| 主题 | 概要 |
|---|---|
| 计算机基础 | 大端小字字节序的概念,及其JAVA与C语言的实现 |
| 编辑 | 时间 |
| 新建 | 20160423 |
| 序号 | 参考资料 |
| 1 | http://blog.csdn.net/sunjiajiang/article/details/7163338 |
| 2 | http://blog.csdn.net/woshinia/article/details/41722085 |
基础概念
字节序定义
字节序,顾名思义字节的顺序,再多说两句就是大于一个字节类型的数据在内存中的存放顺序(一个字节的数据当然就无需谈顺序的问题了)。
字节序又分为两类:Big-Endian和Little-Endian。引用标准的Big-Endian和Little-Endian的定义如下:
a) Little-Endian就是低位字节排放在内存的低地址端,高位字节排放在内存的高地址端。
b) Big-Endian就是高位字节排放在内存的低地址端,低位字节排放在内存的高地址端。
c) 网络字节序:4个字节的32 bit值以下面的次序传输:首先是0~7bit,其次8~15bit,然后16~23bit,最后是24~31bit。这种传输次序称作大端字节序。由于 TCP/IP首部中所有的二进制整数在网络中传输时都要求以这种次序,因此它又称作网络字节序。
高/低地址与高/低字节
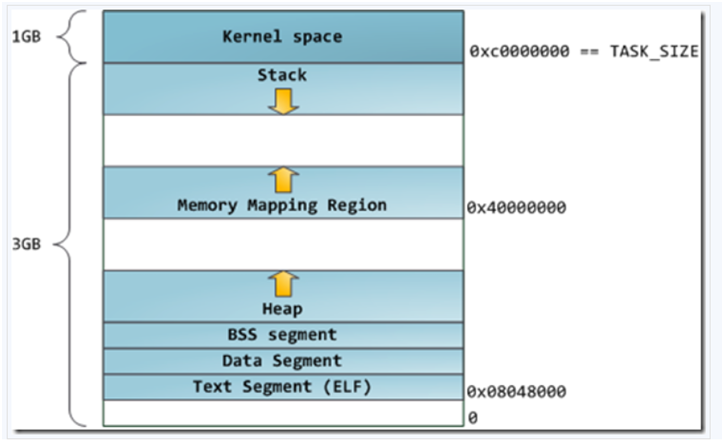
内存是按字节编址,单位是字节,1字节等于8位。32寻址机制中,最高内存地址 0xffffffff,最低内存地址0x00000000。一个运行着的C程序中内存的空间布局情况大致如图所示,堆区向上增长,栈区向下增长。
高低字节,就是靠左边的是高位,靠右边的是低位,比如 0x12345678,从高位到低位的字节依次是0x12、0x34、0x56和0x78。
示例
以unsigned int value = 0x12345678为例,分别看看在两种字节序下其存储情况:
Big-Endian: 低地址存放高位,如下图:
Little-Endian: 低地址存放低位,如下图:
JAVA实现
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class ByteConvert
{
public static byte[] ushortToBytes(int n) {
byte[] b = new byte[2];
b[1] = (byte) ( n & 0xff);
b[0] = (byte) ((n >> 8) & 0xff);
return b;
}
/**
* 将short转为低字节在前,高字节在后的byte数组(网络字节)
*/
public static byte[] ushortToLHBytes(int n)
{
byte[] output = new byte[2];
output[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
output[1] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
return output;
}
public static byte[] uintToBytes( long n )
{
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[3] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (n >> 16 & 0xff);
b[0] = (byte) (n >> 24 & 0xff);
return b;
}
public static byte[] intToBytes( int n )
{
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[3] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (n >> 16 & 0xff);
b[0] = (byte) (n >> 24 & 0xff);
return b;
}
public static byte[] uintToLHBytes( long n )
{
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (n >> 16 & 0xff);
b[3] = (byte) (n >> 24 & 0xff);
return b;
}
public static byte[] ubyteToBytes( short n ){
byte[] b = new byte[1];
b[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
return b;
}
/**
* 将int转为低字节在前,高字节在后的byte数组
*/
public static byte[] intToLHBytes(int n)
{
byte[] output = new byte[4];
output[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
output[1] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
output[2] = (byte) (n >> 16 & 0xff);
output[3] = (byte) (n >> 24 & 0xff);
return output;
}
/**
* 将short转为低字节在前,高字节在后的byte数组(网络字节)
*/
public static byte[] shortToLHBytes(short n)
{
byte[] output = new byte[2];
output[0] = (byte) (n & 0xff);
output[1] = (byte) (n >> 8 & 0xff);
return output;
}
/**
* 将HLbyte转换为int
* @param b byte[]
* @return int
*/
public static int HLBytesToInt(byte[] b)
{
int iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
bLoop = b[i];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xff) << (8 * i);
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static int LHBytesToInt(byte[] b)
{
int iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 4; i >0; i--)
{
bLoop = b[i-1];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xff) <<(8 * (i-1));
}
return iOutcome;
}
/**
* 将HLbyte转换为int
* @param b byte[]
* @return int
*/
`
public static long HL4BytesToLong(byte[] b)
{
long iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
bLoop = b[i];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xffL) << (8L * i);
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static long LH4BytesToLong(byte[] b)
{
long iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 4; i >0; i--)
{
bLoop = b[i-1];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xffL) <<(8L * (i-1));
}
return iOutcome;
}
/**
* 将HLbyte转换为long
* @param b byte[]
* @return long
*/
public static long HLBytesToLong(byte[] b)
{
long iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
bLoop = b[i];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xffL) << (8L * i);
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static long LHBytesToLong(byte[] b)
{
long iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 8; i >0; i--)
{
bLoop = b[i-1];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xffL) <<(8L * (i-1));
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static int LHBytesTouShort(byte[] b)
{
int iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 2; i >0; i--)
{
bLoop = b[i-1];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xff) <<(8 * (i-1));
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static short HLBytesToShort(byte[] b)
{
short iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
bLoop = b[i];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xff) << (8 * i);
}
return iOutcome;
}
public static short LHBytesToShort(byte[] b)
{
short iOutcome = 0;
byte bLoop;
for (int i = 2; i > 0; i-- )
{
bLoop = b[i-1];
iOutcome += (bLoop & 0xff) << (8 * (i-1));
}
return iOutcome;
}
// 解包为String算法
public static String BytesToString(byte[] b)
{
String retStr = "";
try
{
retStr = new String(b, "GBK"); //"GB2312"也可以
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return retStr.trim();
}
public static byte[] StringtoBytes(String str)
{
byte[] retBytes = null;
try
{
retBytes = str.getBytes("GBK"); //"GB2312"也可以
}
catch(UnsupportedEncodingException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return retBytes;
}
public static byte[] StringtoBytes(String str , short bytesLen)
{
byte[] output = new byte[bytesLen];
try
{
byte[] inBytes = str.getBytes("GBK");
System.arraycopy( inBytes,0, output, 0, inBytes.length);
}
catch(UnsupportedEncodingException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return output;
}
public static int toLH(int in)
{
int out = 0;
out = (in & 0xff) << 24;
out |= (in & 0xff00) << 8;
out |= (in & 0xff0000) >> 8;
out |= (in & 0xff000000) >> 24;
return out;
}
public static int toLH(long in)
{
int out = 0;
out = (int) (in & 0xff) << 24;
out |= (int) (in & 0xff00) << 8;
out |= (int) (in & 0xff0000) >> 8;
out |= (int) (in & 0xff000000) >> 24;
return out;
}
}
C语言实现
待续。。。
























 2195
2195

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








