第三章 MyBatis
二、MyBatis 基本使用
1. 向 SQL 语句传参
1.1 mybatis 日志输出配置
-
mybatis配置文件设计标签和顶层结构如下:
-
configuration(配置)
- properties(属性)
- settings(设置)
- typeAliases(类型别名)
- typeHandlers(类型处理器)
- objectFactory(对象工厂)
- plugins(插件)
- environments(环境配置)
- environment(环境变量)
- transactionManager(事务管理器)
- dataSource(数据源)
- environment(环境变量)
- databaseIdProvider(数据库厂商标识)
- mappers(映射器)
-
我们可以在mybatis的配置文件使用settings标签设置,输出运过程SQL日志!
-
通过查看日志,我们可以判定#{} 和 ${}的输出效果!
-
settings设置项:
- logImpl
- 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。
- SLF4J | LOG4J(3.5.9 起废弃) | LOG4J2 | JDK_LOGGING | COMMONS_LOGGING | STDOUT_LOGGING | NO_LOGGING
- 未设置
-
日志配置:
<settings>
<!-- SLF4J 选择slf4j输出! -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="SLF4J"/>
</settings>
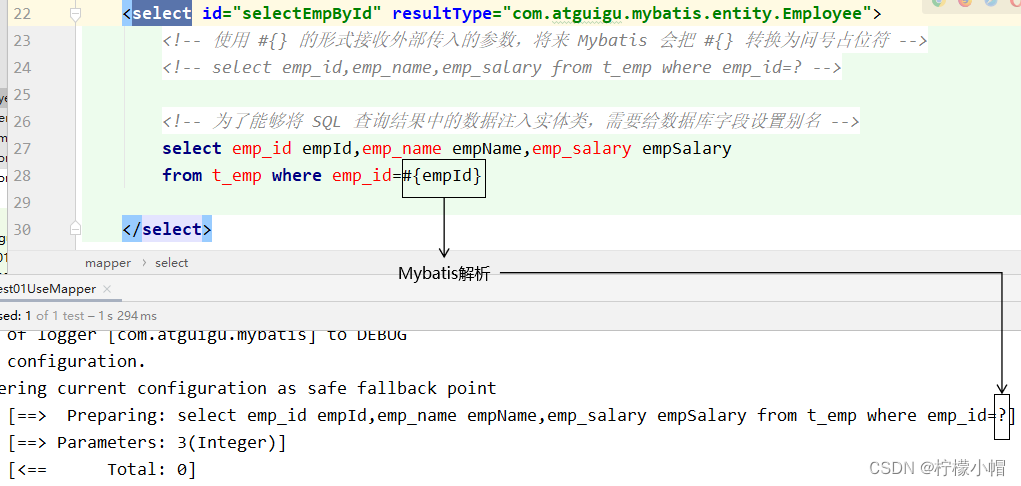
1.2 #{} 形式
- Mybatis会将SQL语句中的#{}转换为问号占位符。
1.3 ${} 形式
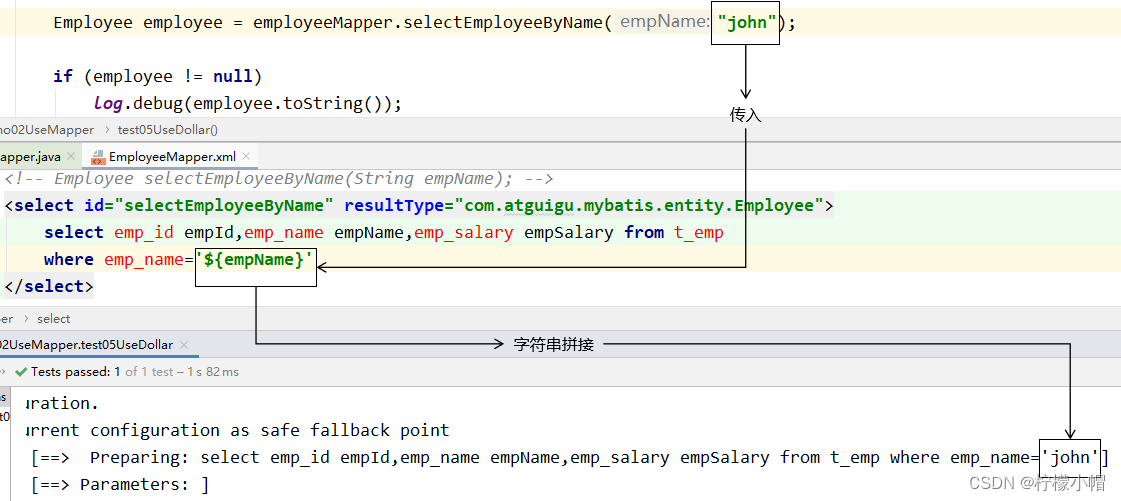
- 通常不会采用${}的方式传值。一个特定的适用场景是:通过Java程序动态生成数据库表,表名部分需要Java程序通过参数传入;而JDBC对于表名部分是不能使用问号占位符的,此时只能使用
- 结论:实际开发中,能用#{}实现的,肯定不用${}。
- 特殊情况: 动态的不是值,是列名或者关键字,需要使用${}拼接
//注解方式传入参数!!
@Select("select * from user where ${column} = #{value}")
User findByColumn(@Param("column") String column,
@Param("value") String value);
2. 数据输入
2.1 Mybatis 总体机制概括

2.2 概念说明
-
这里数据输入具体是指上层方法(例如Service方法)调用Mapper接口时,数据传入的形式。
-
简单类型:只包含一个值的数据类型
- 基本数据类型:int、byte、short、double、……
- 基本数据类型的包装类型:Integer、Character、Double、……
- 字符串类型:String
-
复杂类型:包含多个值的数据类型
- 实体类类型:Employee、Department、……
- 集合类型:List、Set、Map、……
- 数组类型:int[]、String[]、……
- 复合类型:List、实体类中包含集合……
2.3 单个简单类型参数
- Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
Employee selectEmployee(Integer empId);
- SQL语句
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,emp_salary empSalary from t_emp where emp_id=#{empId}
