🎃欢迎大家前去观看我的算法设计与分析专栏: 算法设计与分析_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客 希望对大家有所帮助!
🎃个人专栏:
🐬 算法设计与分析:算法设计与分析_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐳Java基础:Java基础_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐋c语言:c语言_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐟MySQL:数据结构_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🐠数据结构:数据结构_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
💎C++:C++_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🥽C51单片机:C51单片机(STC89C516)_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
💻基于HTML5的网页设计及应用:基于HTML5的网页设计及应用_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
🥏python:python_IT闫的博客-CSDN博客
欢迎收看,希望对大家有用!
目录
🎯目的:
1)了解贪心算法思想及基本原理;
2)掌握使用贪心算法求解问题的一般特征;
3)能够针对实际问题,能够正确选择贪心策略;
4)能够针对选择的贪心策略,证明算法的正确性;
5)能够根据贪心策略,正确编写代码;
6)能够正确分析算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度。
🎯内容:
实现活动安排问题的贪心算法。
测试数据可选用:
i
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Begin
1
3
2
5
3
5
6
8
8
2
End
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
🎯代码(C语言):
#include <stdio.h>
void activity(int start [],int end[],int n){
int result[n];//结果数组,存储选中的活动编号
int prev_end_time=-1;//上一个已选中的活动编号的结束时间
int count =0;//记录已选中的活动数量
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int start_time=start[i];
int end_time=end[i];
if(start_time >=prev_end_time){
result[count]=i;//将活动编码放入结果数组中
prev_end_time=end_time;
count++;
}
}
printf("活动安排的编码顺序为:");
for(int i=0;i<count;i++){
printf("%d ",result[i]+1);//注意活动编号从1号开始
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
int start1[]={1,3,2,5,3,5,6,8,8,2};
int end1[]={4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13};
activity(start1,end1,10);
return 0;
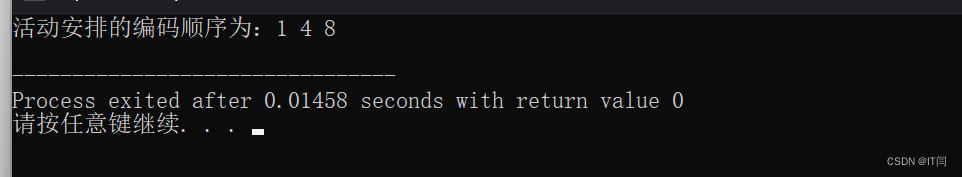
}🎯运行结果:
🎯 算法分析:
当储存n个对象时,
1.时间复杂度分析:
void activity(int start [],int end[],int n)函数中使用了一个循环,循环次数为n。- 循环内部使用常数时间执行操作(比较、赋值等),时间复杂度为O(1)。
- 因此,
void activity(int start [],int end[],int n)函数的时间复杂度为O(n)。综上所述:整段代码在存储n个对象时的时间复杂度为O(n)。
2.空间复杂度分析:
void activity(int start [],int end[],int n)函数中定义了一个大小为n的整型数组result[],用于存储选中的活动编号。因此,该数组的空间复杂度为O(n)。- 另外,函数中还定义了几个整型变量,它们的空间复杂度为O(1)。
综上所述,整段代码在存储n个对象的空间复杂度为O(n)。
需要注意的是,以上的复杂度分析假设输入规模为n,表示活动的数量。如果活动数量很大,复杂度可能会随之增加。
🎯其他程序语言的实现:
注:以下代码均有ai生成,读者如发现bug可以发在评论区,咱们一起解决❤️!
🎐Java程序:
public class ActivitySelection {
public static void activity(int[] start, int[] end, int n) {
int[] result = new int[n]; // 结果数组,存储选中的活动编号
int prevEnd = -1; // 上一个已选中的活动编号的结束时间
int count = 0; // 记录已选中的活动数量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int startTime = start[i];
int endTime = end[i];
if (startTime >= prevEnd) {
result[count] = i; // 将活动编码放入结果数组中
prevEnd = endTime;
count++;
}
}
System.out.print("活动安排的编码顺序为: ");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.print((result[i] + 1) + " "); // 注意活动编号从1号开始
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] start = {1, 3, 2, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2};
int[] end = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13};
int n = 10;
activity(start, end, n);
}
}
需要注意的是,在Java中数组不能动态声明大小,因此在Java代码中,数组
result的大小需要在定义时确定,即为n。另外,Java中的循环语法与C有所不同,需要使用for、while或者do-while语句等。
🎐 python程序:
def activity(start, end, n):
result = [0] * n # 结果数组,存储选中的活动编号
prev_end_time = -1 # 上一个已选中的活动编号的结束时间
count = 0 # 记录已选中的活动数量
for i in range(n):
start_time = start[i]
end_time = end[i]
if start_time >= prev_end_time:
result[count] = i # 将活动编码放入结果数组中
prev_end_time = end_time
count += 1
print("活动安排的编码顺序为:", end=' ')
for i in range(count):
print(result[i] + 1, end=' ') # 注意活动编号从1号开始
print()
start1 = [1, 3, 2, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2]
end1 = [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]
activity(start1, end1, 10)
需要注意的是,在Python中无法直接声明固定大小的数组,因此可以使用列表(List)代替。在Python中,索引从0开始,因此要将活动编号加1后打印。另外,在Python中使用
print()函数代替C语言中的printf()函数进行输出。
🎐C++程序:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void activity(int start[], int end[], int n) {
int result[n]; // 结果数组,存储选中的活动编号
int prev_end_time = -1; // 上一个已选中的活动编号的结束时间
int count = 0; // 记录已选中的活动数量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int start_time = start[i];
int end_time = end[i];
if (start_time >= prev_end_time) {
result[count] = i; // 将活动编码放入结果数组中
prev_end_time = end_time;
count++;
}
}
cout << "活动安排的编码顺序为:";
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
cout << result[i] + 1 << " "; // 注意活动编号从1号开始
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
int start1[] = {1, 3, 2, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2};
int end1[] = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13};
activity(start1, end1, 10);
return 0;
}
C++与C语言类似,但需要注意头文件、命名空间和输入输出等问题。在本例中,我们使用
<iostream>作为标准输入输出库,并加上using namespace std;语句,以在后续的代码中可以省略std::命名空间前缀。输出时使用cout和endl代替C语言中的printf()和\n符号。其他部分与C语言代码类似。


























 705
705











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










