图像可以是看成是一个多维的数组。读取一张图片,可以看成是读入了一系列的像素内容。这些像素内容,按照不同的模式具有不同的格式。对于三通道的 RGB 位图来说,每个像素是一个 8-bit 整数的三元组。图像的像素操作是比较基础的图像算法,下面列举三个常用的像素操作算法。
图像加法
图像的加法表示两个输入图像在同一位置上的像素相加,得到一个输出图像的过程。
imageProcessor = Operator.add(imageProcessor1,imageProcessor2);
if (imageProcessor!=null) {
CV4JImage resultCV4JImage = new CV4JImage(imageProcessor.getWidth(), imageProcessor.getHeight(), imageProcessor.getPixels());
result.setImageBitmap(resultCV4JImage.getProcessor().getImage().toBitmap());
}

Operator的add表示矩阵加法,有一个要求两个图像必须大小一致。
public static ImageProcessor add(ImageProcessor image1, ImageProcessor image2) {
if(!checkParams(image1, image2)) {
return null;
}
int channels = image1.getChannels();
int w = image1.getWidth();
int h = image1.getHeight();
ImageProcessor dst = (channels == 3) ? new ColorProcessor(w, h) : new ByteProcessor(w, h);
int size = w*h;
int a=0, b=0;
int c=0;
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
for(int n=0; n<channels; n++) {
a = image1.toByte(n)[i]&0xff;
b = image2.toByte(n)[i]&0xff;
c = Tools.clamp(a + b);
dst.toByte(n)[i] = (byte)c;
}
}
return dst;
}
在实际工作中,可以通过一张原图和一个mask图像来相加合成一些不规则的效果图片。
像素混合
在这里混合是线性混合,跟之前的图像加法有一定的区别。
imageProcessor = Operator.addWeight(imageProcessor1,2.0f,imageProcessor2,1.0f,4);
if (imageProcessor!=null) {
CV4JImage resultCV4JImage = new CV4JImage(imageProcessor.getWidth(), imageProcessor.getHeight(), imageProcessor.getPixels());
result.setImageBitmap(resultCV4JImage.getProcessor().getImage().toBitmap());
}
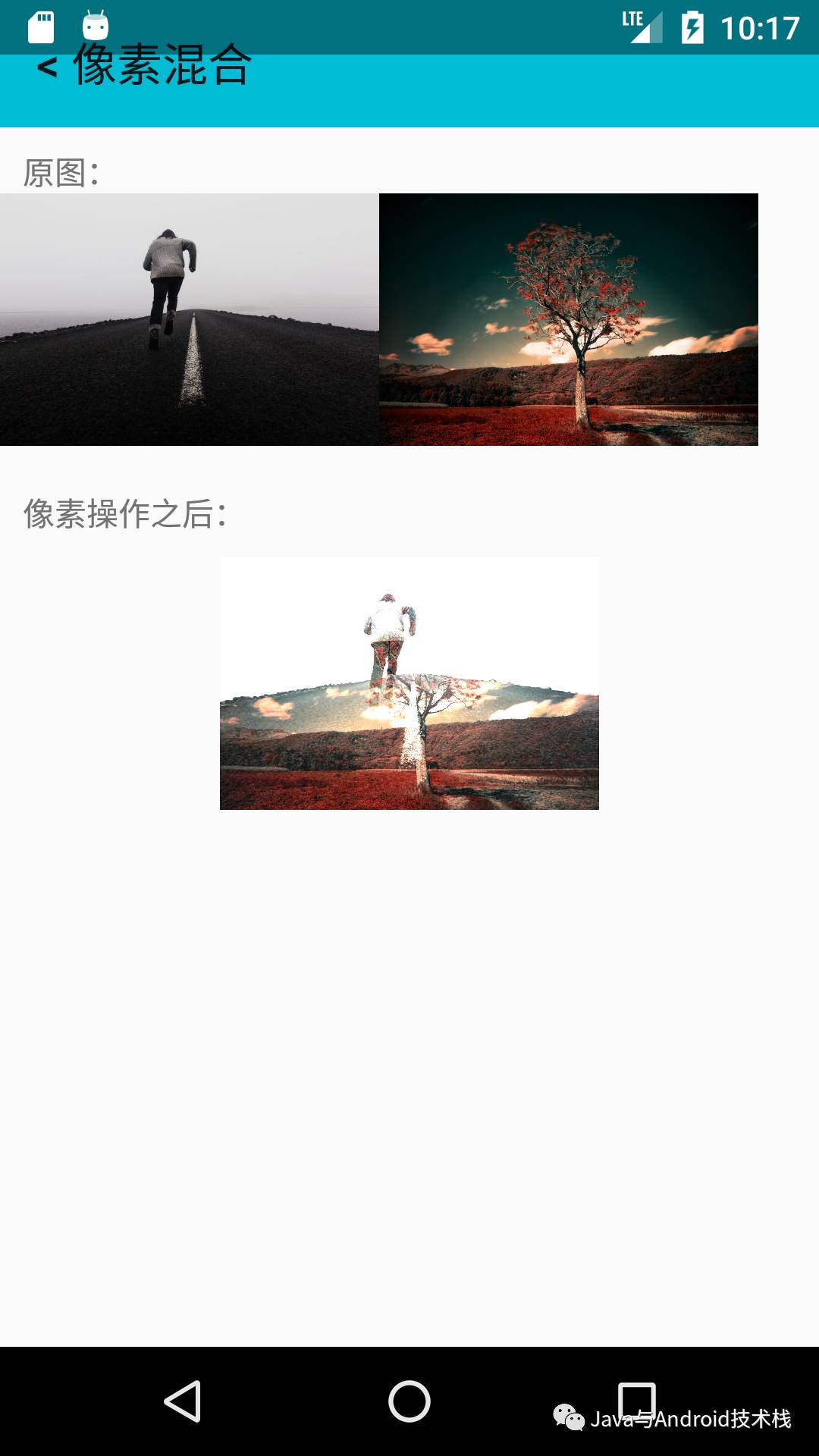
Operator的addWeight方法表示像素混合。
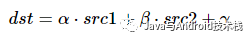
public static ImageProcessor addWeight(ImageProcessor image1, float w1, ImageProcessor image2, float w2, int gamma) {
if(!checkParams(image1, image2)) {
return null;
}
int channels = image1.getChannels();
int w = image1.getWidth();
int h = image1.getHeight();
ImageProcessor dst = (channels == 3) ? new ColorProcessor(w, h) : new ByteProcessor(w, h);
int size = w*h;
int a=0, b=0;
int c=0;
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
for(int n=0; n<channels; n++) {
a = image1.toByte(n)[i]&0xff;
b = image2.toByte(n)[i]&0xff;
c = (int)(a*w1 + b*w2 + gamma);
dst.toByte(n)[i] = (byte)Tools.clamp(c);
}
}
return dst;
}
提取图像中的ROI
ROI(region of interest),表示图像中感兴趣的区域。对于一张图像,可能我们只对图像中某部分感兴趣,或者要对目标进行跟踪时,需要选取目标特征,所以要提取图像的感兴趣区域。
Resources res = getResources();
final Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, R.drawable.pixel_test_3);
image.setImageBitmap(bitmap);
CV4JImage cv4jImage = new CV4JImage(bitmap);
ImageProcessor imageProcessor = cv4jImage.getProcessor();
Rect rect = new Rect();
rect.x = 300;
rect.y = 200;
rect.width = 300;
rect.height = 450;
ImageProcessor resultImageProcessor = null;
try {
resultImageProcessor = Operator.subImage(imageProcessor,rect);
} catch (CV4JException e) {
}
if (resultImageProcessor!=null) {
CV4JImage resultCV4JImage = new CV4JImage(resultImageProcessor.getWidth(), resultImageProcessor.getHeight(), resultImageProcessor.getPixels());
result.setImageBitmap(resultCV4JImage.getProcessor().getImage().toBitmap());
}