</select>
单个简单类型参数,在#{}中可以随意命名,但是没有必要。通常还是使用和接口方法参数同名。
2.4 实体类类型参数
- Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
int insertEmployee(Employee employee);
- SQL语句
<insert id="insertEmployee">
insert into t_emp(emp_name,emp_salary) values(#{empName},#{empSalary})
</insert>
- 对应关系
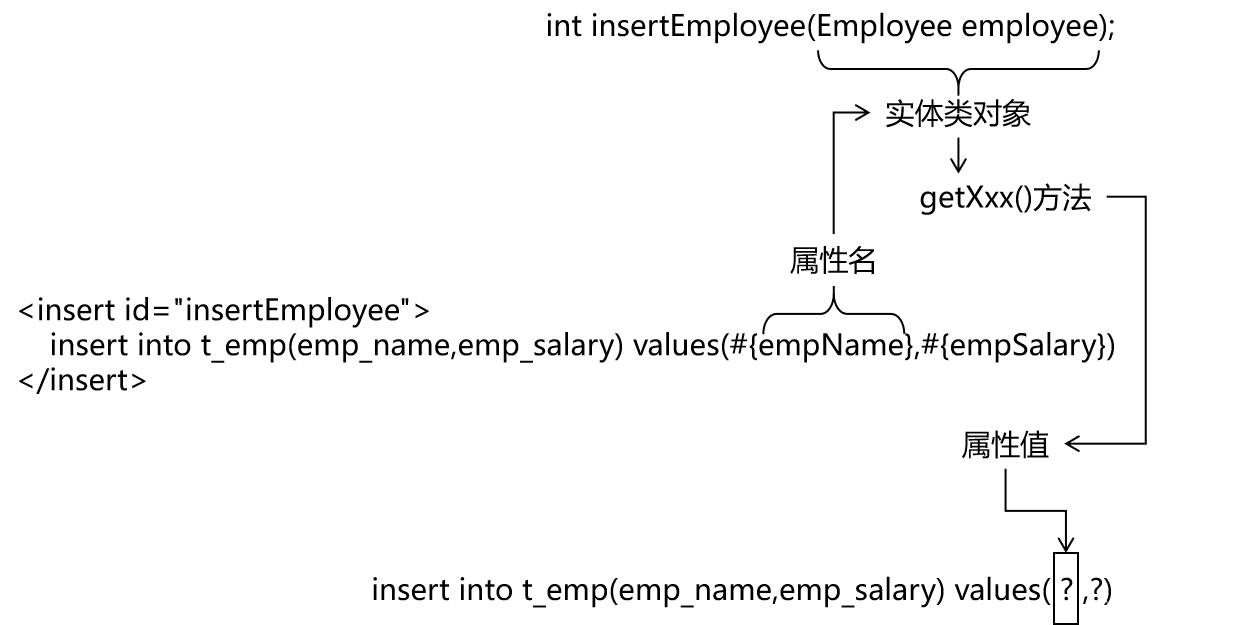
- 结论
- Mybatis会根据#{}中传入的数据,加工成getXxx()方法,通过反射在实体类对象中调用这个方法,从而获取到对应的数据。填充到#{}解析后的问号占位符这个位置。
2.5 零散的简单类型数据
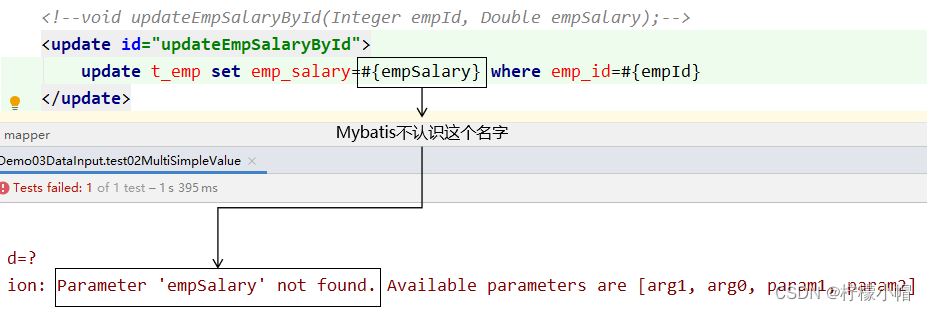
- Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
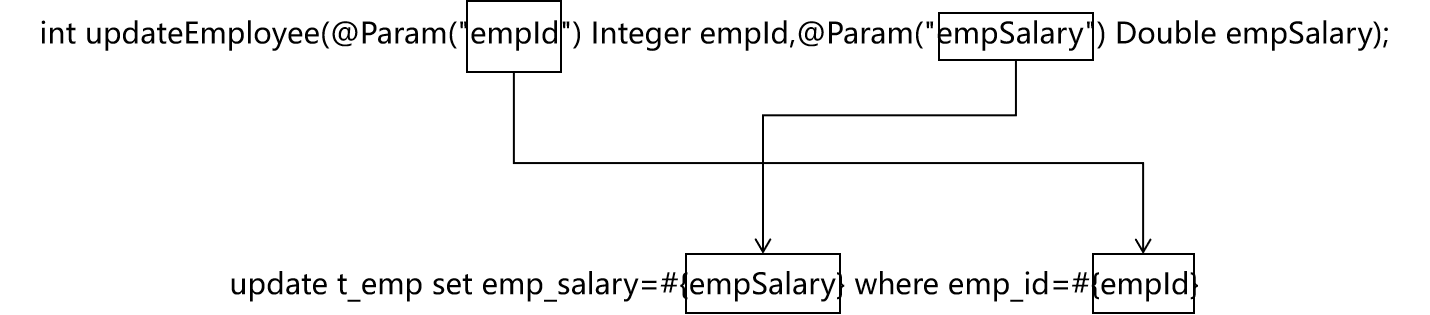
int updateEmployee(@Param("empId") Integer empId,@Param("empSalary") Double empSalary);
- SQL语句
<update id="updateEmployee">
update t_emp set emp_salary=#{empSalary} where emp_id=#{empId}
</update>
- 对应关系
2.6 Map 类型参数
- Mapper接口中抽象方法的声明
int updateEmployeeByMap(Map<String, Object> paramMap);
- SQL语句
<update id="updateEmployeeByMap">
update t_emp set emp_salary=#{empSalaryKey} where emp_id=#{empIdKey}
</update>
- junit测试
private SqlSession session;
//junit5会在每一个@Test方法前执行@BeforeEach方法
@BeforeEach
public void init() throws IOException {
session = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(
Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"))
.openSession();
}
@Test
public void testUpdateEmpNameByMap() {
EmployeeMapper mapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("empSalaryKey", 999.99);
paramMap.put("empIdKey", 5);
int result = mapper.updateEmployeeByMap(paramMap);
log.info("result = " + result);
}
//junit5会在每一个@Test方法后执行@@AfterEach方法
@AfterEach
public void clear() {
session.commit();
session.close();
}
-
对应关系
- #{}中写Map中的key
-
使用场景
- 有很多零散的参数需要传递,但是没有对应的实体类类型可以使用。使用@Param注解一个一个传入又太麻烦了。所以都封装到Map中。
