题目:快速找到未知长度单链表的中间结点
首先分析一下,既然是一个面试题,就一定有普通方法和高级方法,而高级方法无疑会为你大大加分!
普通方法很简单:首先遍历一遍单链表以确定单链表的长度L。然后再此从头结点出发循环L/2次找到单链表的中间结点。
普通方法的算法复杂度为:O(L+L/2) = O(3L/2)
普通方法的实现代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
struct node
{
int data; //elementype表示一种数据类型,可能是int/char等等
struct node *next; //next 指针,用于链表结构指向下一个节点
};
typedef struct node node; //重定义struct node类型为node
int GetMidNode(node* L); //函数声明
void List(node* head);
node* Creat(int Count);
int Length(node *L);
int main()
{
node* head;
int a;
int Num;
printf("1.Creat linklist\n2.View linklist\n3.Length of linklist\n4.Value of middle node\n0.Exit\n");
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
switch(a)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the number of linked list nodes:\n");
scanf("%d",&Num);
head = Creat(Num);
printf("\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("List:\n");
List(head);
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Length of linklist:\n");
printf("%d",Length(head));
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Value of middle node:\n");
printf("%d",GetMidNode(head));
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 0:
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
node* Creat(int Count) //创建链表
{
node *p1,*p2,*head;
int n;
srand(time(NULL));//生成种子
head = p1 = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
head->data = rand()%1000;
head->next = NULL;
for (n = 1;n < Count;n++)
{
p2 = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p2->data = rand()%1000;
p1->next = p2;
p1 = p2;
}
p1->next = NULL;
return(head);
}
void List(node* head) //打印链表
{
node *p1;
p1 = head;
while(p1!= NULL)
{
printf("%4d",p1->data);
p1 = p1->next;
}
}
int GetMidNode(node* L) //寻找链表中间值
{
int a,i,n;
n = Length(L); //获取链表长度
for (i = 1;i < (n+1)/2;i++)
{
L = L->next; //从头查找链表,到链表一半
}
a = L->data;
return a;
}
int Length(node *L) //计算链表长度
{
int n = 0;
while(L->next!= NULL)
{
n++;
L = L->next;
}
n++;
return n;
}这段代码实现了4个功能:1. 创建链表 2. 查看链表 3. 计算链表长度 4. 查询链表中间值
在第四个功能中我们使用了普通的方法,也就是 int GetMidNode(node* L) 函数
=================================================
高级方法利用快慢指针原理:设置两个指针*search和*mid都指向单链表的头结点。其中*search的移动速度是*mid的2倍。当*search指向末尾结点的时候,*mid正好在中间了。也就是一种标尺的思想。
高级方法的算法复杂度为:O(L/2)
高级方法实现代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
struct node
{
int data; //elementype表示一种数据类型,可能是int/char等等
struct node *next; //next 指针,用于链表结构指向下一个节点
};
typedef struct node node; //重定义struct node类型为node
int GetMidNode(node* L); //函数声明
void List(node* head);
node* Creat(int Count);
int Length(node *L);
int main()
{
node* head;
int a;
int Num;
printf("1.Creat linklist\n2.View linklist\n3.Length of linklist\n4.Value of middle node\n0.Exit\n");
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
switch(a)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter the number of linked list nodes:\n");
scanf("%d",&Num);
head = Creat(Num);
printf("\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("List:\n");
List(head);
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("Length of linklist:\n");
printf("%d",Length(head));
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 4:
printf("Value of middle node:\n");
printf("%d",GetMidNode(head));
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
break;
case 0:
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
node* Creat(int Count) //创建链表
{
node *p1,*p2,*head;
int n;
srand(time(NULL));//生成种子
head = p1 = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
head->data = rand()%1000;
head->next = NULL;
for (n = 1;n < Count;n++)
{
p2 = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
p2->data = rand()%1000;
p1->next = p2;
p1 = p2;
}
p1->next = NULL;
return(head);
}
void List(node* head) //打印链表
{
node *p1;
p1 = head;
while(p1!= NULL)
{
printf("%4d",p1->data);
p1 = p1->next;
}
}
int GetMidNode(node* L) //寻找链表中间值
{
int a;
node *search,*mid;
mid = search = L;
while(search->next != NULL)
{
if(search->next->next != NULL)
{
search = search->next->next;
mid= mid->next;
}
else
{
search = search->next;
}
}
a = mid->data;
return a;
}
int Length(node *L) //计算链表长度
{
int n = 0;
while(L->next!= NULL)
{
n++;
L = L->next;
}
n++;
return n;
}
与之前代码的不同点在于int GetMidNode(node* L) 函数的实现,用到了快慢指针的原理。当快指针遍历了链表的时候慢指针正好到达链表的一半位置。
结果展示:
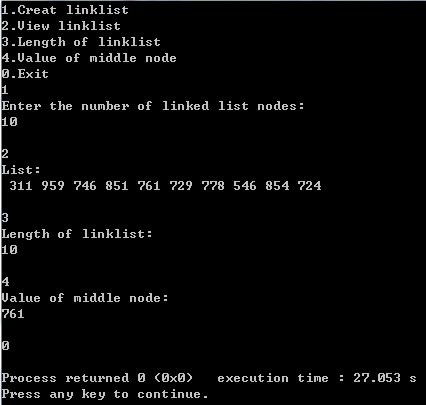
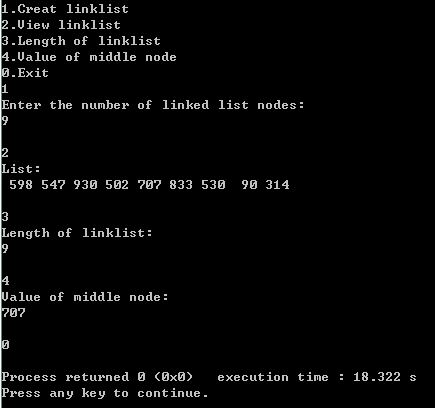






















 1527
1527











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








