
日志是任何软件或操作系统的关键组件。日志通常记录用户的操作、系统事件、网络活动等等,具体取决于它们的用途。Linux 系统上使用最广泛的日志系统之一是rsyslog。
Rsyslog是一个强大、安全和高性能的日志处理系统,它接受来自不同类型源(系统/应用程序)的数据并将其输出为多种格式。
它已经从常规的syslog守护进程发展成为功能齐全的企业级日志系统。它采用客户端/服务器模型设计,因此可以配置为客户端和/或其他服务器、网络设备和远程应用程序的中央日志服务器。
测试环境
出于本指南的目的,我们将使用以下主机:
- 服务器:192.168.108.128
- 客户端:192.168.108.149/150 + 生产环境交换机 Log
- Cisco : 交换机/路由器日志配置远程Syslog采集
Cisco交换机/路由器日志配置远程Syslog采集
第一步:通过SSH登录系统控制台
使用root管理员登录系统,并进入config模式,这里以Catalyst2900为例。
<Catalyst2900># config terminal
第二步:配置syslog日志采集
<Catalyst2900>(config)# logging on
<Catalyst2900>(config)# logging <10.x.x.x>
## 注意syslog日志服务器接收地址,根据实际情况修改。
第三步:可选的配置:日志级别配置
ogging facility local7 ## 将记录事件类型定义为local6 local7。
logging trap notifications ## 将记录事件严重级别定义为从notifications开始,一直到最紧急级
logging trap notifications
logging facility local6
logging source-interface VlanXX
logging host 172.23.X.X一、安装和配置 Rsyslog 服务器;
1.1 修改计算机名称 关闭防火墙:SELINUX=enforcing 修改为 disabled
时区配置:timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Ho_Chi_Minh
[root@Centostest01 ~]# vi /etc/hostname
[root@Centostest01 ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@Centostest01 ~]# systemctl disable firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/selinux/config
[root@localhost ~]# reboot
1.2 安装 rsyslog Server
[root@rsyslog ~]# yum -y install rsyslog
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl enable rsyslog
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl start rsyslog
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl status rsyslog
[root@rsyslog ~]# vi /etc/rsyslog.conf
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog-----------------直接全部替换 rsyslog.conf 内容
-----------------替换时候不要选择i编辑状态,直接清空旧的Esc取消编辑粘贴 wq 退出
# rsyslog configuration file
# For more information see /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-*/rsyslog_conf.html
# or latest version online at http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/rsyslog_conf.html
# If you experience problems, see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/troubleshoot.html
#### GLOBAL DIRECTIVES ####
# Where to place auxiliary files
global(workDirectory="/var/lib/rsyslog")
# Use default timestamp format
module(load="builtin:omfile" Template="RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat")
# Include all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/
include(file="/etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf" mode="optional")
#### MODULES ####
module(load="imuxsock" # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
SysSock.Use="off") # Turn off message reception via local log socket;
# local messages are retrieved through imjournal now.
module(load="imjournal" # provides access to the systemd journal
StateFile="imjournal.state") # File to store the position in the journal
#module(load="imklog") # reads kernel messages (the same are read from journald)
#module(load="immark") # provides --MARK-- message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
# for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imudp.html
#module(load="imudp") # needs to be done just once
#input(type="imudp" port="514")
# Provides TCP syslog reception
# for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imtcp.html
#module(load="imtcp") # needs to be done just once
#input(type="imtcp" port="514")
#### RULES ####
# Log all kernel messages to the console.
# Logging much else clutters up the screen.
#kern.* /dev/console
# Log anything (except mail) of level info or higher.
# Don't log private authentication messages!
#*.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
*.error;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
# The authpriv file has restricted access.
authpriv.* /var/log/secure
# Log all the mail messages in one place.
mail.* -/var/log/maillog
# Log cron stuff
cron.* /var/log/cron
# Everybody gets emergency messages
*.emerg :omusrmsg:*
# Save news errors of level crit and higher in a special file.
uucp,news.crit /var/log/spooler
# Save boot messages also to boot.log
local7.* /var/log/boot.log
$FileOwner elk
$FileGroup elk
$FileCreateMode 0755
$DirCreateMode 0755
$Umask 0022
#####开启udp接收日志
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerRun 514
$template RemoteHost,"/data/rsyslog/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%/%FROMHOST-IP%.log"
*.* ?RemoteHost
& ~
####开启tcp协议接受日志
$ModLoad imtcp
$InputTCPServerRun 514
$WorkDirectory /var/lib/rsyslog
$ActionFileDefaultTemplate RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat
# ### sample forwarding rule ###
#action(type="omfwd"