3. 数据输出
3.1 输出概述
-
数据输出总体上有两种形式:
- 增删改操作返回的受影响行数:直接使用 int 或 long 类型接收即可
- 查询操作的查询结果
-
我们需要做的是,指定查询的输出数据类型即可!
-
并且插入场景下,实现主键数据回显示!
3.2 单个简单类型
- Mapper接口中的抽象方法
int selectEmpCount();
- SQL语句
<select id="selectEmpCount" resultType="int">
select count(*) from t_emp
</select>
Mybatis 内部给常用的数据类型设定了很多别名。 以 int 类型为例,可以写的名称有:int、integer、Integer、java.lang.Integer、Int、INT、INTEGER 等等。
- junit测试
@Test
public void testEmpCount() {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
int count = employeeMapper.selectEmpCount();
log.info("count = " + count);
}
-
细节解释:
-
select标签,通过resultType指定查询返回值类型!
-
resultType = “全限定符 | 别名 | 如果是返回集合类型,写范型类型即可”
-
-
别名问题:
- 类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。例如:
<typeAliases> <typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/> <typeAlias alias="Blog" type="domain.blog.Blog"/> </typeAliases>-
当这样配置时,
Blog可以用在任何使用domain.blog.Blog的地方。 -
也可以指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean,比如:
<typeAliases> <package name="domain.blog"/> </typeAliases>- 每一个在包
domain.blog中的 Java Bean,在没有注解的情况下,会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为它的别名。 比如domain.blog.Author的别名为author;若有注解,则别名为其注解值。见下面的例子:
@Alias("author") public class Author { ... } -
下面是Mybatis为常见的 Java 类型内建的类型别名。它们都是不区分大小写的,注意,为了应对原始类型的命名重复,采取了特殊的命名风格。
| 别名 | 映射的类型 |
|---|---|
| _byte | byte |
| _char (since 3.5.10) | char |
| _character (since 3.5.10) | char |
| _long | long |
| _short | short |
| _int | int |
| _integer | int |
| _double | double |
| _float | float |
| _boolean | boolean |
| string | String |
| byte | Byte |
| char (since 3.5.10) | Character |
| character (since 3.5.10) | Character |
| long | Long |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| integer | Integer |
