7.1 图论基础
节点
边
应用:交通运输,社交网络,互联网,工作安排,脑区活动,程序状态执行
-
图的分类:有向图,无向图
后文讲解以无向图为主
无向图是一种特殊的有向图(两个节点相互指向),有向图由于其不对称型,演变出更多复杂的问题和专门针对有向图的算法(暂不涉及) -
图的分类:无权图,有权图
-
图的连通性
-
简单图:自环边,平行边。
7.2 图的表示
- 邻接矩阵:适合表示稠密图(Dense Graph),例如完全图
#ifndef DENSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#define DENSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
//稠密图 -- 邻接矩阵
class DenseGraph{
private:
int n,m;
bool directed;
vector<vector<bool>> g;
public:
DenseGraph(int n,bool directed)
{
this->n=n;
this->m=0;
this->directed=directed;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
g.push_back(vector<bool>(n,false));
}
~DenseGraph()
{
}
int V()
{
return n;
}
int E()
{
return m;
}
void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
//严谨一些,先考虑v和w都不能越界
assert(v>=0 && v<n);
assert(w>=0 && w<n);
if(hasEdge(v,w))
return;
g[v][w]=true;
if(!directed)
g[w][v]=true;
m++;
}
bool hasEdge(int v,int w)
{
assert(v>=0 && v<n);
assert(w>=0 && w<n);
return g[v][w];
}
};
#endif // DENSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
- 邻接表:适合表示稀疏图(Sparse Graph)
#ifndef SPARSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#define SPARSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
//稀疏图 —— 邻接表
class SparseGraph{
private:
int n,m;
bool directed;
vector<vector<int>> g;
public:
SparseGraph(int n,bool directed)
{
this->n=n;
this->m=0;
this->directed=directed;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
g.push_back(vector<int>());
}
~SparseGraph()
{
}
int V()
{
return n;
}
int E()
{
return m;
}
void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
//严谨一些,先考虑v和w都不能越界
assert(v>=0 && v<n);
assert(w>=0 && w<n);
if(hasEdge(v,w))
return;
g[v].push_back(w);
if(v!=w && !directed)//防止有自环边问题
g[w].push_back(v)
m++;
}
bool hasEdge(int v,int w)
{
assert(v>=0 && v<n);
assert(w>=0 && w<n);
for(int i=0;i<g[v].size();i++)
if(g[v][i]==w)
return true;
return false;
}
};
#endif // SPARSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
7.3 相邻点迭代器
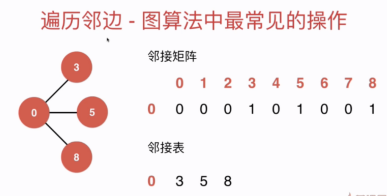
使用上述的思路其实就是遍历class里的二维数组g就可以得到一个点相邻的点,但这的前提是要把vector<vector<bool>> g设为public,但其实,这样会让外部用户访问到g,有可能会泄露或修改数据,不够安全
如何在vector<vector<bool>> g保持为private的情况下遍历一个点的相临点?
答:使用迭代器,用户通过迭代器找到图中一个结点的相邻接点
稀疏图
#ifndef SPARSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#define SPARSEGRAPH_H_INCLUDED
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
//稀疏图 —— 邻接表
class SparseGraph{
private:
int n,m;
bool directed;
vector<vector<int> > g;
public:
SparseGraph(int n,bool directed)
{
this->n=n;
this->m=0;
this->directed=directed;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
g.push_back(vector<int>());
}
~SparseGraph()
{
}
int V()
{
return n;
}
int E()
{
return m;
}
void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
//严谨一些,先考虑v和w都不能越界
assert(v>=0 && v<n);
assert(w>=0 && w<n);
if







 本文介绍了图论的基础知识,包括节点、边和图的分类。重点讲述了无向图和有向图的区别,以及无权图和有权图的概念。讨论了图的表示方法,如邻接矩阵和邻接表,特别强调了在保持数据安全性的前提下遍历相邻点的方法。还概述了图的算法框架,包括读取图数据的类和测试函数。最后,提到了深度优先遍历、连通分量、寻路问题以及广度优先遍历在寻找无权图最短路径中的应用。
本文介绍了图论的基础知识,包括节点、边和图的分类。重点讲述了无向图和有向图的区别,以及无权图和有权图的概念。讨论了图的表示方法,如邻接矩阵和邻接表,特别强调了在保持数据安全性的前提下遍历相邻点的方法。还概述了图的算法框架,包括读取图数据的类和测试函数。最后,提到了深度优先遍历、连通分量、寻路问题以及广度优先遍历在寻找无权图最短路径中的应用。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 501
501











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








