presto的QueryExecution的start方法
标签(空格分隔): presto
1 在queryExecution中,start方法代码如下:
public void start()
{
try (SetThreadName ignored = new SetThreadName("Query-%s", stateMachine.getQueryId())) {
try {
// transition to planning
if (!stateMachine.transitionToPlanning()) {
// query already started or finished
return;
}
// analyze query
PlanRoot plan = analyzeQuery();//查询分析,随后详细分析
// plan distribution of query
planDistribution(plan);//计划query的分发,随后详细分析
// transition to starting
if (!stateMachine.transitionToStarting()) {
// query already started or finished
return;
}
// if query is not finished, start the scheduler, otherwise cancel it
SqlQueryScheduler scheduler = queryScheduler.get();
if (!stateMachine.isDone()) {
scheduler.start();
}
}
catch (Throwable e) {
fail(e);
Throwables.propagateIfInstanceOf(e, Error.class);
}
}
}analyzeQuery()方法分析
planDistribution(plan)方法分析
-
- 最重要的代码块,创建调度器,这其中会创建多个stage:
// build the stage execution objects (this doesn't schedule execution)
SqlQueryScheduler scheduler = new SqlQueryScheduler(
stateMachine,
locationFactory,
outputStageExecutionPlan,
nodePartitioningManager,
nodeScheduler,
remoteTaskFactory,
stateMachine.getSession(),
plan.isSummarizeTaskInfos(),
scheduleSplitBatchSize,
queryExecutor,
rootOutputBuffers,
nodeTaskMap,
executionPolicy);创建stage:
List<SqlStageExecution> stages = createStages(
Optional.empty(),
new AtomicInteger(),
locationFactory,
plan.withBucketToPartition(Optional.of(new int[1])),
nodeScheduler,
remoteTaskFactory,
session,
splitBatchSize,
partitioningHandle -> partitioningCache.computeIfAbsent(partitioningHandle, handle -> nodePartitioningManager.getNodePartitioningMap(session, handle)),
executor,
nodeTaskMap,
stageSchedulers,
stageLinkages);2.Task创建和提交
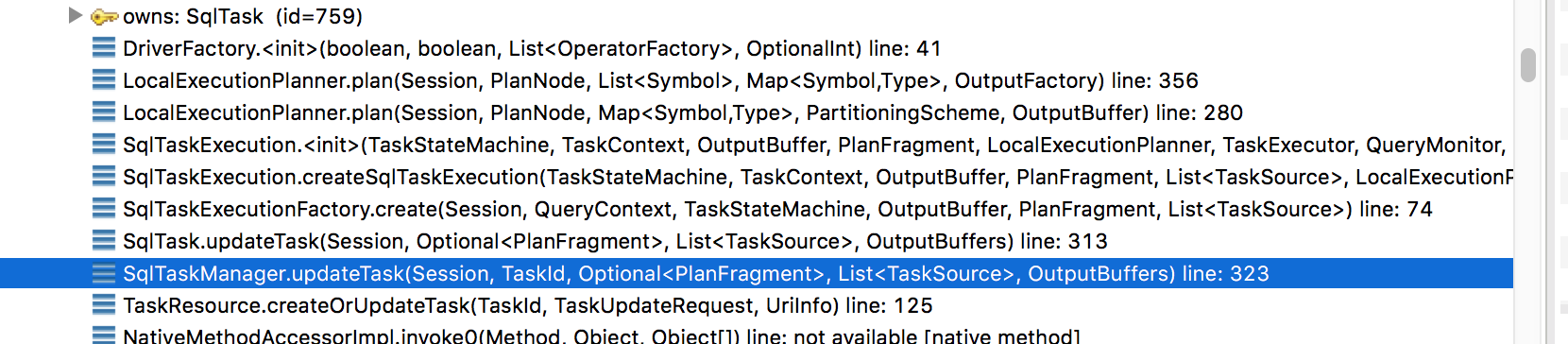
1) TaskResource接收到http请求后,会调用createOrUpdateTask方法,调用栈如下:
代码如下:
@POST
@Path("{taskId}")
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Response createOrUpdateTask(@PathParam("taskId") TaskId taskId, TaskUpdateRequest taskUpdateRequest, @Context UriInfo uriInfo)
{
requireNonNull(taskUpdateRequest, "taskUpdateRequest is null");
Session session = taskUpdateRequest.getSession().toSession(sessionPropertyManager);
TaskInfo taskInfo = taskManager.updateTask(session,
taskId,
taskUpdateRequest.getFragment(),//原始sql解析后的子sql,由协调节点下发而来
taskUpdateRequest.getSources(),//task的数据源,是个List<TaskSource>,说明一个task对应了多个split要进行处理
taskUpdateRequest.getOutputIds());
if (shouldSummarize(uriInfo)) {
taskInfo = taskInfo.summarize();
}
return Response.ok().entity(taskInfo).build();
}2) sqlTaskManager管理多个task,没一个task对应一个SqlTask对象和一个taskid,在构造SqlTaskManager时全部创建好。调用sqlTaskManager的updateTask的代码如下:
@Override
public TaskInfo updateTask(Session session, TaskId taskId, Optional<PlanFragment> fragment, List<TaskSource> sources, OutputBuffers outputBuffers)
{
requireNonNull(session, "session is null");
requireNonNull(taskId, "taskId is null");
requireNonNull(fragment, "fragment is null");
requireNonNull(sources, "sources is null");
requireNonNull(outputBuffers, "outputBuffers is null");
if (resourceOvercommit(session)) {
// TODO: This should have been done when the QueryContext was created. However, the session isn't available at that point.
