一个图像有不同的像素值构成,像素值在图像中的分布情况是这幅图片的一重要特征。直方图可以描述图像内容、检测图像中的特定对象或纹理,你将学习如何计算直方图来修改图像外观。opencv提供了 cv::calcHist这个函数,可以计算任意类型的多通道图像。下面我们先定义一个类
class
Histogram1D,成员变量
private:
float m_hranges[2];//像素的最小及最大值 0.0 255.0
int m_histSize[1];//项的数目 256
const float*m_ranges[1];//像素的最大最小数组指针
int channels[1];//仅用到一个通道 通道0
然后在构造函数中初始化:
public:
Histogram1D()
{
//准备1D 直方图的参数
m_hranges[0] = 0.0;
m_hranges[1] = 255.0;
m_histSize[0] = 256;
m_ranges[0] = m_hranges;
channels[0] = 0;
};
然后计算直方图:
//计算1D直方图
cv::
MatND getHistogram(const cv::Mat &image)
{
cv::MatND hist;
//计算直方图
cv::calcHist(&image, //图片
1, //计算单张图片的直方图
channels, //通道数量
cv::Mat(), //不使用图像作为掩码
hist, //返回的直方图
1, //这是1D的直方图
m_histSize, //项的数量
m_ranges //像素值的范围
);
return hist;
};
接着你可以遍历 hist 的256个条目,它是一个一维数组
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
//遍历这256个值对应的像素点个数
cout << "value" << i << "=" << histo.at<float>(i) << endl;
为了更直观的把数值显示出来,更方便的方式是将直方图可视化,我们在类
class
Histogram1D 添加 getHistogramImage() 方法,计算1D的直方图,并返回柱状图。
//计算1D直方图,并返回一张图像
cv::Mat getHistogramImage(const cv::Mat & image)
{
//首先计算直方图
cv::MatND hist = getHistogram(image);
//获取最大值和最小值
double maxVal = 0;
double minVal = 0;
cv::minMaxLoc(hist, &minVal, &maxVal, 0, 0);
cv::Mat histImg(m_histSize[0], m_histSize[0], CV_8U, cv::Scalar(255));
int hpt = static_cast<int>(0.9*m_histSize[0]);
//每个条目都绘制一条垂直线
for (int h = 0; h < m_histSize[0]; h++)
{
float binVal = hist.at<float>(h);
int intensity = static_cast<int>(binVal*hpt / maxVal);
//两点之间绘制一条直线
cv::line(histImg, cv::Point(h, m_histSize[0]), //底部点
cv::Point(h, m_histSize[0] - intensity),//顶部点
cv::Scalar::all(0));//黑色
}
return histImg;
};
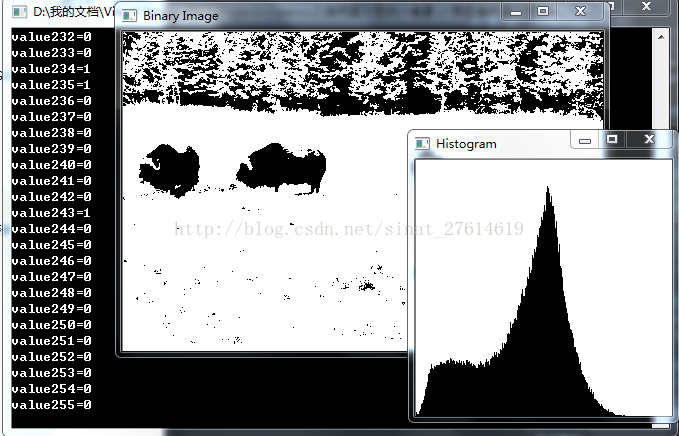
相似的,我们可以定义一个类来计算彩色的 BGR 图像的直方图:
class
Colorhistogram
{
private
:
int
m_histSize[3];
//项的数目
float
m_hranges[2];
//像素的最小及最大值
const
float
*m_ranges[3];
int
m_channels[3];
public
:
Colorhistogram()
{
m_histSize[0] = m_histSize[1] = m_histSize[2] = 256;
m_hranges[0] = 0.0;
m_hranges[1] = 255.0;
m_ranges[0] = m_hranges;
m_ranges[1] = m_hranges;
m_ranges[2] = m_hranges;
m_channels[0] = 0;
m_channels[1] = 0;
m_channels[2] = 0;
};
cv::
MatND
getHistogram(
const
cv::
Mat
&
image
)
{
cv::
MatND
hist;
// BGR color histogram
m_hranges[0] = 0.0;
// BRG range
m_hranges[1] = 255.0;
m_channels[0] = 0;
// the three channels
m_channels[1] = 1;
m_channels[2] = 2;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&
image
,
1,
// histogram of 1 image only
m_channels,
// the channel used
cv::
Mat
(),
// no mask is used
hist,
// the resulting histogram
3,
// it is a 3D histogram
m_histSize,
// number of bins
m_ranges
// pixel value range
);
return
hist;
}
// Computes the histogram.