| double | Double |
| float | Float |
| boolean | Boolean |
| date | Date |
| decimal | BigDecimal |
| bigdecimal | BigDecimal |
| biginteger | BigInteger |
| object | Object |
| object[] | Object[] |
| map | Map |
| hashmap | HashMap |
| list | List |
| arraylist | ArrayList |
| collection | Collection |
3.3 返回实体类对象
- Mapper接口的抽象方法
Employee selectEmployee(Integer empId);
- SQL语句
<!-- 编写具体的SQL语句,使用id属性唯一的标记一条SQL语句 -->
<!-- resultType属性:指定封装查询结果的Java实体类的全类名 -->
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
<!-- Mybatis负责把SQL语句中的#{}部分替换成“?”占位符 -->
<!-- 给每一个字段设置一个别名,让别名和Java实体类中属性名一致 -->
select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,emp_salary empSalary from t_emp where emp_id=#{maomi}
</select>
-
通过给数据库表字段加别名,让查询结果的每一列都和Java实体类中属性对应起来。
-
增加全局配置自动识别对应关系
-
在 Mybatis 全局配置文件中,做了下面的配置,select语句中可以不给字段设置别名
<!-- 在全局范围内对Mybatis进行配置 -->
<settings>
<!-- 具体配置 -->
<!-- 从org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration类中可以查看能使用的配置项 -->
<!-- 将mapUnderscoreToCamelCase属性配置为true,表示开启自动映射驼峰式命名规则 -->
<!-- 规则要求数据库表字段命名方式:单词_单词 -->
<!-- 规则要求Java实体类属性名命名方式:首字母小写的驼峰式命名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
3.4 返回 Map 类型
-
适用于SQL查询返回的各个字段综合起来并不和任何一个现有的实体类对应,没法封装到实体类对象中。能够封装成实体类类型的,就不使用Map类型。
-
Mapper接口的抽象方法
Map<String,Object> selectEmpNameAndMaxSalary();
- SQL语句
<!-- Map<String,Object> selectEmpNameAndMaxSalary(); -->
<!-- 返回工资最高的员工的姓名和他的工资 -->
<select id="selectEmpNameAndMaxSalary" resultType="map">
SELECT
emp_name 员工姓名,
emp_salary 员工工资,
(SELECT AVG(emp_salary) FROM t_emp) 部门平均工资
FROM t_emp WHERE emp_salary=(
SELECT MAX(emp_salary) FROM t_emp
)
</select>
- junit测试
@Test