其中,rect.x和rect.y表示ROI的起始点,rect.width和rect.height表示ROI的宽和高。Operator的subImage()表示从原图中提取ROI,之所以在这里还用到了try catch,是为了防止出现ROI的宽度或者高度过大,从而导致数组越界。
subImage方法的代码也很简单
/**
* ROI sub image by rect.x, rect.y, rect.width, rect.height
* @param image
* @param rect
* @return
* @throws CV4JException
*/
public static ImageProcessor subImage(ImageProcessor image, Rect rect) throws CV4JException{
int channels = image.getChannels();
int w = rect.width;
int h = rect.height;
ImageProcessor dst = (channels == 3) ? new ColorProcessor(w, h) : new ByteProcessor(w, h);
int a=0;
int index = 0;
try {
for(int n=0; n<channels; n++) {
for(int row=rect.y; row < (rect.y+rect.height); row++) {
for(int col=rect.x; col < (rect.x+rect.width); col++) {
index = row*image.getWidth() + col;
a = image.toByte(n)[index]&0xff;
index = (row - rect.y)*w + (col - rect.x);
dst.toByte(n)[index] = (byte)a;
}
}
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new CV4JException("数组越界了");
}
return dst;
}
总结
cv4j (https://github.com/imageprocessor/cv4j)是gloomyfish (http://blog.csdn.net/jia20003)和我一起开发的图像处理库,纯java实现,目前还处于早期的版本。
像素操作是 cv4j 的基本功能之一,所有的像素操作算法都在Operator类中。除了本文介绍的三个算法之外,还有substract表示矩阵减法、multiple表示矩阵逐元素乘法、division表示矩阵逐元素除法以及bitwiseand、bitwisenot、bitwiseor、bitwisexor表示每个元素进行位运算分别是和、非、或、异或。
如果您想看该系列先前的文章可以访问下面的文集:http://www.jianshu.com/nb/10401400
关注【Java与Android技术栈】
更多精彩内容请关注:





















 1223
1223











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








