作者简介:大家好,我是smart哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现某互联网公司CTO
联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬
学习必须往深处挖,挖的越深,基础越扎实!
阶段1、深入多线程
阶段2、深入多线程设计模式
阶段3、深入juc源码解析
码哥源码部分
码哥讲源码-原理源码篇【2024年最新大厂关于线程池使用的场景题】
码哥讲源码-原理源码篇【揭秘join方法的唤醒本质上决定于jvm的底层析构函数】
码哥源码-原理源码篇【Doug Lea为什么要将成员变量赋值给局部变量后再操作?】
码哥讲源码【谁再说Spring不支持多线程事务,你给我抽他!】
打脸系列【020-3小时讲解MESI协议和volatile之间的关系,那些将x86下的验证结果当作最终结果的水货们请闭嘴】
redis 可能存在大量过期数据,一次性遍历检查不太现实。
redis 有丰富的数据结构,key-value, value 数据结构对象可能存储大量数据,key 过期了,value 也不建议在进程中实时回收。
为了保证系统高性能,每次处理一点点,逐渐完成大任务,“分而治之” 这是 redis 处理大任务的一贯作风。
1. 流程
主服务检查过期/删除过期逻辑 -> 删除过期键值 -> 异步/同步删除数据 -> 主从同步。
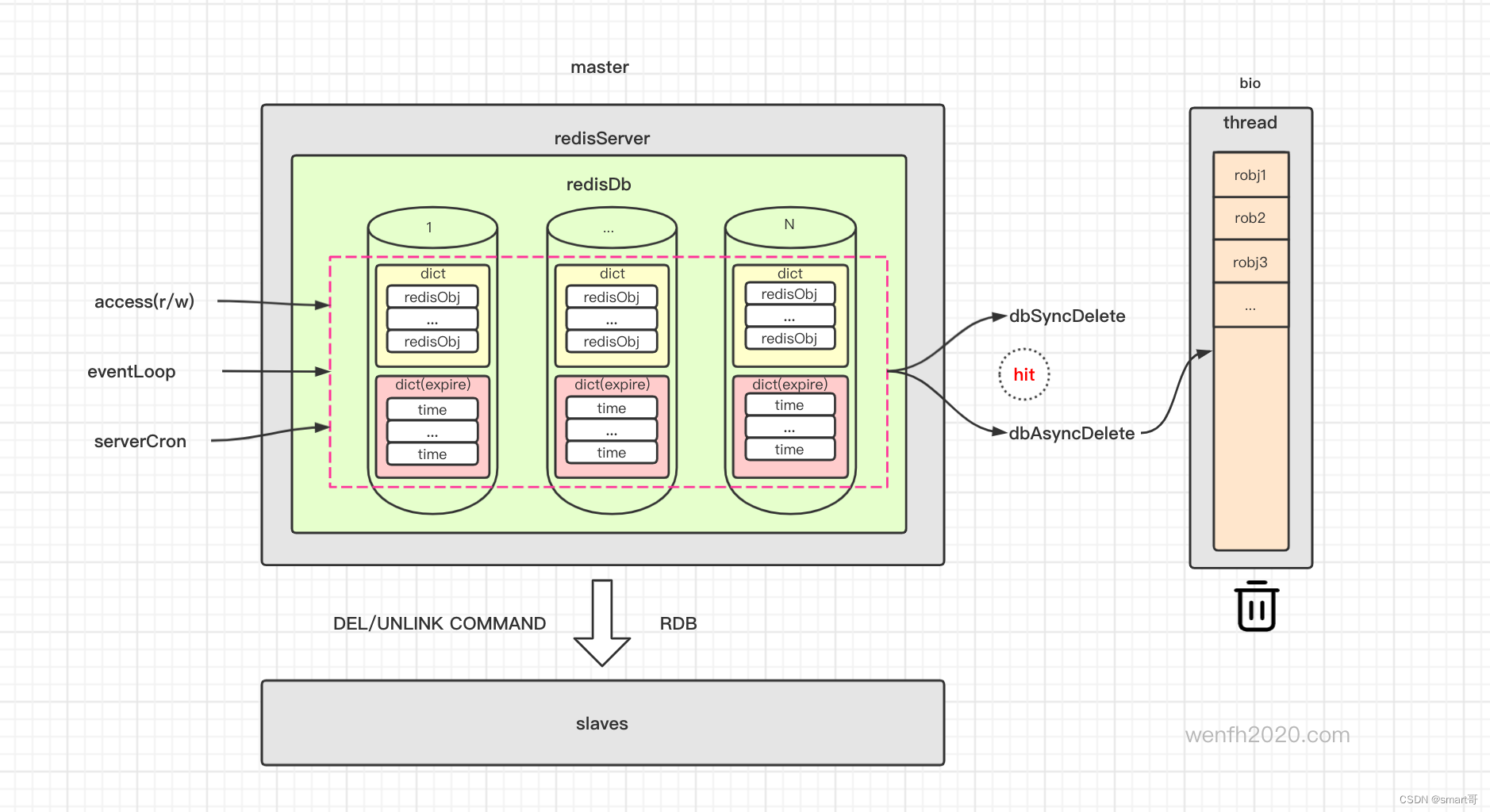
redis 数据库,数据内容和过期时间是分开保存。expires 保存了键值对应的过期时间。
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
...
