目录
神经网络2通常依赖反向传播求梯度来更新网络参数,求梯度过程中通常是一件非常复杂而且容易出错的事情。而深度学习框架可以帮助我们自动完成这种求梯度的运算。
Tensorflow 一般使用梯度磁带 tf.GradientTape 来记录正向运算过程,然后反播磁带自动得到梯度值。
这种利用tf.GradientTape求取微分的方法叫做TensorFlow的自动微分机制。
一、利用梯度磁带求导
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# f(x) = a*x**2 + b*x + c 的导数
x = tf.Variable(0.0, name="x", dtype=tf.float32)
a = tf.constant(1.0)
b = tf.constant(-2.0)
c = tf.constant(1.0)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y = a * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
dy_dx = tape.gradient(y, x)
print(dy_dx)
# 对张量也可以求导,需要增加 watch
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([a, b, c])
y = a * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
dy_dx, dy_da, dy_db, dy_dc = tape.gradient(y, [x, a, b, c])
print(dy_da)
print(dy_dc)
print(dy_db)
print(dy_dx)
# 也可以求二阶导数
with tf.GradientTape() as tape2:
with tf.GradientTape() as tape1:
y = a * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
dy_dx = tape1.gradient(y, x)
dy2_dx2 = tape2.gradient(dy_dx, x)
print(dy2_dx2)
# 可以在autograph中使用
@tf.function
def f(xx):
aa = tf.constant(1.0)
bb = tf.constant(-2.0)
cc = tf.constant(1.0)
# 自变量转换成tf.float32
xx = tf.cast(xx, tf.float32)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape3:
tape3.watch(xx)
yy = aa * tf.pow(xx, 2) + b * xx + c
dyy_dxx = tape3.gradient(yy, xx)
return dyy_dxx, yy
tf.print(f(tf.constant(0.0)))
tf.print(f(tf.constant(1.0)))

二,利用梯度磁带和优化器求最小值
# 利用梯度磁带和优化器求最小值
# 求f(x)=a*x**2 + b*x + c 最小值
# optimizer.apply_gradients
x = tf.Variable(0.0, name="x", dtype=tf.float32)
a = tf.constant(1.0)
b = tf.constant(-2.0)
c = tf.constant(1.0)
# SGD 随机梯度下降算法
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
for _ in range(1000):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y = a * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
dy_dx = tape.gradient(y, x)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=[(dy_dx,x)])
tf.print("y = ", y, ";, x =", x)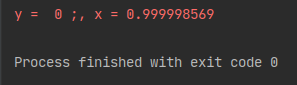
# 使用 optimizer.minimize
# 求f(x)=a*x**2 + b*x + c 最小值
# optimizer.minimize相当于先用tape求gradient,再 apply_gradient
x = tf.Variable(0.0, name="x", dtype=tf.float32)
# 注意f() 无参数
def f():
a_my = tf.constant(1.0)
b_my = tf.constant(-2.0)
c_my = tf.constant(1.0)
y_my = a_my * tf.pow(x, 2) + b_my * x + c
return y_my
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
for _ in range(1000):
optimizer.minimize(f, [x])
tf.print("y = ", y, ";, x =", x)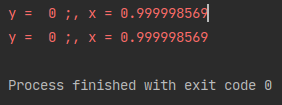
# 方法3:
# 在 autograph 中
# 求f(x)=a*x**2 + b*x + c 最小值
# 使用 optimizer.apply_gradients
x = tf.Variable(0.0, name="x", dtype=tf.float32)
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
@tf.function
def minimizef():
a_c = tf.constant(1.0)
b_c = tf.constant(-2.0)
c_c = tf.constant(1.0)
# 注意autograph时使用tf.range(1000)而不是range(1000)
for _ in tf.range(1000):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape4:
y_v = a * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
dyv_dx = tape4.gradient(y_v, x)
optimizer.apply_gradients(grads_and_vars=[(dyv_dx, x)])
y_v = a_c * tf.pow(x, 2) + b * x + c
return y_v
tf.print(minimizef())
tf.print(x)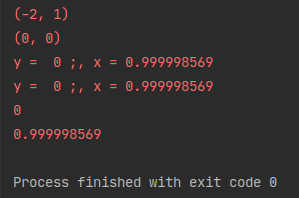






















 337
337











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