# # An on-disk queue is created for this action. If the remote host is
# # down, messages are spooled to disk and sent when it is up again.
#queue.filename="fwdRule1" # unique name prefix for spool files
#queue.maxdiskspace="1g" # 1gb space limit (use as much as possible)
#queue.saveonshutdown="on" # save messages to disk on shutdown
#queue.type="LinkedList" # run asynchronously
#action.resumeRetryCount="-1" # infinite retries if host is down
# # Remote Logging (we use TCP for reliable delivery)
# # remote_host is: name/ip, e.g. 192.168.0.1, port optional e.g. 10514
#Target="remote_host" Port="XXX" Protocol="tcp")
或者
# rsyslog configuration file
# For more information see /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-*/rsyslog_conf.html
# or latest version online at http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/rsyslog_conf.html
# If you experience problems, see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/troubleshoot.html
#### GLOBAL DIRECTIVES ####
# Where to place auxiliary files
global(workDirectory="/var/lib/rsyslog")
# Use default timestamp format
module(load="builtin:omfile" Template="RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat")
# Include all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/
include(file="/etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf" mode="optional")
#### MODULES ####
module(load="imuxsock" # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
SysSock.Use="off") # Turn off message reception via local log socket;
# local messages are retrieved through imjournal now.
module(load="imjournal" # provides access to the systemd journal
StateFile="imjournal.state") # File to store the position in the journal
#module(load="imklog") # reads kernel messages (the same are read from journald)
#module(load="immark") # provides --MARK-- message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
# for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imudp.html
#module(load="imudp") # needs to be done just once
#input(type="imudp" port="514")
# Provides TCP syslog reception
# for parameters see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/imtcp.html
#module(load="imtcp") # needs to be done just once
#input(type="imtcp" port="514")
#### RULES ####
# Log all kernel messages to the console.
# Logging much else clutters up the screen.
#kern.* /dev/console
# Log anything (except mail) of level info or higher.
# Don't log private authentication messages!
#*.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
*.error;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
# The authpriv file has restricted access.
authpriv.* /var/log/secure
# Log all the mail messages in one place.
mail.* -/var/log/maillog
# Log cron stuff
cron.* /var/log/cron
# Everybody gets emergency messages
*.emerg :omusrmsg:*
# Save news errors of level crit and higher in a special file.
uucp,news.crit /var/log/spooler
# Save boot messages also to boot.log
local7.* /var/log/boot.log
$FileOwner elk
$FileGroup elk
$FileCreateMode 0755
$DirCreateMode 0755
$Umask 0022
#####开启udp接收日志
$ModLoad imudp
$UDPServerRun 514
$template RemoteHost,"/data/rsyslog/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%/%FROMHOST-IP%.log"
*.* ?RemoteHost
& ~
####开启tcp协议接受日志
$ModLoad imtcp
$InputTCPServerRun 514
$WorkDirectory /var/lib/rsyslog
$ActionFileDefaultTemplate RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat
-----------------------------------
# ### sample forwarding rule ###
#action(type="omfwd"