} redisDb;
2. 策略概述
2.1. 过期检查
过期数据检查有三个策略:
-
访问键值触发检查。访问包括外部读写命令,内部逻辑调用。
不可能每个过期键都能实时被访问触发,所以要结合其它策略。
-
事件驱动处理事件前触发快速检查。
将过期检查负载一点点分摊到每个事件处理中。
-
时钟定期慢速检查。
2.2. 数据回收
数据回收有同步和异步两种方式,配置文件可以设置,一般默认异步回收数据。
异步数据回收有两个策略:
-
小数据实时回收。
-
大数据放到任务队列,后台线程处理任务队列异步回收内存。
可以看看
bio.c的实现。
2.2.1. 同步
int dbSyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
/* Deleting an entry from the expires dict will not free the sds of
* the key, because it is shared with the main dictionary. */
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0)
dictDelete(db->expires, key->ptr);
if (dictDelete(db->dict, key->ptr) == DICT_OK) {
if (server.cluster_enabled)
slotToKeyDel(key);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
2.2.2. 异步
unlink 逻辑删除 key,数据放在 bio 线程异步删除。
#define LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD 64
int dbAsyncDelete(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (dictSize(db->expires) > 0) dictDelete(db->expires,key->ptr);
dictEntry *de = dictUnlink(db->dict,key->ptr);
if (de) {
robj *val = dictGetVal(de);
size_t free_effort = lazyfreeGetFreeEffort(val);
if (free_effort > LAZYFREE_THRESHOLD && val->refcount == 1) {
atomicIncr(lazyfree_objects,1);
// 删除数据对象,要注意对象计数,decrRefCount 删除。
bioCreateBackgroundJob(BIO_LAZY_FREE,val,NULL,NULL);
dictSetVal(db->dict,de,NULL);
}
}
if (de) {
dictFreeUnlinkedEntry(db->dict,de);
if (server.cluster_enabled) slotToKeyDel(key);
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
3. 检查具体策略
3.1. 访问检查
3.1.1. expireIfNeeded
外部读写命令/内部逻辑调用,基本所有的键值读写操作都会触发 expireIfNeeded 过期检查。
db.c
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
// 传播数据更新,传播到集群中去,如果数据库是 `aof` 格式存储,更新落地 `aof` 文件。
propagateExpire(db,key,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, "expired",key,db->id);
return server.lazyfree_lazy_expire ? dbAsyncDelete(db,key) :
dbSyncDelete(db,key);
}
void propagateExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key, int lazy) {
robj *argv[2];
argv[0] = lazy ? shared.unlink : shared.del;
argv[1] = key;
incrRefCount(argv[0]);
incrRefCount(argv[1]);
// aof 存储,del/unlink 命令入库
if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF)
feedAppendOnlyFile(server.delCommand, db->id, argv, 2);
// 同步 del/unlink 命令到从库
replicationFeedSlaves(server.slaves, db->id, argv, 2);
decrRefCount(argv[0]);
decrRefCount(argv[1]);
}
3.1.2. 修改/删除过期 key
部分命令会修改或删除过期时间。
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| del | 删除指定key。 |
| unlink | 逻辑删除指定key,数据在线程异步删除。 |
| set | 设置一个键的值,ex选项可以设置过期时间 |
| persist | 移除key的过期时间 |
| rename | 重命名key,会删除原来key的过期时间。 |
| flushdb | 清空当前数据库。 |
| flushall | 清空所有数据。 |
| expire | 设置key的过期时间秒数。 |
| expireat | 设置一个UNIX时间戳的过期时间。 |
| pexpireat | 设置key到期UNIX时间戳,以毫秒为单位。 |
3.1.3. maxmemory 淘汰
超出最大内存 maxmemory,触发数据淘汰。
typedef struct redisObject {
...
