介绍
本方案做的是采用Swiper组件实现容器视图居中完全展示,两边等长露出,并且跟手滑动效果。
效果图预览

实现思路
本解决方案通过维护所有卡片偏移的数组,实时更新卡片的偏移量,以实现swiper子组件内图片居中展示,两边等长露出。
- 左右露出效果静态实现。
Swiper组件基础视图效果如下。

如果所有子组件卡片大小一样,子组件内卡片居中展示即可实现效果。但是当子组件的卡片大小不一样时,无法通过简单的设置居中布局实现左右的等长露出。 此时需要计算当前状态下的卡片的偏移量。

/**
* 计算指定卡片的最大偏移量。
* @param index {number} target card's index.
* @returns offset value.
*/
getMaxOffset(index: number): number {
/*
* 这里的偏移量指相对容器左侧的值。
* 计算公式为:屏幕宽度 - Swiper两侧突出的偏移量 - 卡片自身的宽度。
* 此值即为卡片可偏移的最大值,也就是卡片右对齐的状态值。
* 如果居中,则将最大偏移量 / 2。
*/
return this.displayWidth - this.cardsList[index].width - 2 * this.swiperMargin;
}
/**
* 计算卡片偏移量,并维护偏移量列表。
* @param targetIndex { number } swiper target card's index.
*/
calculateOffset(target: number) {
let left = target - 1;
let right = target + 1;
// 计算上一张卡片的偏移值
if (this.isIndexValid(left)) {
this.cardsOffset[left] = this.getMaxOffset(left);
}
// 计算当前卡片的偏移值
if (this.isIndexValid(target)) {
this.cardsOffset[target] = this.getMaxOffset(target) / 2;
}
// 下一张片的偏移值
if (this.isIndexValid(right)) {
this.cardsOffset[right] = 0;
}
}- 滑动跟手实现
滑动swiper组件动态位置更新原理和上一步静态位置获取原理一样,只不过在滑动过程通过相应的回调函数实时位置更新。 在以下这三个swiper回调接口中,分别实现卡片跟手、离手、导航点切换时的卡片偏移量更新。
| 接口名 | 基本功能 |
|---|---|
| onGestureSwipe | 在页面跟手滑动过程中,逐帧触发该回调。 |
| onAnimationStart | 切换动画开始时触发该回调。 |
| onChange | 子组件索引变化时触发该事件。 |
具体api接口信息查看:Swiper事件。
- 在onGestureSwiper回调中,根据手指滑动的距离实时维护卡片的偏移量。
.onGestureSwipe((index, event) => {
let currentOffset = event.currentOffset;
// 获取当前卡片(居中)的原始偏移量
let maxOffset = this.getMaxOffset(index) / 2;
// 实时维护卡片的偏移量列表,做到跟手效果
if (currentOffset < 0) {
// 向左偏移
/*
* 此处计算原理为:按照比例设置卡片的偏移量。
* 当前卡片居中,向左滑动后将在左边,此时卡片偏移量即为 maxOffset * 2(因为向右对齐)。
* 所以手指能够滑动的最大距离(this.displayWidth)所带来的偏移量即为 maxOffset。
* 易得公式:卡片实时偏移量 = (手指滑动长度 / 屏幕宽度) * 卡片最大可偏移量 + 当前偏移量。
* 之后的计算原理相同,将不再赘述。
*/
this.cardsOffset[index] = (-currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset + maxOffset;
if (this.isIndexValid(index + 1)) {
// 下一个卡片的偏移量
let maxOffset = this.getMaxOffset(index + 1) / 2;
this.cardsOffset[index + 1] = (-currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset;
}
if (this.isIndexValid(index - 1)) {
// 上一个卡片的偏移量
let maxOffset = this.getMaxOffset(index - 1) / 2;
this.cardsOffset[index - 1] = (currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset + 2 * maxOffset;
}
} else if (currentOffset > 0) {
// 向右滑动
this.cardsOffset[index] = maxOffset - (currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset;
if (this.isIndexValid(index + 1)) {
let maxOffset = this.getMaxOffset(index + 1) / 2;
this.cardsOffset[index + 1] = (currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset;