queryContexts.getUnchecked(taskId.getQueryId()).setResourceOvercommit();
}
SqlTask sqlTask = tasks.getUnchecked(taskId);
sqlTask.recordHeartbeat();
return sqlTask.updateTask(session, fragment, sources, outputBuffers);
}3) SqlTask中调用updateTask方法:
public TaskInfo updateTask(Session session, Optional<PlanFragment> fragment, List<TaskSource> sources, OutputBuffers outputBuffers)
{
try {
// The LazyOutput buffer does not support write methods, so the actual
// output buffer must be established before drivers are created (e.g.
// a VALUES query).
outputBuffer.setOutputBuffers(outputBuffers);
// assure the task execution is only created once
SqlTaskExecution taskExecution;
synchronized (this) {
// is task already complete?
TaskHolder taskHolder = taskHolderReference.get();
if (taskHolder.isFinished()) {
return taskHolder.getFinalTaskInfo();
}
taskExecution = taskHolder.getTaskExecution();
if (taskExecution == null) {
checkState(fragment.isPresent(), "fragment must be present");
taskExecution = sqlTaskExecutionFactory.create(session, queryContext, taskStateMachine, outputBuffer, fragment.get(), sources);//一个task对应多个split源,多个split源最终由TaskExecution对象完成执行
taskHolderReference.compareAndSet(taskHolder, new TaskHolder(taskExecution));
needsPlan.set(false);
}
}
if (taskExecution != null) {
taskExecution.addSources(sources);
}
}4) 创建SqlTaskExecution,SqlTaskExecution的构造函数如下:
创建多个driverFactory,每个对应处理一个split
LocalExecutionPlan localExecutionPlan = planner.plan(
taskContext.getSession(),
fragment.getRoot(),
fragment.getSymbols(),
fragment.getPartitioningScheme(),
outputBuffer);
driverFactories = localExecutionPlan.getDriverFactories();需要重点分析plan方法,该方法属于LocalExecutionPlanner,返回一个本地执行计划LocalExecutionPlan对象,方法源码如下:
public LocalExecutionPlan plan(
Session session,
PlanNode plan,//从协调节点发送过来的fragment中获取,这里是outputNode,
Map<Symbol, Type> types,//fragment中的symbols,记录了相关的字段和字段类型
PartitioningScheme partitioningScheme, //来自fragment,具体什么作用还不清楚
OutputBuffer outputBuffer) //用于构造输出
{
List<Symbol> outputLayout = partitioningScheme.getOutputLayout();
if (partitioningScheme.getPartitioning().getHandle().equals(FIXED_BROADCAST_DISTRIBUTION) ||
partitioningScheme.getPartitioning().getHandle().equals(SINGLE_DISTRIBUTION) ||
partitioningScheme.getPartitioning().getHandle().equals(COORDINATOR_DISTRIBUTION)) {
//什么情况下走这个流程是不是很清楚,
return plan(session, plan, outputLayout, types, new TaskOutputFactory(outputBuffer));
}
}如果不走上边的流程,最后调用私有的plan方法,代码如下:
return plan(
session,
plan,
outputLayout,
types,
new PartitionedOutputFactory(partitionFunction, partitionChannels, partitionConstants, nullChannel, outputBuffer, maxPagePartitioningBufferSize));LocalExecutionPlanner的plan方法代码如下:
public LocalExecutionPlan plan(Session session,
PlanNode plan,
List<Symbol> outputLayout,
Map<Symbol, Type> types,
OutputFactory outputOperatorFactory)
{
LocalExecutionPlanContext context = new LocalExecutionPlanContext(session, types);
PhysicalOperation physicalOperation = plan.accept(new Visitor(session), context);
Function<Page, Page> pagePreprocessor = enforceLayoutProcessor(outputLayout, physicalOperation.getLayout());
List<Type> outputTypes = outputLayout.stream()
.map(types::get)
.collect(toImmutableList()); //从输入的types参数中获取信息,转化成输出需要的类型
DriverFactory driverFactory = new DriverFactory(
context.isInputDriver(),
true,
ImmutableList.<OperatorFactory>builder()
.addAll(physicalOperation.getOperatorFactories())
.add(outputOperatorFactory.createOutputOperator(context.getNextOperatorId(), plan.getId(), outputTypes, pagePreprocessor))
.build(),
context.getDriverInstanceCount());
context.addDriverFactory(driverFactory);
addLookupOuterDrivers(context);
// notify operator factories that planning has completed
context.getDriverFactories().stream()
.map(DriverFactory::getOperatorFactories)
.flatMap(List::stream)
.filter(LocalPlannerAware.class::isInstance)
.map(LocalPlannerAware.class::cast)
.forEach(LocalPlannerAware::localPlannerComplete);
return new LocalExecutionPlan(context.getDriverFactories());
}





















 1888
1888

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








