SpringMVC执行流程
文章目录
前言:
springmvc是在spring的基础上,增加了一个springmvc的容器,并且将这个两个容器运行在tomcat中,springmvc用来处理客户端发来的请求,主要的处理依靠的是springmvc中九大内置组件,在doDispatch()中完成请求的处理,视图处理,最终前端页面渲染。
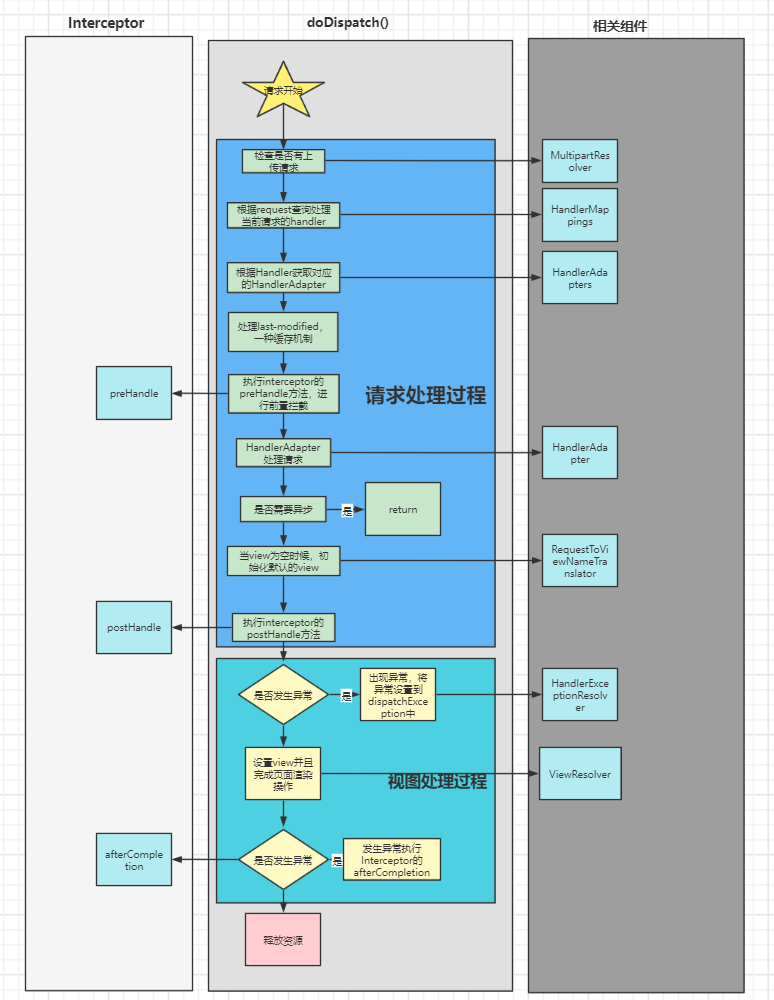
spring九大内置组件
- HandlerMapping:映射器,用来完成request和controller的对应
- HandlerAdapter:处理器适配器,主要包含Http请求处理器适配器,简单控制处理适配器,注解方法处理器
- LocalResolver:主要用来处理国际化配置,基于URL参数的配置
- ThemeResolver:主要用来设置主题
- MulitpartResolver:主要用来处理文件上传
- HandlerExceptionResolver:主要用来对异常进行处理,主要有三个实现类
- RequestToViewResolver:当Controller处理方法没有返回一个View对象的时候,用当前处理器来赋予一个默认值
- ViewResolver:将ModelAndView选择合适的视图进行渲染处理器
- FlashMapManager:提供请求存储方法,主要在重定向的请求中使用它来传递参数
1.处理上传请求
检查是不是上传文件请求,调用checkMultipart()
- 调用resolveMultipart(),来解析请求,最终都是封装一个MultipartHttpServletRequest对象返回
@Override
public MultipartHttpServletRequest resolveMultipart(final HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
Assert.notNull(request, "Request must not be null");
// 是否是懒加载
if (this.resolveLazily) {
return new DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest(request) {
@Override
protected void initializeMultipart() {
MultipartParsingResult parsingResult = parseRequest(request);
setMultipartFiles(parsingResult.getMultipartFiles());
setMultipartParameters(parsingResult.getMultipartParameters());
setMultipartParameterContentTypes(parsingResult.getMultipartParameterContentTypes());
}
};
}
else {
// 不是懒加载,直接解析
MultipartParsingResult parsingResult = parseRequest(request);
// 将解析的结果封装成DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest返回
return new DefaultMultipartHttpServletRequest(request, parsingResult.getMultipartFiles(),
parsingResult.getMultipartParameters(), parsingResult.getMultipartParameterContentTypes());
}
}
- 调用parseRequest()进行解析,在这个方法中会遍历每一个上传过来的属性值,遍历处理,判断值是不是文件类型,创建一个FileItem对象,然后将解析到的属性值封装到MultipartParsingResult对象中返回
protected MultipartParsingResult parseRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
// 确定编码
String encoding = determineEncoding(request);
FileUpload fileUpload = prepareFileUpload(encoding);
try {
// 获取表单提交的所有属性值
List<FileItem> fileItems = ((ServletFileUpload) fileUpload).parseRequest(request);
// 将解析到的结果封装成MultipartParsingResult返回
return parseFileItems(fileItems, encoding);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.SizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadBase.FileSizeLimitExceededException ex) {
throw new MaxUploadSizeExceededException(fileUpload.getFileSizeMax(), ex);
}
catch (FileUploadException ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Failed to parse multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}
2.获取请求处理处理器
根据request获取到对应Handler,调用getHandler()方法
- 遍历所有的HandlerMapping,来寻找能处理当前请求的Handler,也就是Controller,默认的三种HandlerMapping,按照处理不同配置的Controller来分类
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:解析xml文件中配置Controller,名字必须以“/”开头
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping:解析注解@Controller标注的类
- RouterFunctionMapping:不常用