}
if (this.isIndexValid(index - 1)) {
let maxOffset = this.getMaxOffset(index -1) / 2;
this.cardsOffset[index - 1] = 2 * maxOffset - (currentOffset / this.displayWidth) * maxOffset;
}
}
})- 在onAnimationStart回调中,计算手指离开屏幕时卡片的偏移量,避免产生突变的偏移量。
.onAnimationStart((_, targetIndex) => {
this.calculateOffset(targetIndex);
})这里的 calculateOffset 函数即步骤1中维护卡片偏移量的函数。
- 在onChange回调中提前计算Swiper滑动后卡片的位置。
.onChange((index) => {
logger.info(TAG, `Target index: ${index}`);
this.calculateOffset(index);
})计算方式同上一步。
- 图片预览效果实现
图片预览动效是通过共享元素转场结合全屏模态实现的。 通过geometryTransition属性绑定两个需要“一镜到底”的组件(本案例中的图片),结合模态窗口转场即可。
// 以下代码仅展示关键部分,详请查看源码
Row() {
Image(this.cardInfo.src)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Cover)
.borderRadius($r('app.integer.photo_radius'))
// TODO 知识点:geometryTransition通过id参数绑定两个组件转场关系,实现一镜到底动画
.geometryTransition(this.cardIndex.toString(), { follow: true })
.transition(TransitionEffect.OPACITY.animation({ duration: Constants.DURATION, curve: Curve.Friction }))
}
...
.bindContentCover(
this.isPhotoShow,
this.photoShowBuilder(this.cardInfo.src, this.cardIndex.toString()),
{ backgroundColor: $r('app.color.photo_preview_build_background'), modalTransition: ModalTransition.ALPHA }
)
...
// 全屏模态组件
@Builder photoShowBuilder(img: Resource, id: string) {
Column() {
Image(img)
.borderRadius($r('app.integer.photo_radius'))
.geometryTransition(id, { follow: true })
.width($r('app.string.photo_preview_width'))
.transition(TransitionEffect.opacity(Constants.OPACITY))
}
...
.onClick(() => {
animateTo({
duration: Constants.DURATION,
curve: Curve.Friction
}, () => {
this.isPhotoShow = !this.isPhotoShow;
})
})
}高性能知识点
- 本示例使用了LazyForEach进行数据懒加载以降低内存占用。
- Swiper组件的onGestureSwipe事件是个高频回调,注意在里面不要调用冗余操作和耗时操作。
工程结构&模块类型
cardswiperanimation // har包
├─components
│ ├─mainpage
│ │ └─ CardSwiper.ets // 卡片滑动组件入口
│ ├─model
│ │ └─ CardModel.ets // 定义卡片类型
│ ├─viewmodel
│ └─ CardViewModel.ets // 定义卡片组件
├─utils
│ ├─ Constants.ets // 常量数据模块依赖
最后
有很多小伙伴不知道学习哪些鸿蒙开发技术?不知道需要重点掌握哪些鸿蒙应用开发知识点?而且学习时频繁踩坑,最终浪费大量时间。所以有一份实用的鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料用来跟着学习是非常有必要的。
这份鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)资料包含了鸿蒙开发必掌握的核心知识要点,内容包含了(ArkTS、ArkUI开发组件、Stage模型、多端部署、分布式应用开发、音频、视频、WebGL、OpenHarmony多媒体技术、Napi组件、OpenHarmony内核、Harmony南向开发、鸿蒙项目实战等等)鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)技术知识点。
希望这一份鸿蒙学习资料能够给大家带来帮助,有需要的小伙伴自行领取,限时开源,先到先得~无套路领取!!
如果你是一名有经验的资深Android移动开发、Java开发、前端开发、对鸿蒙感兴趣以及转行人员,可以直接领取这份资料
获取这份完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
鸿蒙(HarmonyOS NEXT)最新学习路线