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
...
} robj;
int processCommand(client *c) {
...
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = freeMemoryIfNeededAndSafe() == C_ERR;
...
}
...
}
int freeMemoryIfNeededAndSafe(void) {
if (server.lua_timedout || server.loading) return C_OK;
return freeMemoryIfNeeded();
}
3.2. 事件触发
在事件模型中,处理事件前,触发快速检查。将过期检查负载分散到各个事件中去。
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
...
aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep);
...
aeMain(server.el);
...
}
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}
void beforeSleep(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
...
if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL)
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST);
...
}
3.3. 定期检查
通过时钟实现,定期检查过期键值。
void initServer(void) {
...
// 创建时钟事件
if (aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
serverPanic("Can't create event loop timers.");
exit(1);
}
...
}
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) {
...
databasesCron();
...
}
// 主库中检查即可,主库会同步结果到从库。
void databasesCron(void) {
if (server.active_expire_enabled) {
if (server.masterhost == NULL) {
// 主库慢速检查
activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW);
} else {
// 从库如果设置了可写功能。
expireSlaveKeys();
}
}
...
}
redis 主逻辑在单进程主线程中实现,要保证不能影响主业务前提下,检查过期数据,不能太影响系统性能。主要三方面进行限制:
- 检查时间限制。
- 过期数据检查数量限制。
- 过期数据是否达到可接受比例。
被检查的数据到期了,系统会把该键值从字典中逻辑删除,切断数据与主逻辑联系。键值对应的数据,放到线程队列,后台线程进行异步回收(如果配置设置了异步回收)。
activeExpireCycle 检查有“快速”和“慢速”两种,时钟定期检查属于慢速类型。慢速检查被分配更多的检查时间。在一个时间范围内,到期数据最好不要太密集,因为系统发现到期数据很多,会迫切希望尽快处理掉这些过期数据,所以每次检查都要耗尽分配的时间片,直到到期数据到达一个可接受的密度比例。
#define CRON_DBS_PER_CALL 16 /* 每次检查的数据库个数 */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP 20 /* Keys for each DB loop. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 1000 /* Microseconds. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 25 /* Max % of CPU to use. */
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE 10 /* % of stale keys after which
we do extra efforts. */
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* Adjust the running parameters according to the configured expire
* effort. The default effort is 1, and the maximum configurable effort
* is 10. */
unsigned long
// 努力力度,默认 1,也就是遍历过期字典的力度,力度越大,遍历数量越多,但是性能损耗更多。
effort = server.active_expire_effort-1, /* Rescale from 0 to 9. */
// 每次循环遍历键值个数。力度越大,遍历个数越多。
config_keys_per_loop = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP/4*effort,
// 快速遍历时间范围,力度越大,给予遍历时间越多。
config_cycle_fast_duration = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION/4*effort,
// 慢速遍历检查时间片
config_cycle_slow_time_perc = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC +
2*effort,
// 已经到期数据 / 检查数据 比例。达到可以接受的比例。
config_cycle_acceptable_stale = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE-
effort;
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Last DB tested. */
// 检查是否已经超时。
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
// 上一次快速检查数据起始时间。
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */
// iteration 迭代检查个数,每 16 次循环遍历,确认一下是否检查超时。
int j, iteration = 0;
// 每次周期检查的数据库个数。redis 默认有 16 个库。
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL;
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
/* 如果链接已经停止了,那么要保留现场,不允许修改数据,也不允许到期淘汰数据。
* 使用命令 ‘pause’ 暂停 redis 工作或者主服务正在进行从服务的故障转移。*/
if (clientsArePaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* 检查还没超时,但是到期数据密集度已经达到了可以接受的范围,不要快速检查了,
毕竟它是快速的,留给其它方式的检查。*/
if (!timelimit_exit &&
server.stat_expired_stale_perc < config_cycle_acceptable_stale)
return;
/* 限制快速检查频次,在两个 config_cycle_fast_duration 内,只能执行一次快速检查。 */
if (start < last_fast_cycle + (long long)config_cycle_fast_duration*2)
return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* 检查过期数据,但是不能太损耗资源,得有个限制。server.hz 默认为 10
hz 是执行后台任务的频率,越大表明执行的次数越频繁,一般用默认值 10 */
timelimit = config_cycle_slow_time_perc*1000000/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
// 如果是快速模式,更改检查周期时间。
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = config_cycle_fast_duration; /* in microseconds. */
/* 过期数据一般是异步方式,检查到过期数据,都是从字典中移除键值信息,
* 避免再次使用,但是数据回收放在后台回收,不是实时的,有数据有可能还存在数据库里。*/
// 检查数据个数。
long total_sampled = 0;
// 检查数据,数据已经过期的个数。
long total_expired = 0;
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
unsigned long expired, sampled;
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
current_db++;
// 遍历数据库检查过期数据,直到超出检查周期时间,或者过期数据比例已经很少了。
do {
// num 数据量,slots 哈希表大小(字典数据如果正在迁移,双表大小)
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
iteration++;
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
now = mstime();
/* 过期存储数据结构是字典,数据经过处理后,字典存储的数据可能已经很少,
* 但是字典还是大字典,这样遍历数据有效命中率会很低,处理起来会浪费资源,
* 后面的访问会很快触发字典的缩容,缩容后再进行处理效率更高。*/
if (num && slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
// 过期的数据个数。
expired = 0;
// 检查的数据个数。
sampled = 0;
// 没有过期的数据时间差之和。
ttl_sum = 0;
// 没有过期的数据个数。
ttl_samples = 0;
// 每次检查的数据限制。
if (num > config_keys_per_loop)
num = config_keys_per_loop;
/* 哈希表本质上是一个数组,可能有键值碰撞的数据,用链表将碰撞数据串联起来,
* 放在一个数组下标下,也就是放在哈希表的一个桶里。max_buckets 是最大能检查的桶个数。
* 跳过空桶,不处理。*/
long max_buckets = num*20;
// 当前已经检查哈希表桶的个数。
long checked_buckets = 0;
// 一个桶上有可能有多个数据。所以检查从两方面限制:一个是数据量,一个是桶的数量。
while (sampled < num && checked_buckets < max_buckets) {
for (int table = 0; table < 2; table++) {
// 如果 dict 没有正在进行扩容,不需要检查它的第二张表了。
if (table == 1 && !dictIsRehashing(db->expires)) break;
unsigned long idx = db->expires_cursor;
idx &= db->expires->ht[table].sizemask;
dictEntry *de = db->expires->ht[table].table[idx];
long long ttl;
checked_buckets++;
while(de) {
dictEntry *e = de;
de = de->next;
// 检查数据是否已经超时。
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(e)-now;
// 如果数据过期了,进行回收处理。
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,e,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet
* not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
sampled++;
}
}
db->expires_cursor++;
}
total_expired += expired;
total_sampled += sampled;
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
/* Do a simple running average with a few samples.
