Eat the Trees
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2502 Accepted Submission(s): 1222
Problem Description
Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
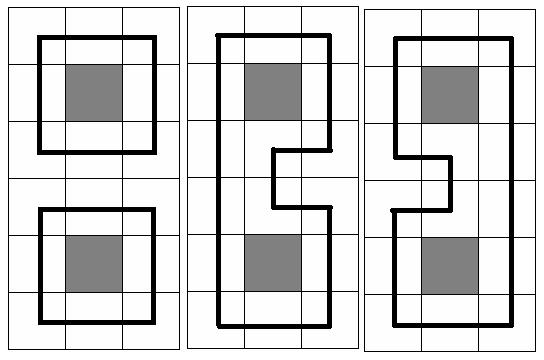
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))

Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 2
63 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2 6 3 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 4 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees. Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
Source
Recommend
wangye
从很久以前就开始看插头dp,一直学不会,看的大神的博客代码都优化的太精简,直到看了kuangbin大神的博客,才算稍稍入门,先贴一个代码,以后有优化好的代码再补充,希望能帮助到其他初学者
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
long long dp[13][13][1<<12];
int vis[13][13];
int n,m;
int main()
{
int t,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
scanf("%d",&vis[i][j]);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0][0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
int q=1<<j;//q p为左插头和上插头
int p=q<<1;
for(int k=0;k<1<<(m+1);k++){
if(vis[i][j]){
if((k&p)&&(k&q))
dp[i][j+1][k-p-q]=dp[i][j][k];//有上插头和左插头时,必然不能有下插头和右插头(在下一个轮廓线时p q表示下插头和右插头)
else if(!(k&p)&&!(k&q))
dp[i][j+1][k+p+q]=dp[i][j][k];//没有上插头和左插头时,必然要有下插头和右插头
else{
dp[i][j+1][k]+=dp[i][j][k];//有左插头和下插头,以及有上插头和右插头的情况
dp[i][j+1][k^p^q]+=dp[i][j][k];//直线的情况
}
}
else if(!(k&p)&&!(k&q))
dp[i][j+1][k]=dp[i][j][k];//该处有障碍时 在这个格子无插头的状态转移到下一格子
}
}
for(int j=0;j<(1<<m);j++)
dp[i+1][0][j<<1]=dp[i][m][j];//转移到下一行
}
printf("Case %d: There are %I64d ways to eat the trees.\n",cas++,dp[n][0][0]);
}
return 0;
}
再贴一个模板化代码,初学模板参考kuangbin
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
const int MAXD=15;
const int HASH=10007;
const int STATE=1000010;
using namespace std;
int N,M,cas=1;
int maze[MAXD][MAXD];
int code[MAXD];
int ch[MAXD];
struct HASHMAP
{
int head[HASH],next[STATE],size;
long long state[STATE];
long long f[STATE];
void init(){
size=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void push(long long st,long long ans){
int i;
int h=st%HASH;
for(i=head[h];i!=-1;i=next[i])
if(state [i]==st){
f[i]+=ans;
return;
}
state[size]=st;
f[size]=ans;
next[size]=head[h];
head[h]=size++;
}
}hm[2];
void decode(int *code,int m,long long st)
{
for(int i=m;i>=0;i--){
code[i]=st&1;
st>>=1;
}
}
long long encode(int *code,int m)
{
int st=0;
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++){
st<<=1;
st|=code[i];
}
return st;
}
void shift(int *code,int m)
{
for(int i=m;i>0;i--)code[i]=code[i-1];
code[0]=0;
}
void dpblank(int i,int j,int cur)
{
int k,left,up;
for(k=0;k<hm[cur].size;k++){
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);
left=code[j-1];
up=code[j];
if(left&&up){
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
else if(left||up){
if(maze[i][j+1]){
code[j-1]=0;
code[j]=1;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
if(maze[i+1][j]){
code[j-1]=1;
code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
else{
if(maze[i][j+1]&&maze[i+1][j]){
code[j-1]=code[j]=1;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
}
}
void dpblock(int i,int j,int cur)
{
int k;
for(k=0;k<hm[cur].size;k++)
{
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
void init()
{
memset(maze,0,sizeof(maze));
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=M;j++)
scanf("%d",&maze[i][j]);
}
void solve()
{
int i,j,cur=0;
long long ans=0;
hm[cur].init();
hm[cur].push(0,1);
for(i=1;i<=N;i++)
for(j=1;j<=M;j++){
hm[cur^1].init();
if(maze[i][j])dpblank(i,j,cur);
else dpblock(i,j,cur);
cur^=1;
}
for(i=0;i<hm[cur].size;i++)
ans+=hm[cur].f[i];
printf("Case %d: There are %I64d ways to eat the trees.\n",cas++,ans);
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
init();
solve();
}
return 0;
}






















 670
670

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