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 遍历所有的HandlerMapping,主要是三个 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping(处理xml配置的controller)、
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping(处理注解@Controller)
// RouterFunctionMapping
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
- 这里说明@Controller方式,也就RequestMappingHandlerMapping方式
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取handler,以及具体方法,返回的对象是HandlerMethod
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
...
// 对HandlerMethod进行类型强转,并且添加上拦截器返回HandlerExecutionChain对象
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
...
return executionChain;
}
1. 进入方法后调用<font style="color:#ECAA04;">getHandlerInternal()</font>方法来获取具体<font style="color:#ECAA04;">Controller</font>,并且其中会返回一个<font style="color:#ECAA04;">HandlerMethod</font>对象,里面封装了处理当前请求的<font style="color:#ECAA04;">Controller</font>,还有具体的方法
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
2. 解析出具体处理方法<font style="color:#ECAA04;">lookupHandlerMethod</font>,可以获取到请求处理的<font style="color:#ECAA04;">Controller</font>名称以及方法名称
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 存放匹配请求的集合
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取当前请求路径的集合
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
...
}
// 将对应处理器方法设置到request中
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);
// 处理匹配项
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// 返回处理方法
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
3. 如果有匹配的处理器发方法,就调用<font style="color:#ECAA04;">createWithResolvedBean()</font>来创建一个<font style="color:#ECAA04;">HandlerMethod</font>对象,在这里会真正获取处理请求的<font style="color:#ECAA04;">Controller</font>对象,设置到处理器<font style="color:#ECAA04;">HandlerMethod</font>中,最终返回<font style="color:#ECAA04;">HandlerMethod</font>对象
public HandlerMethod createWithResolvedBean() {
// 取出Bean,这个时候还是名称
Object handler = this.bean;
if (this.bean instanceof String) {
Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "Cannot resolve bean name without BeanFactory");
String beanName = (String) this.bean;
// 从缓存中获取,或者创建Bean对象,正常来说都是在spirngmvc创建的时候就创建完成了
handler = this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
// 返回对象分装
return new HandlerMethod(this, handler);
}
调用构造方法
private HandlerMethod(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Object handler) {
Assert.notNull(handlerMethod, "HandlerMethod is required");
Assert.notNull(handler, "Handler object is required");
this.bean = handler;
this.beanFactory = handlerMethod.beanFactory;
this.beanType = handlerMethod.beanType;
this.method = handlerMethod.method;
this.bridgedMethod = handlerMethod.bridgedMethod;
this.parameters = handlerMethod.parameters;
this.responseStatus = handlerMethod.responseStatus;
this.responseStatusReason = handlerMethod.responseStatusReason;
this.resolvedFromHandlerMethod = handlerMethod;
this.description = handlerMethod.description;
}
- 对HandlerMethod进行类型强转,并且添加上拦截器返回HandlerExecutionChain对象
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request, LOOKUP_PATH);