* We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2%
* and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
// 对没过期的数据,平均过期时间进行采样,上一次统计的平均时间占 98 %,本次占 2%。
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
/* 避免检查周期太长,当前数据库每 16 次循环迭代检查,检查是否超时,超时退出。*/
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* 当前数据库,如果没有检查到数据,或者过期数据已经达到可接受比例
* 就退出该数据库检查,进入到下一个数据库检查。*/
} while (sampled == 0 ||
(expired*100/sampled) > config_cycle_acceptable_stale);
}
// 添加统计信息
elapsed = ustime()-start;
server.stat_expire_cycle_time_used += elapsed;
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);
double current_perc;
if (total_sampled) {
current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled;
} else
current_perc = 0;
// 通过累加每次检查的过期概率影响,保存过期数据占数据比例。
server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+
(server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);
}
- 删除过期数据
int activeExpireCycleTryExpire(redisDb *db, dictEntry *de, long long now) {
long long t = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
if (now > t) {
sds key = dictGetKey(de);
robj *keyobj = createStringObject(key,sdslen(key));
propagateExpire(db,keyobj,server.lazyfree_lazy_expire);
if (server.lazyfree_lazy_expire)
dbAsyncDelete(db,keyobj);
else
dbSyncDelete(db,keyobj);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_EXPIRED, "expired", keyobj, db->id);
trackingInvalidateKey(keyobj);
decrRefCount(keyobj);
server.stat_expiredkeys++;
return 1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
4. 总结
- 要熟悉字典dict实现原理,
dict是 redis 常用的几个基础数据结构之一。 - 看了几天源码,大致理解了键值过期处理策略。很多细节,感觉理解还是不够深刻,以后还是要结合实战多思考。
- redis 为了保证系统的高性能,采取了很多巧妙的“分治策略”,例如键值过期检查。过期数据检查和处理流程看,它不是一个实时的操作,有一定的延时,这样系统不能很好地保证数据一致性。有得必有失。
- 从定期回收策略的慢速检查中,我们可以看到,redis 处理到期数据,通过采样,判断到期数据的密集度。到期数据越密集,处理时间越多。我们在使用过程中,不应该把大量数据设置在同一个时间段到期。
redis.conf配置里面有比较详细的过期键处理策略描述。很多细节,可以参考源码注释和文档。文档极其详细,redis 作者的耐心,在开源项目中,是比较少见的 。例如:
############################# LAZY FREEING ####################################
# Redis has two primitives to delete keys. One is called DEL and is a blocking
# deletion of the object. It means that the server stops processing new commands
# in order to reclaim all the memory associated with an object in a synchronous
# way. If the key deleted is associated with a small object, the time needed
# in order to execute the DEL command is very small and comparable to most other
# O(1) or O(log_N) commands in Redis. However if the key is associated with an
# aggregated value containing millions of elements, the server can block for
# a long time (even seconds) in order to complete the operation.
#
# For the above reasons Redis also offers non blocking deletion primitives
# such as UNLINK (non blocking DEL) and the ASYNC option of FLUSHALL and
# FLUSHDB commands, in order to reclaim memory in background. Those commands
# are executed in constant time. Another thread will incrementally free the
# object in the background as fast as possible.
#
# DEL, UNLINK and ASYNC option of FLUSHALL and FLUSHDB are user-controlled.
# It's up to the design of the application to understand when it is a good
# idea to use one or the other. However the Redis server sometimes has to
# delete keys or flush the whole database as a side effect of other operations.
# Specifically Redis deletes objects independently of a user call in the
# following scenarios:
#
# 1) On eviction, because of the maxmemory and maxmemory policy configurations,
# in order to make room for new data, without going over the specified
# memory limit.
# 2) Because of expire: when a key with an associated time to live (see the
# EXPIRE command) must be deleted from memory.
# 3) Because of a side effect of a command that stores data on a key that may
# already exist. For example the RENAME command may delete the old key
# content when it is replaced with another one. Similarly SUNIONSTORE
# or SORT with STORE option may delete existing keys. The SET command
# itself removes any old content of the specified key in order to replace
# it with the specified string.
# 4) During replication, when a replica performs a full resynchronization with
# its master, the content of the whole database is removed in order to
# load the RDB file just transferred.
#
# In all the above cases the default is to delete objects in a blocking way,
# like if DEL was called. However you can configure each case specifically
# in order to instead release memory in a non-blocking way like if UNLINK
# was called, using the following configuration directives:
lazyfree-lazy-eviction no
lazyfree-lazy-expire no
lazyfree-lazy-server-del no
replica-lazy-flush no





















 15
15

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