# # An on-disk queue is created for this action. If the remote host is
# # down, messages are spooled to disk and sent when it is up again.
#queue.filename="fwdRule1" # unique name prefix for spool files
#queue.maxdiskspace="1g" # 1gb space limit (use as much as possible)
#queue.saveonshutdown="on" # save messages to disk on shutdown#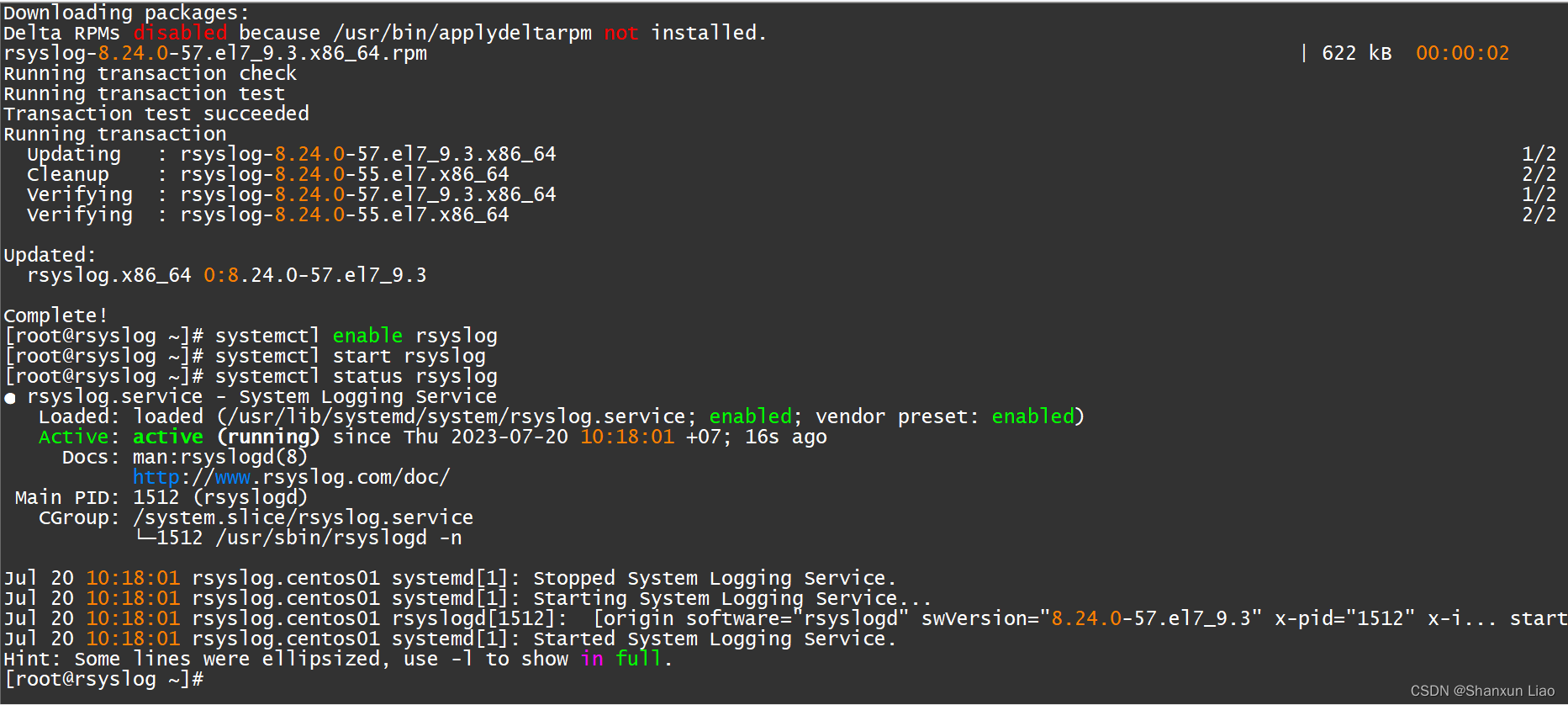
1.3 建立 Rsyslog 数据收集存放的目录:
[root@rsyslog ~]# cd /
[root@rsyslog /]# mkdir data
[root@rsyslog /]# cd data
[root@rsyslog data]# mkdir rsyslog
[root@rsyslog data]# chmod 777 rsyslog
二、安装 Apache HTTP Server
[root@rsyslog ~]# yum install httpd -y
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service #systemctl enable httpd
