练习1:
双向链表的创建,创建结点,头插,头删,尾插,尾删,按位置插入,按位置删除
#include"link.h" //创建双向链表 node_p create_double() { node_p H=(node_p)malloc(sizeof(node)); if(H==NULL) { printf("空间申请失败\n"); return NULL; } H->data=0; H->next=NULL; H->pri=NULL; return H; } //创建结点 node_p cread_node(int data) { node_p new=(node_p)malloc(sizeof(node)); if(new==NULL) { printf("空间申请失败\n"); return NULL; } new->data=data; return new; } //判空 int empty_double(node_p H) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return -1; } return H->next==NULL?1:0; } //头插 void insert_head(node_p H,int data) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } node_p new=cread_node(data); new->next=H->next; if(H->next!=NULL) { H->next->pri=new; } new->pri=H; H->next=new; H->data++; } //输出 void show_double(node_p H) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } if(empty_double(H)) { printf("链表为空\n"); } node_p p=H->next; while(p!=NULL) { printf("%d ",p->data); p=p->next; } putchar(10); } //头删 void del_head(node_p H) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } if(empty_double(H)) { printf("链表为空\n"); } node_p p=H->next; if(H->next->next!=NULL) { H->next->next->pri=H; } H->next=H->next->next; free(p); } //尾插 void insert_tail(node_p H,int data) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } node_p p=H; while(p->next!=NULL) { p=p->next; } node_p new=cread_node(data); new->next=p->next; p->next=new; new->pri=p; H->data++; } //尾删 void dele_tail(node_p H) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } if(empty_double(H)) { printf("链表为空\n"); } node_p p=H; while(p->next->next!=NULL) { p=p->next; } node_p temp=p->next; p->next=NULL; free(temp); } //按位置插入 void insert_pos(node_p H,int data,int pos) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } if(pos<=0||pos>H->data+1) { printf("位置不合理\n"); return; } node_p p=H; for(int i=0;i<pos-1;i++) { p=p->next; } node_p new=cread_node(data); new->next=p->next; if(p->next!=NULL) { p->next->pri=new; } new->pri=p; p->next=new; H->data++; } //按位置删除 void dele_pos(node_p H,int pos) { if(H==NULL) { printf("入参为空\n"); return; } if(empty_double(H)) { printf("链表为空\n"); return; } if(pos<=0||pos>H->data) { printf("位置不合理\n"); return; } node_p p=H; for(int i=0;i<pos-1;i++) { p=p->next; } node_p temp=p->next; if(p->next->next!=NULL) { p->next->next->pri=p; } p->next=p->next->next; free(temp); H->data--; }
总结:
单向链表与顺序表区别
1.顺序表:
数据之间逻辑连续物理地址也连续
插入删除需要遍历
支持随机访问
单向链表:
物理地址不连续插入删除直接通过修改指针
访问需要从结点开始遍历
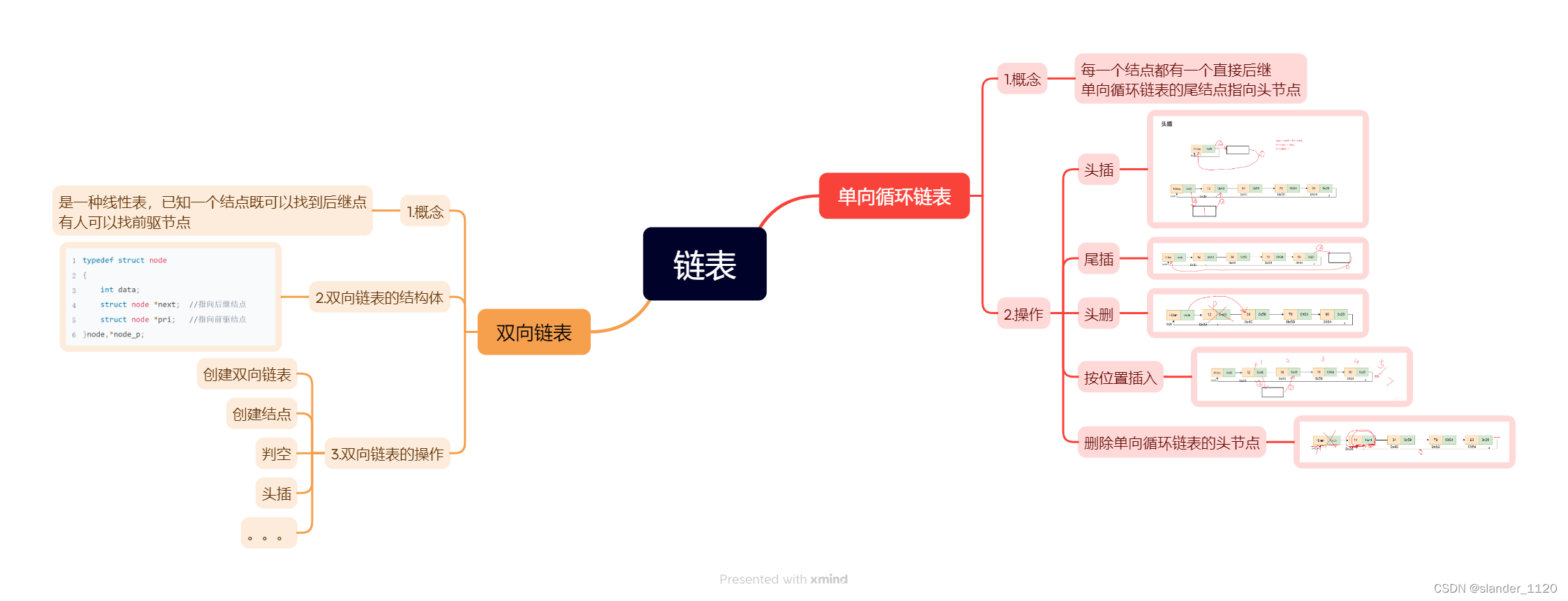
思维导图





















 263
263











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