public void testQueryEmpNameAndSalary() {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Map<String, Object> resultMap = employeeMapper.selectEmpNameAndMaxSalary();
Set<Map.Entry<String, Object>> entrySet = resultMap.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : entrySet) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
log.info(key + "=" + value);
}
}
3.5 返回 List 类型
-
查询结果返回多个实体类对象,希望把多个实体类对象放在List集合中返回。此时不需要任何特殊处理,在resultType属性中还是设置实体类类型即可。
-
Mapper接口中抽象方法
List<Employee> selectAll();
- SQL语句
<!-- List<Employee> selectAll(); -->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,emp_salary empSalary
from t_emp
</select>
- junit测试
@Test
public void testSelectAll() {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
List<Employee> employeeList = employeeMapper.selectAll();
for (Employee employee : employeeList) {
log.info("employee = " + employee);
}
}
3.6 返回主键值
3.6.1 自增长类型主键
- Mapper接口中的抽象方法
int insertEmployee(Employee employee);
- SQL语句
<!-- int insertEmployee(Employee employee); -->
<!-- useGeneratedKeys属性字面意思就是“使用生成的主键” -->
<!-- keyProperty属性可以指定主键在实体类对象中对应的属性名,Mybatis会将拿到的主键值存入这个属性 -->
<insert id="insertEmployee" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="empId">
insert into t_emp(emp_name,emp_salary)
values(#{empName},#{empSalary})
</insert>
- junit测试
@Test
public void testSaveEmp() {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = session.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setEmpName("john");
employee.setEmpSalary(666.66);
employeeMapper.insertEmployee(employee);
log.info("employee.getEmpId() = " + employee.getEmpId());
}
-
注意
- Mybatis是将自增主键的值设置到实体类对象中,而不是以Mapper接口方法返回值的形式返回。
3.6.2 非自增长类型主键
- 而对于不支持自增型主键的数据库(例如 Oracle)或者字符串类型主键,则可以使用 selectKey 子元素:selectKey 元素将会首先运行,id 会被设置,然后插入语句会被调用!