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl start httpd.service
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl status httpd.service
[root@rsyslog ~]# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl restart httpd.service 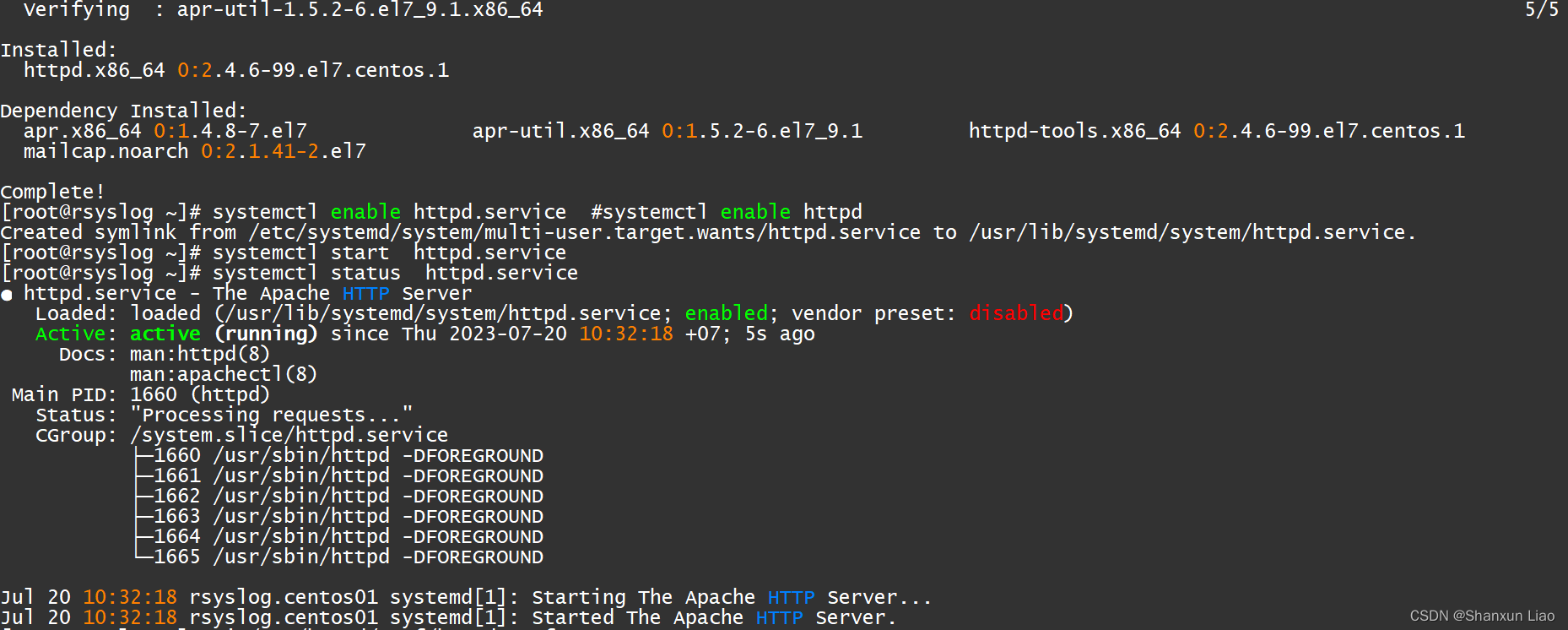
2.1 在 Apache 原始/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf文件最后加入以下内容:
Alias /rsyslog /data/rsyslog
<Directory "/data/rsyslog/">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
IndexOptions FancyIndexing NameWidth=*
AllowOverride None
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
AllowOverride none
Require all granted
</Directory>
2.2 编辑完成后 systemctl restart httpd.service 重启一下 httpd.service rsyslog.service