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
3.获取请求处理器适配器
由于Controller有多种方式实现,对于一个请求该调用处理器中的那个方法,我们是未知的,如果是实现了Contorller接口或者实现HttpRequestHandler接口的都是调用handleRequest方法,对于@Controller注解实现的处理器,方法是自己定义的,所以需要调用什么方法是未知的,所以需要一个处理器适配器来进行调用。
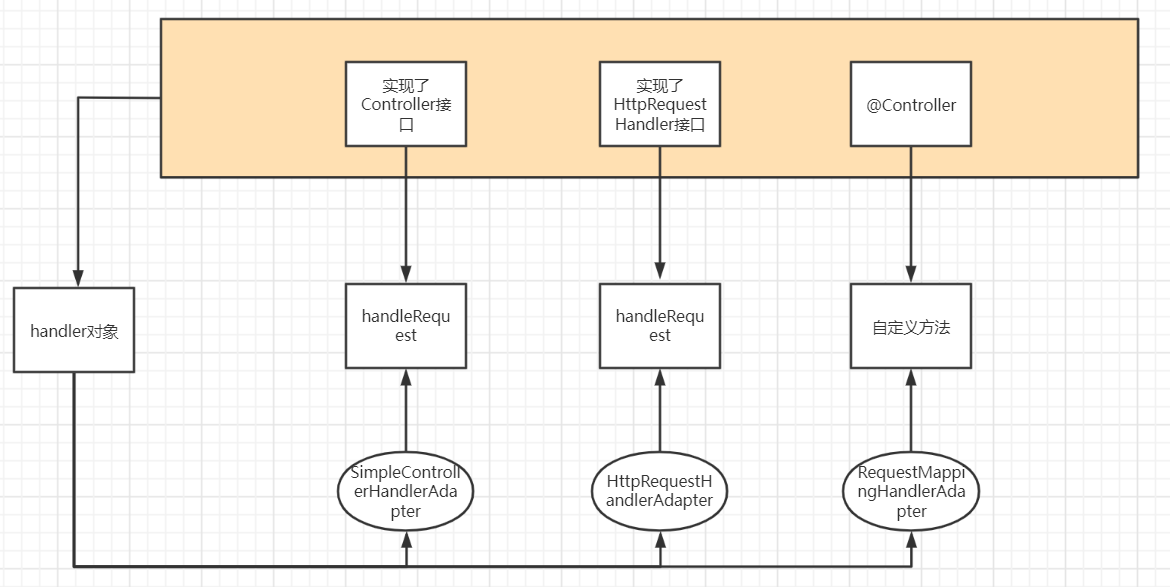
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
// 遍历所有处理器
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
3.处理last-modified
处理last-modified,是一种缓存机制,对于js,css这种不会变动资源,在这里记录上一次更新的时间
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
4.执行拦截器前置处理方法
如果设置了前置拦截器,在这里进行拦截器前置方法的执行
// 执行interceptor的preHandle方法,进行前置拦截
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
5. 请求处理的具体流程
前面都是为当前处理请求的方法做准备,在这里调用ha.handle()进行请求的处理,并且返回一个ModelAndView对象
1.请求检查
checkRequest(request),如果不支持就会报错
protected final void checkRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException {
// Check whether we should support the request method.
// 判断当前请求方式是不是不被支持
String method = request.getMethod();
if (this.supportedMethods != null && !this.supportedMethods.contains(method)) {
throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(method, this.supportedMethods);
}
// Check whether a session is required.
// session处理
if (this.requireSession && request.getSession(false) == null) {
throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Pre-existing session required but none found");
}
}
2.进行请求的处理
先判断是否需要同步,都会调用invokeHandlerMethod方法返回一个ModelAndView对象,也就是真正进行请求处理的方法。
// 是否需要加锁同步执行,默认是false,不需要
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) { //加锁
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
// 没有HttpSession可用->不需要互斥锁
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
方法中主要有以下几个步骤,主要分为两个阶段,准备阶段和请求处理阶段:
- 创建BinderFactory和ModelFactory工厂,用来解析当前处理器上面和@ControllerAdvice注解修饰的类的@InitBinder注解和@ModelAttrbute注解,封装到工厂中进行返回
// 创建WebDataBinderFactory对象,此对象用在创建WebDataBinder对象,进行参数绑定
// 实现参数跟String类型之间的类型转换,ArgumentResolver在进行参数解析过程中会用到
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
// 创建ModelFactory对象,此对象主要用来处理model
// 主要是两个功能,1是在处理器具体处理之前对model进行初始化,2是在处理完请求后对model进行更新,和上面的处理逻辑一致
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
- 创建了ServletInvocableHandlerMethod对象将request和response进行了封装,并向里面填充了参数解析器和返回值解析器
// 创建一个ServletInvocableHandlerMethod对象,将当前HandlerMethod对象封装
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
// 创建完成后,进行一些属性值的设置
// 设置参数解析器 26个
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
// 设置返回值处理器
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
- 创建一个ModelAndViewContainer对象,往mavContainer中设置一些属性值
// 设置BinderFactory
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
// 设置参数名字发现,主要是三种
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
// 创建ModelAndViewContainer对象
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
// 将flashmap中的数据设置到model中
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
// 初始化initModel对象,使用modelFactory将@sessionAttributes和注释了@ModelAttribute方法中的参数设置到model中
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