-
HarmonOS基础技能

- HarmonOS就业必备技能

- HarmonOS多媒体技术

- 鸿蒙NaPi组件进阶

- HarmonOS高级技能
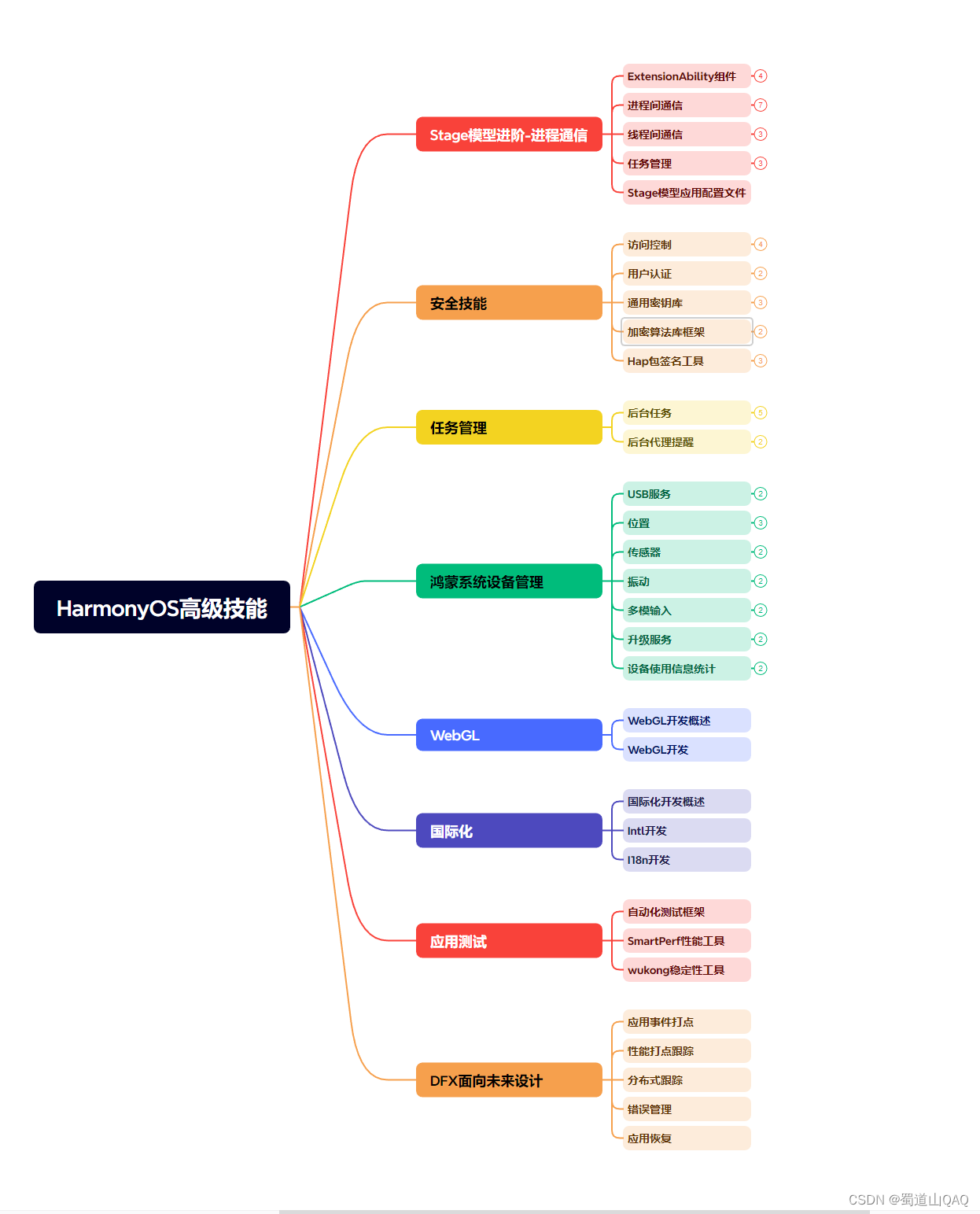
- 初识HarmonOS内核

- 实战就业级设备开发

有了路线图,怎么能没有学习资料呢,小编也准备了一份联合鸿蒙官方发布笔记整理收纳的一套系统性的鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )学习手册(共计1236页)与鸿蒙(OpenHarmony )开发入门教学视频,内容包含:ArkTS、ArkUI、Web开发、应用模型、资源分类…等知识点。
获取以上完整版高清学习路线,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发入门教学视频》

《鸿蒙生态应用开发V2.0白皮书》

《鸿蒙 (OpenHarmony)开发基础到实战手册》
OpenHarmony北向、南向开发环境搭建

《鸿蒙开发基础》
- ArkTS语言
- 安装DevEco Studio
- 运用你的第一个ArkTS应用
- ArkUI声明式UI开发
- .……

《鸿蒙开发进阶》
- Stage模型入门
- 网络管理
- 数据管理
- 电话服务
- 分布式应用开发
- 通知与窗口管理
- 多媒体技术
- 安全技能
- 任务管理
- WebGL
- 国际化开发
- 应用测试
- DFX面向未来设计
- 鸿蒙系统移植和裁剪定制
- ……

《鸿蒙进阶实战》
- ArkTS实践
- UIAbility应用
- 网络案例
- ……

获取以上完整鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料,请点击→纯血版全套鸿蒙HarmonyOS学习资料
总结
总的来说,华为鸿蒙不再兼容安卓,对中年程序员来说是一个挑战,也是一个机会。只有积极应对变化,不断学习和提升自己,他们才能在这个变革的时代中立于不败之地。



























 1374
1374

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