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl restart httpd.service
[root@rsyslog ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog.service
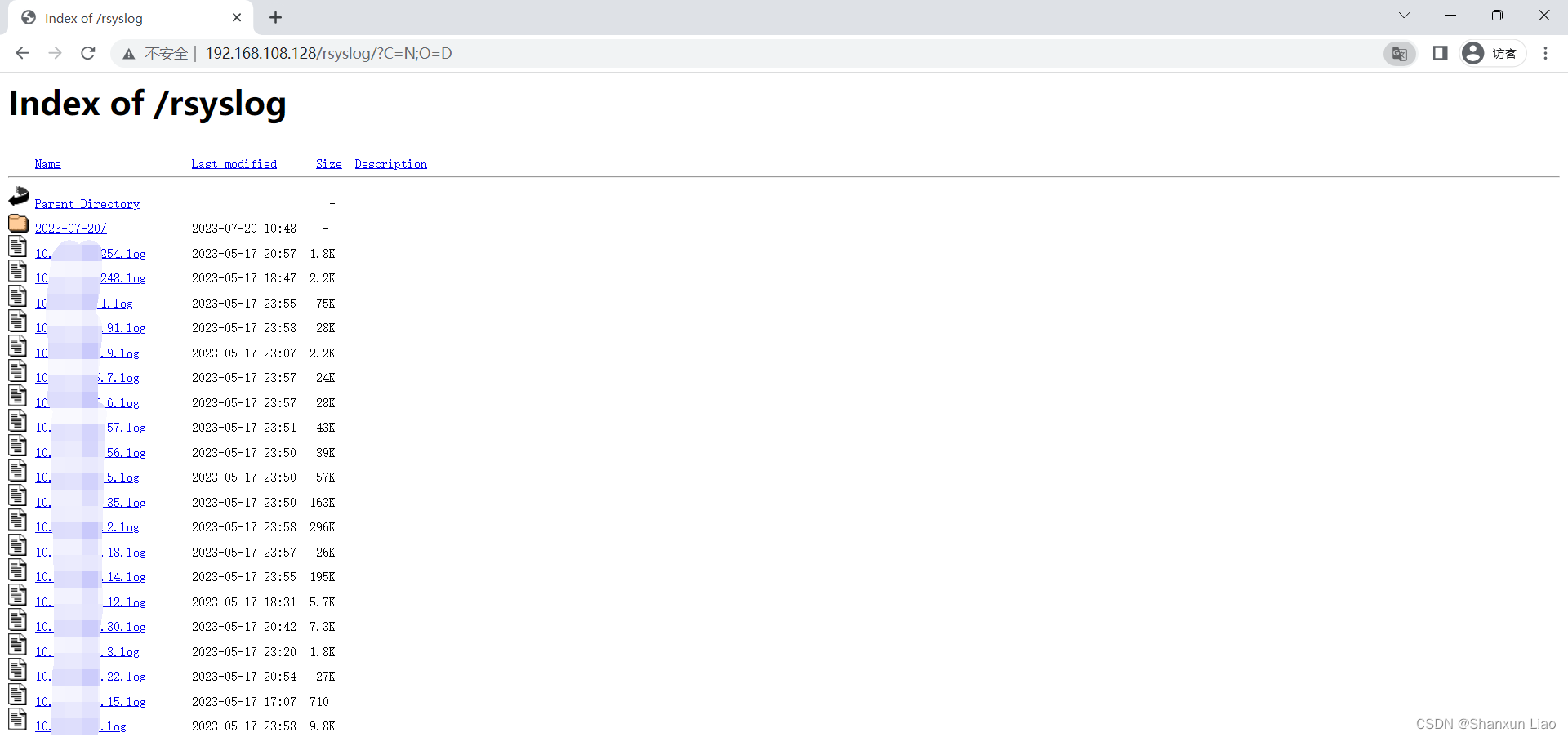
2.3 访问 web 看看 Apache HTTP Server 是否正常:http://192.168.108.128/rsyslog/

2.4 可以看到 Apache HTTP Server 是正常的,但没有生产本机的 log 重启一下 rsyslog 服务:
![]()


2.5 现在从其他 rsyslog 拷贝一些 log 到 /data/rsyslog 目录下看效果:
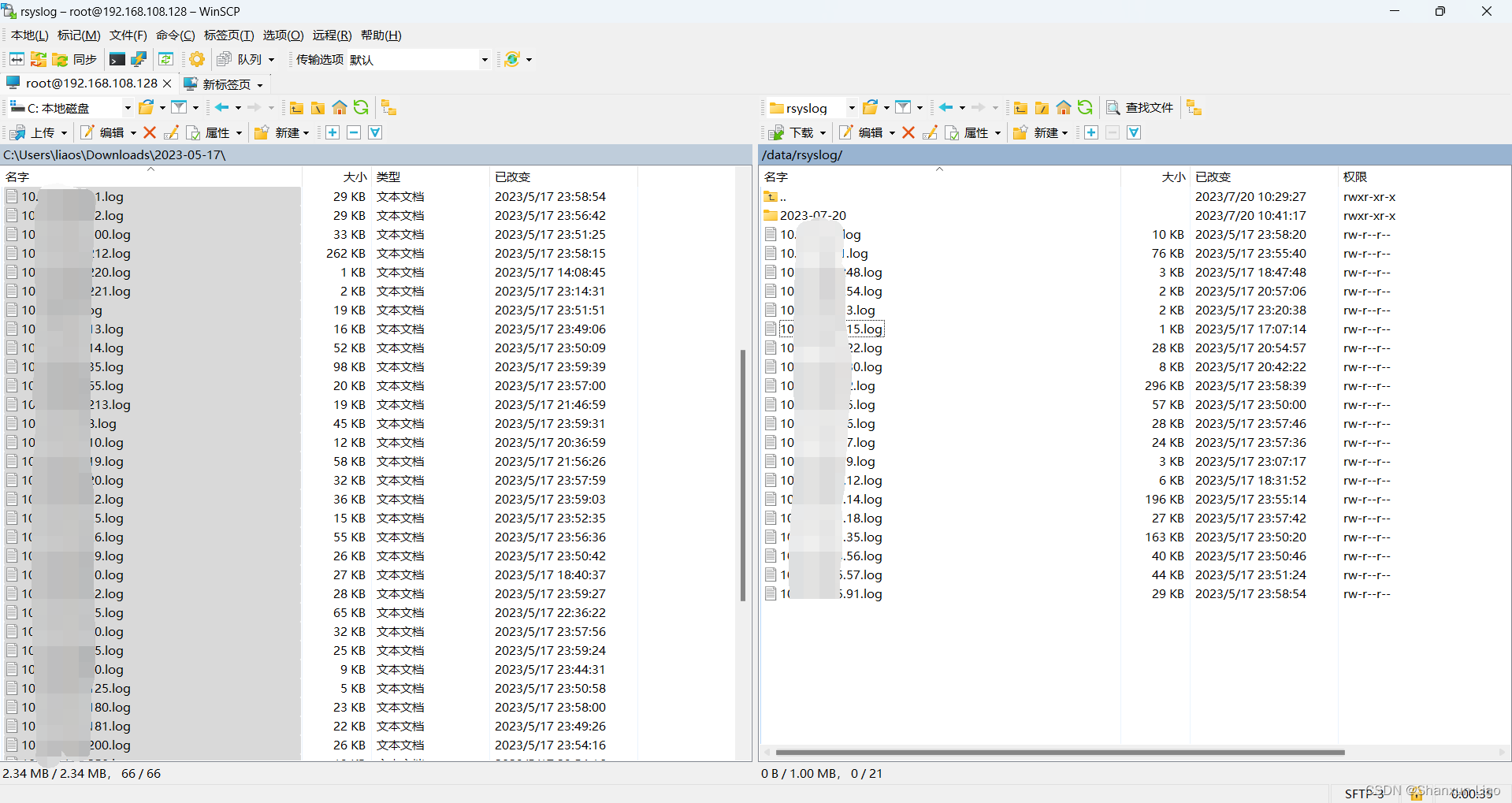

三、收集交换机log 的配置:
emergencies System is unusable (severity=0)
alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1)
critical Critical conditions (severity=2)
errors Error conditions (severity=3)
warnings Warning conditions (severity=4)
notifications Normal but significant conditions (severity=5)
informational Informational messages (severity=6)
debugging Debugging messages (severity=7)
通过命令行方式在路由器上配置日志服务器的 ip 地址和端口
通过 Telnet 或者串口登陆到路由器
在控制台输入命令 enable 或 en 进入到特权模式
输入命令 configure terminal 或 conf t 进入配置模式
输入如下命令行:
Cisco 路由器配置
(config)# Logging on //启用日志服务
(config)# Logging trap debug //决定什么级别的日志信息发送到服务器,一般有八个级别(emergency 紧急 ;alert 必须立即采取措施 ;critical 致命情况 ;error 错误情况 ;warn 警告情况 ; notice 一般重要情况 ;info 普通信息 ;debug 调试信息),debug 级别可以记录所有可以记录的信息
(config)# Logging host //指定日志服务器的 IP 地址
Cisco 交换机配置
cisco>en
cisco #conf t //进入到配置模式
cisco(config)#logging on //启用日志服务
cisco(config)#logging x.x.x.x //指定日志服务器 IP 地址//注:By de fault, the logging level is set to 3 (error).