// 根据配置对ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect进行设置
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
- 关于异步请求的处理
异步请求处理,在这里创建一个WebAsyncManager对象,该对象会对异步请求进行调用
- 开始请求处理,调用invocableMethod的invokeAndHandle方法进行请求的具体处理,这里会先调用定义的处理器的具体处理方法,获得一个返回值,然后再对返回值进行处理
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 调用处理请求,并且获得返回值
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
// 设置返回值状态
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
// 如果返回值为null,直接进行返回处理
if (returnValue == null) {
// 满足其中一个直接返回
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
// 如果ResponseStatusReason有值的话直接返回
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
// 设置请求已经被处理了
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
// 用返回值处理器,遍历处理返回值,并且加入到mav
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
1. invokeForRequest() 处理请求,先获取请求参数,然后将参数传递给方法,进行解析,这里解析参数,会对穿过来的参数和方法上的参数通过参数解析器进行解析,并且将参数封装成我们需要的类型,处理过程中会用到我们定义的InitBinder中的转换器等
2. 获取到参数之后,直接调用我们定义的处理器中的方法进行处理
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 获取请求参数
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
// 执行请求处理方法
return doInvoke(args);
}
3. handleReturnValue对返回值进行处理,首先根据返回值查询能够查理当前返回值的返回值处理器,然后调用返回值处理器的方法进行处理,将处理之后的返回值设置到mavContainer中
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
3.处理一下Cache-Control
// 处理请求头中的Cache-Control
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
6.设置默认视图
返回视图之后,调用applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv)方法,判断一下视图是否为空,如果视图为空,就会给它设置一个默认的视图名称
private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
// 获取一个默认的名字,一般来说都是请求的名字
String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
// 进行设置
mv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
}
7.执行拦截器后置处理方法
遍历所有的拦截器进行处理
void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv)
throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv);
}
}
}
8.如果发生异常
如果发生异常,会将异常赋值给全局异常处理对象
dispatchException = ex;
9.视图渲染
前面已经获取了ModelAndView对象,接下来就是对视图进行渲染,调用processDispatchResult方法对视图进行处理和渲染
- 如果前面发生了异常,会在这里进行判断,并且获取到对应ExceptionHandler进行处理,获取到具体的处理器之后和正常的请求处理的过程是一样的,最终返回一个ModelAndView对象
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 对异常进行处理,查找出异常对应的解析器和处理器
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
// 获取异常处理器
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
// 处理异常烦返回ModelAndView对象
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
// 页面渲染
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
...
}
- 如果一切正常就会调用视图渲染render方法,这个方法会对当前modelAndView对象进行处理,会返回一个View对象,这个对象中有视图在本地的地址,这里会调用的视图解析器ViewResource来进行解析。
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
// 设置本地语言
response.setLocale(ocale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
...
}
至此,完成了完整的请求处理和视图解析,最终会调用tomcat中的方法来完成视图渲染
10.视图渲染发生异常
如果在视图处理阶段发生了异常,就会调用拦截器的AfterCompletion方法来对异常进行处理
最终释放资源,完成处理
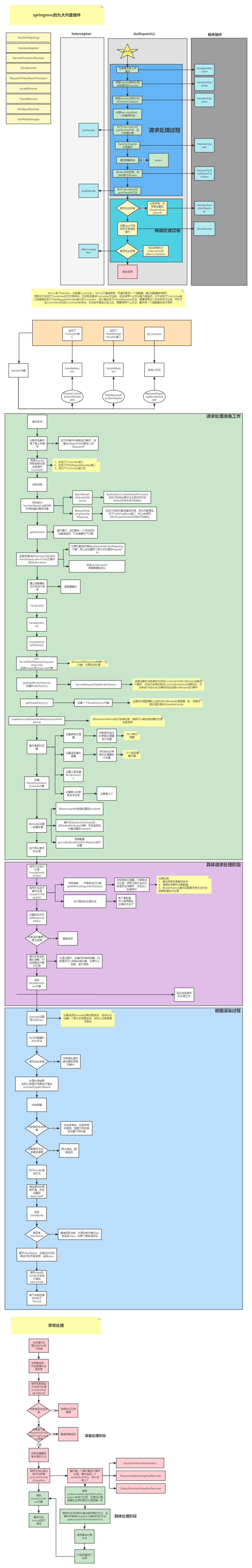
整体大图



























 1833
1833

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








