
//从META-INF/spring.factories文件获取ApplicationContextInitializer类型的类
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//从META-INF/spring.factories文件获取ApplicationListener类型的类
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//获取运行的主方法的类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
创建了SpringApplication对象后,接着执行它的run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();//性能监控
//Spring容器类
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//SpringBootExceptionReporter类
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();//设置系统的“java.awt.headless”属性
//从META-INF/spring.factories中获得SpringApplicationRunListener类型的类,放进SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();//开始事件
try {
//命令行启动的参数封装到DefaultApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//【标记1】实例或配置好environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//对系统中的“spring.beaninfo.ignore”属性进行处理
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印招牌
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//【标记2】创建容器,三种类型
context = createApplicationContext();
//从META-INF/spring.factories中获取SpringBootExceptionReporter类型的类
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//【标记3】准备容器
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//刷新容器
refreshContext(context);
//留给子类实现
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//性能监控停止
stopWatch.stop();
//打印信息,主要关于启动时间
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//监听器回调started
listeners.started(context);
//执行实现了ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner接口的bean的run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//会回调listener的failed方法
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//监听器回调running方法
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
上面的springboot的启动流程一目了然了,准备好环境environment,准备好容器context,然后加载好各种资源到容器中,接着启动。
【标记1】实例或配置好environment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建Environment类型对象,三种:StandardServletEnvironment|StandardReactiveWebEnvironment|StandardEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置Environment的一些属性
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//监听器回调environmentPrepared方法
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//绑定environment(其实还没看懂干嘛)
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
//这里再次检测是否需要把environment转为对应类型的environment,上面getOrCreateEnvironment里不是判断过了吗??
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
//这里把environment中的propertySources成员中的configurationProperties键对应的值替换为SpringConfigurationPropertySources
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
【标记2】创建容器,三种类型
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch...
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
【标记3】准备容器
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置environment
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//设置bean名字生成器、resourceloader、classloader、ApplicationConversionService
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//执行从META-INF/spring.factories中获取的ApplicationContextInitializer类型的initialize方法
applyInitializers(context);
//监听器回调contextPrepared方法,容器已经准备好
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
//打印信息:主要关于active profile的
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//向beanFactory注册了bean
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
//设置是否允许覆盖bean
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//开始加载资源
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//监听器回调contextLoaded,容器已经加载完
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
prepareContext方法中会执行ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法,执行完的时候,当prepareContext方法执行完容器已加载好了资源
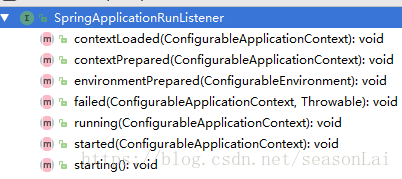
总结一下SpringApplicationRunListener的回调顺序
SpringApplicationRunListener共7个方法,回调顺序为:
starting -> environmentPrepared -> contextPrepared -> contextLoaded -> started -> running
failed方法在running前执行有错误发现才回调
对应事件为:
ApplicationStartingEvent -> ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent -> ApplicationContextInitializedEvent -> ApplicationPreparedEvent -> ApplicationStartedEvent -> ApplicationReadyEvent
----------------------------- 分割线 -----------------------------
SpringBoot是使用内嵌的服务容器运行起来的,上面没提及到哪里启动了服务容器,如servlet、reactive。其实是在refreshContext(context)刷新容器的时候启动的。
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);//刷新容器
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();//注册钩子方法
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
...
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
...
try {
...
this.onRefresh();
...
this.finishRefresh();
} catch ...
}
}
上面有提到applicationContext会在三种类型中选一种,其中ServletWebServerApplicationContext和ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext都重写了onRefresh()、finishRefresh()方法。
以ServletWebServerApplicationContext为例
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
protected void finishRefresh() {
super.finishRefresh();
WebServer webServer = startWebServer();
if (webServer != null) {
publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this));
}
}
可以看到在onRefresh()创建服务容器,在finishRefresh()启动容器。
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//去spring容器中找ServletWebServerFactory类型的bean
//springboot默认注入TomcatServletWebServerFactory
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context",
ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();//向servletContext存入相关配置属性
}
上面通过工厂模式抽象出ServletWebServerFactory 类,用户可以随意切换servlet容器,如tomcat、jetty等。接下来就是具体工厂根据不同的servlet容器,编程式地创建相关的对象。如tomcat的话就创建Tomcat对象,并配置好service,host、connector等属性。这方面知识需要深入了解相关容器。






















 959
959











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