cisco(config)#logging trap errors //指定发送日志级别,可选的级别有 0-7,0最低
Cisco防火墙配置
cisco>en
cisco #conf t //进入到配置模式
cisco(config)#logging on //启用日志服务
cisco(config)#logging x.x.x.x //指定日志服务器 IP 地址
cisco(config)#logging trap informational //发送日志级别,可选的级别有 0-7,0最低
hauwei 交换机配置
<Quidway>system-view
[Quiaway] info-center enable //启用日志服务
[Quiaway] info-center loghost x.x.x.x //指定日志服务器 IP 地址
H3C 交换机配置
<H3C-s8812-01 >system-view
[H3C-s8812-01] info-center enable //启用日志服务
[H3C-s8812-01] info-center loghost x.x.x.x //指定日志服务器 IP 地址
三、收集linux 服务器 的配置:
3.1 rsyslog 守护进程充当日志客户端并将所有本地生成的日志消息转发到远程 rsyslog 服务器,在文件末尾添加此转发规则,如以下屏幕截图所示。
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/rsyslog.conf
*.* @@192.168.108.128:514
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog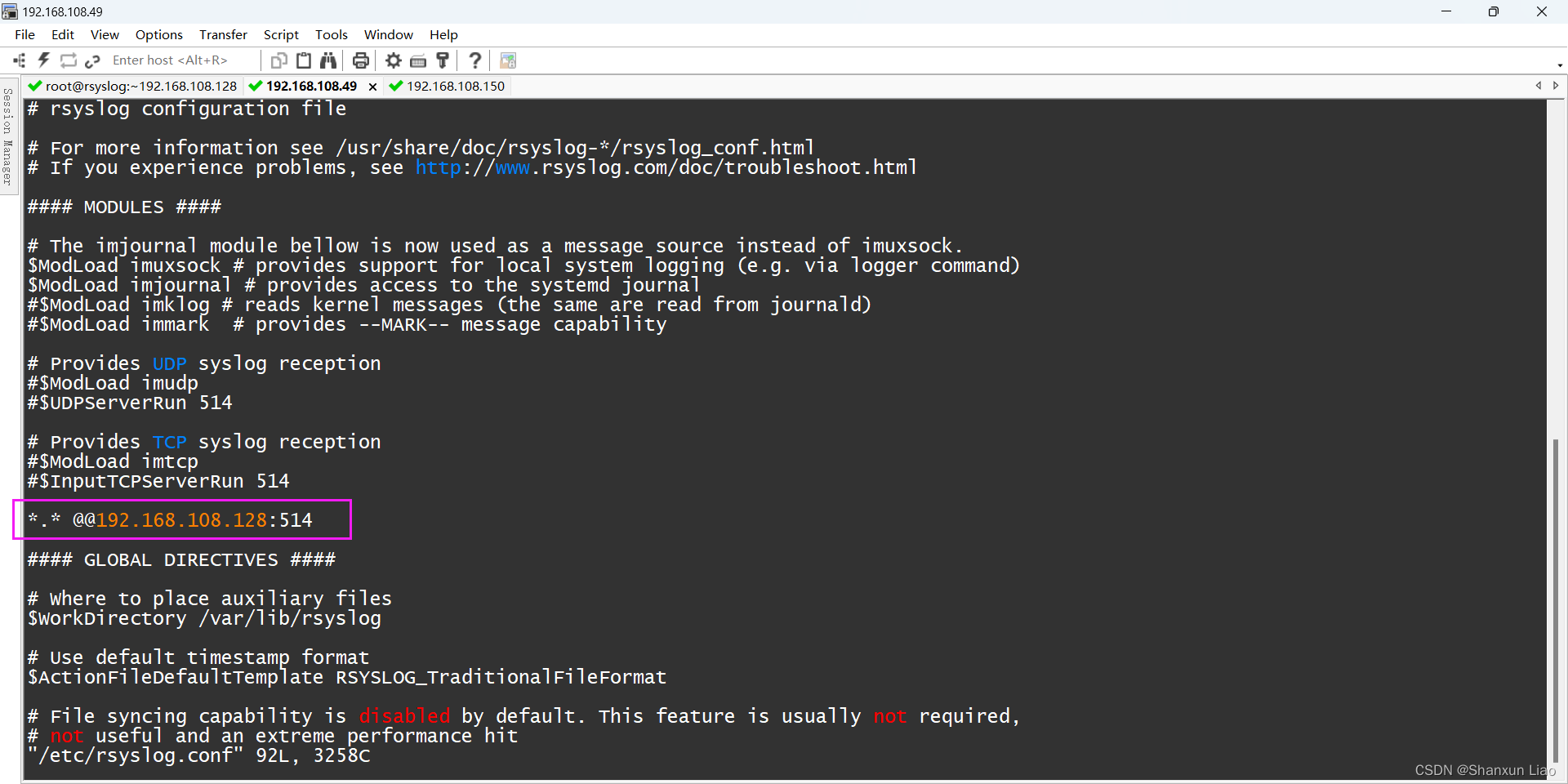
3.2 查看两台Linux 主机 192.168.108.149 / 192.168.108.150 是否正常收集

四、HTML 网页测试: 这里测试 世界探索家:
4.1 需要准备一份 HTML 网站文件目录,网上搜索下载:

4.2 将 HTML 网页全部拷贝到 /var/www/html 目录下 这个是 Apache 网页目录:
4.3 访问测试:
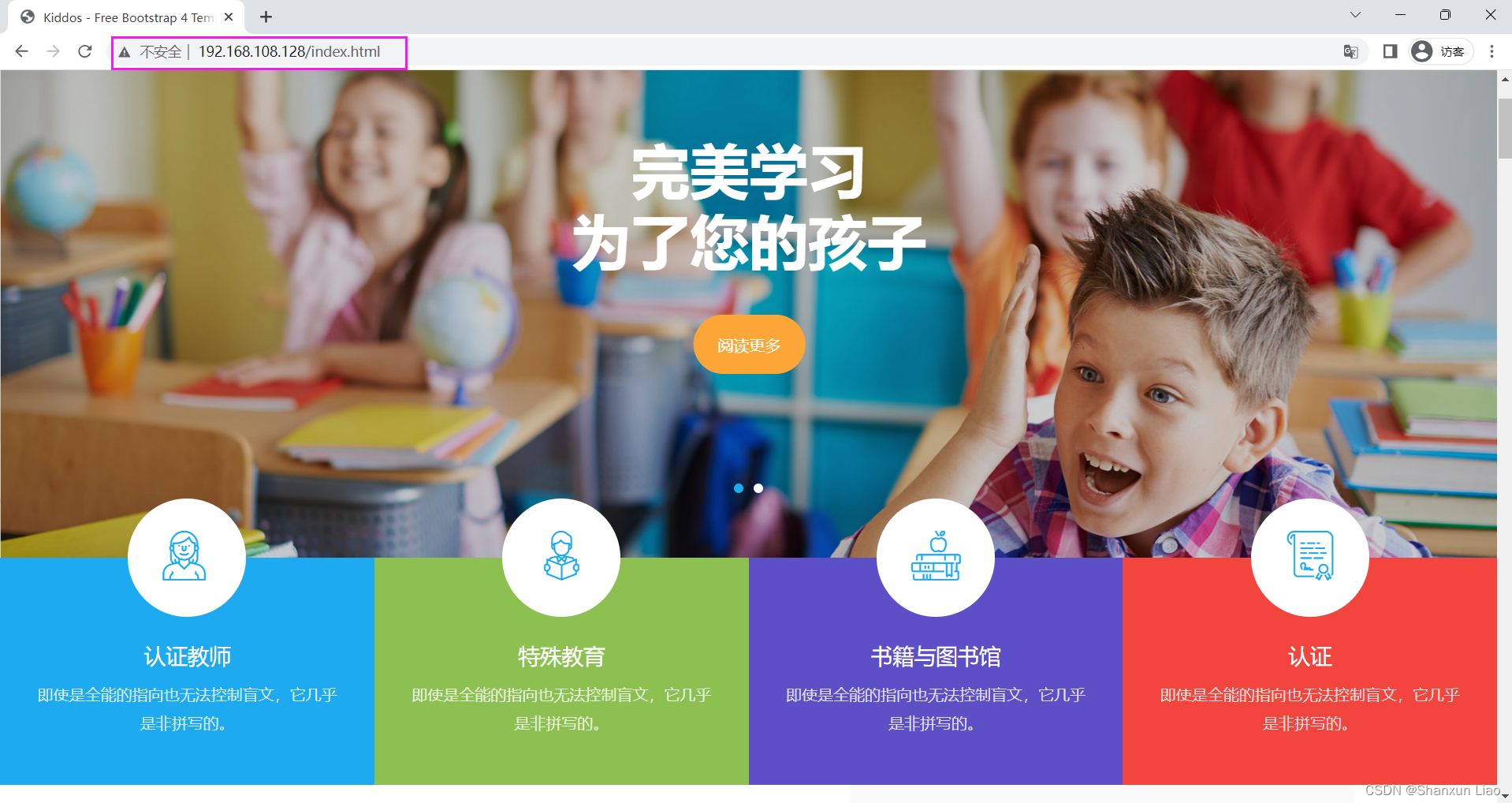



4.4 经测试 各项页面都很正常,源 HTML 是英文,通过谷歌翻译插件可以识别成中文语言





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