- 使用
selectKey帮助插入UUID作为字符串类型主键示例:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="java.lang.String"
order="BEFORE">
SELECT UUID() as id
</selectKey>
INSERT INTO user (id, username, password)
VALUES (
#{id},
#{username},
#{password}
)
</insert>
- 在上例中,我们定义了一个
insertUser的插入语句来将User对象插入到user表中。我们使用selectKey来查询 UUID 并设置到id字段中。 - 通过
keyProperty属性来指定查询到的 UUID 赋值给对象中的id属性,而resultType属性指定了 UUID 的类型为java.lang.String。 - 需要注意的是,我们将
selectKey放在了插入语句的前面,这是因为 MySQL 在insert语句中只支持一个select子句,而selectKey中查询 UUID 的语句就是一个select子句,因此我们需要将其放在前面。 - 最后,在将
User对象插入到user表中时,我们直接使用对象中的id属性来插入主键值。 - 使用这种方式,我们可以方便地插入 UUID 作为字符串类型主键。当然,还有其他插入方式可以使用,如使用Java代码生成UUID并在类中显式设置值等。需要根据具体应用场景和需求选择合适的插入方式。
3.7 实体类属性和数据库字段对应关系
3.7.1 别名对应
- 将字段的别名设置成和实体类属性一致。
<!-- 编写具体的SQL语句,使用id属性唯一的标记一条SQL语句 -->
<!-- resultType属性:指定封装查询结果的Java实体类的全类名 -->
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
<!-- Mybatis负责把SQL语句中的#{}部分替换成“?”占位符 -->
<!-- 给每一个字段设置一个别名,让别名和Java实体类中属性名一致 -->
select emp_id empId,emp_name empName,emp_salary empSalary from t_emp where emp_id=#{maomi}
</select>
关于实体类属性的约定:
getXxx()方法、setXxx()方法把方法名中的get或set去掉,首字母小写。
3.7.2 全局配置自动识别驼峰式命名规则
- 在Mybatis全局配置文件加入如下配置:
<!-- 使用settings对Mybatis全局进行设置 -->
<settings>
<!-- 将xxx_xxx这样的列名自动映射到xxXxx这样驼峰式命名的属性名 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
- SQL语句中可以不使用别名
<!-- Employee selectEmployee(Integer empId); -->
<select id="selectEmployee" resultType="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
select emp_id,emp_name,emp_salary from t_emp where emp_id=#{empId}
</select>
3.7.3 使用resultMap
- 使用resultMap标签定义对应关系,再在后面的SQL语句中引用这个对应关系
<!-- 专门声明一个resultMap设定column到property之间的对应关系 -->
<resultMap id="selectEmployeeByRMResultMap" type="com.alex.mybatis.entity.Employee">
<!-- 使用id标签设置主键列和主键属性之间的对应关系 -->
<!-- column属性用于指定字段名;property属性用于指定Java实体类属性名 -->
<id column="emp_id" property="empId"/>
<!-- 使用result标签设置普通字段和Java实体类属性之间的关系 -->
<result column="emp_name" property="empName"/>
<result column="emp_salary" property="empSalary"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- Employee selectEmployeeByRM(Integer empId); -->
<select id="selectEmployeeByRM" resultMap="selectEmployeeByRMResultMap">
select emp_id,emp_name,emp_salary from t_emp where emp_id=#{empId}
</select>























 233
233











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










