1. 基本的入队出队
public class LinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
static class Node<E> {
E item;
/**
* 下列三种情况之一
* - 真正的后继节点
* - 自己, 发生在出队时
* - null, 表示是没有后继节点, 是最后了
*/
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) { item = x; }
}
}
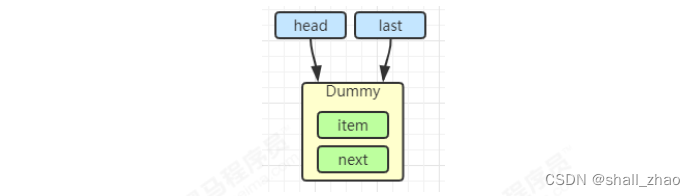
初始化链表 last = head = new Node(null); Dummy 节点用来占位,item 为 null
当一个节点入队 last = last.next = node;
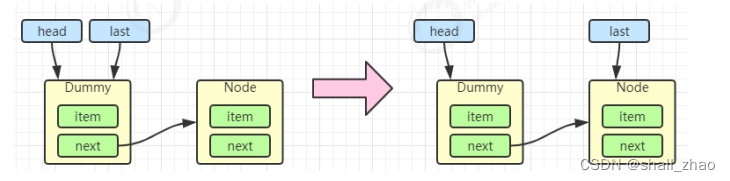
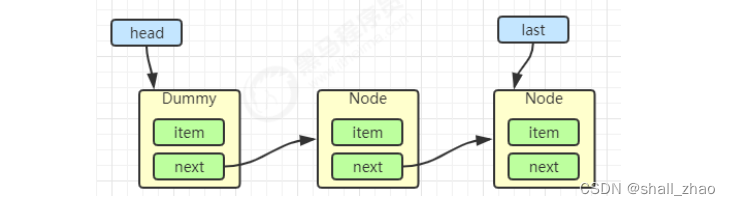
再来一个节点入队 last = last.next = node;
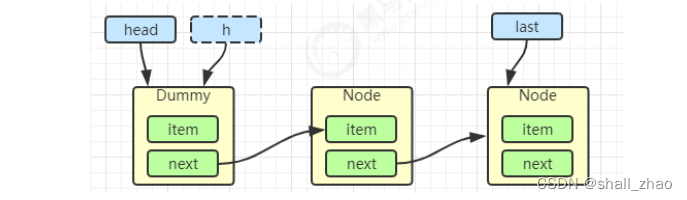
出队
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
h = head
first = h.next
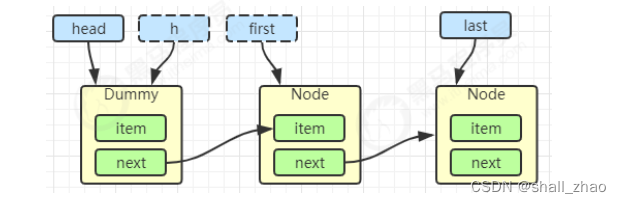
h.next = h
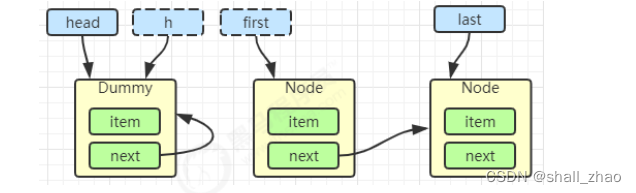
head = first
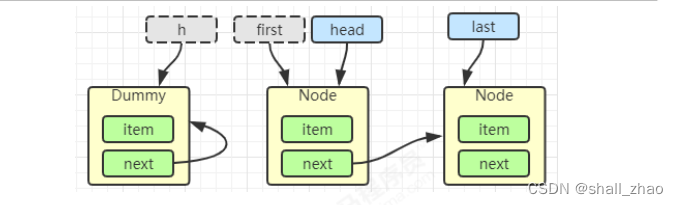
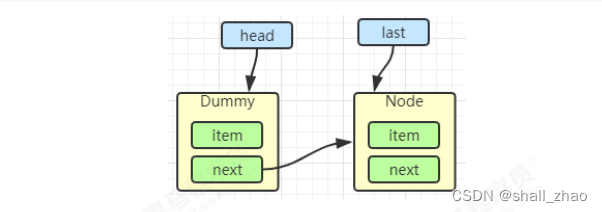
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
2. 加锁分析
高明之处在于用了两把锁和 dummy 节点
- 用一把锁,同一时刻,最多只允许有一个线程(生产者或消费者,二选一)执行
- 用两把锁,同一时刻,可以允许两个线程同时(一个生产者与一个消费者)执行
- 消费者与消费者线程仍然串行
- 生产者与生产者线程仍然串行
线程安全分析
- 当节点总数大于 2 时(包括 dummy 节点),putLock 保证的是 last 节点的线程安全,takeLock 保证的是head 节点的线程安全。两把锁保证了入队和出队没有竞争
- 当节点总数等于 2 时(即一个 dummy 节点,一个正常节点)这时候,仍然是两把锁锁两个对象,不会竞争
- 当节点总数等于 1 时(就一个 dummy 节点)这时 take 线程会被 notEmpty 条件阻塞,有竞争,会阻塞
// 用于 put(阻塞) offer(非阻塞)
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
// 用户 take(阻塞) poll(非阻塞)
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
put 操作
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// count 用来维护元素计数
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 满了等待
while (count.get() == capacity) {
// 倒过来读就好: 等待 notFull
notFull.await();
}
// 有空位, 入队且计数加一
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 除了自己 put 以外, 队列还有空位, 由自己叫醒其他 put 线程
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
// 如果队列中有一个元素, 叫醒 take 线程
if (c == 0)
// 这里调用的是 notEmpty.signal() 而不是 notEmpty.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争
signalNotEmpty();
}
take 操作
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
// 如果队列中只有一个空位时, 叫醒 put 线程
// 如果有多个线程进行出队, 第一个线程满足 c == capacity, 但后续线程 c < capacity
if (c == capacity)
// 这里调用的是 notFull.signal() 而不是 notFull.signalAll() 是为了减少竞争
signalNotFull()
return x;
}
由 put 唤醒 put 是为了避免信号不足
3. 性能比较
主要列举 LinkedBlockingQueue 与 ArrayBlockingQueue 的性能比较
- Linked 支持有界,Array 强制有界
- Linked 实现是链表,Array 实现是数组
- Linked 是懒惰的,而 Array 需要提前初始化 Node 数组
- Linked 每次入队会生成新 Node,而 Array 的 Node 是提前创建好的
- Linked 两把锁,Array 一把锁





















 12万+
12万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