cv::
SparseMat
getSparseHistogram(
const
cv::
Mat
&
image
) {
cv::
SparseMat
hist(3, m_histSize,
CV_32F
);
// BGR color histogram
m_hranges[0] = 0.0;
// BRG range
m_hranges[1] = 255.0;
m_channels[0] = 0;
// the three channels
m_channels[1] = 1;
m_channels[2] = 2;
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&
image
,
1,
// histogram of 1 image only
m_channels,
// the channel used
cv::
Mat
(),
// no mask is used
hist,
// the resulting histogram
3,
// it is a 3D histogram
m_histSize,
// number of bins
m_ranges
// pixel value range
);
return
hist;
}
// Computes the 2D ab histogram.
// BGR source image is converted to Lab
cv::
MatND
getabHistogram(
const
cv::
Mat
&
image
) {
cv::
MatND
hist;
// Convert to Lab color space
cv::
Mat
lab;
cv::cvtColor(
image
, lab,
CV_BGR2Lab
);
// Prepare arguments for a 2D color histogram
m_hranges[0] = -128.0;
m_hranges[1] = 127.0;
m_channels[0] = 1;
// the two channels used are ab
m_channels[1] = 2;
// Compute histogram
return
hist;
}
// Computes the 1D Hue histogram with a mask.
// BGR source image is converted to HSV
cv::
MatND
getHueHistogram(
const
cv::
Mat
&
image
) {
cv::
MatND
hist;
// Convert to Lab color space
cv::
Mat
hue;
cv::cvtColor(
image
, hue,
CV_BGR2HSV
);
// Prepare arguments for a 1D hue histogram
m_hranges[0] = 0.0;
m_hranges[1] = 180.0;
m_channels[0] = 0;
// the hue channel
// Compute histogram
cv::calcHist(&hue,
1,
// histogram of 1 image only
m_channels,
// the channel used
cv::
Mat
(),
// no mask is used
hist,
// the resulting histogram
1,
// it is a 1D histogram
m_histSize,
// number of bins
m_ranges
// pixel value range
);
return
hist;
}
cv::
Mat
colorReduce(
const
cv::
Mat
&
image
,
int
div
= 64) {
int
n =
static_cast
<
int
>(log(
static_cast
<
double
>(
div
)) / log(2.0));
// mask used to round the pixel value
uchar
mask = 0xFF << n;
// e.g. for div=16, mask= 0xF0
cv::
Mat_
<cv::
Vec3b
>::
const_iterator
it =
image
.begin<cv::
Vec3b
>();
cv::
Mat_
<cv::
Vec3b
>::
const_iterator
itend =
image
.end<cv::
Vec3b
>();
// Set output image (always 1-channel)
cv::
Mat
result(
image
.rows,
image
.cols,
image
.type());
cv::
Mat_
<cv::
Vec3b
>::
iterator
itr = result.begin<cv::
Vec3b
>();
for
(; it
!=
itend;
++
it,
++
itr) {
(
*
itr)
[
0
]
= ((
*
it)
[
0
]
& mask) +
div
/ 2;
(
*
itr)
[
1
]
= ((
*
it)
[
1
]
& mask) +
div
/ 2;
(
*
itr)
[
2
]
= ((
*
it)
[
2
]
& mask) +
div
/ 2;
}
return
result;
}
};
























 6680
6680

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








